Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain work done during a thermodynamic process.
Solution
- Consider the system is initially at state A with its pressure is pi and volume is Vi. Let the state be indicated as coordinates (Vi, pi). It can attain the final state (Vf, pf) along different possible paths as shown in the p-V diagram below.
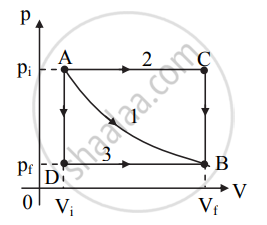
Different ways to change a system - Consider a system that changes its state from initial state A to final state B via path 1 as shown in the figure.
Pressure and volume both change
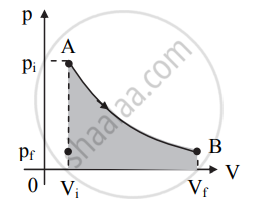
a. When the system changes itself from A to B, both its pressure and volume change. The pressure decreases while volume increases.
b. The work done by the system is given by the area under the curve. It is positive when the volume increases (as shown in the figure) or negative when the volume decreases. - Consider the system changes its state from A to B via path 2 as shown in figure (a).
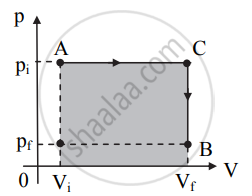
Figure (a)
a. In this case, the volume increases to Vi from point A up to point C at the constant pressure pi.
b. After point C, the pressure of the system decreases to pf at constant volume as shown in figure (a).
c. The system thus, reaches its final state B with co-ordinates (Vf, pf). Work done in this process is represented by the shaded area under the curve in figure (a). - Consider the system changes its state from A to B via path 3 as shown in figure (b).
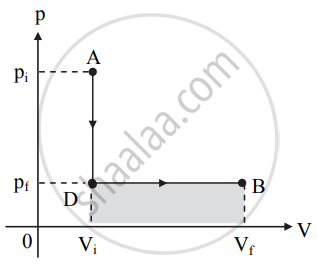
Figure (b)
a. In this case, the pressure decreases from pi to pf at constant volume Vi along the path AD.
b. After point D, the volume of the system increases to Vf at constant pressure pf as shown in figure (b). c. Work done in this process is represented by the shaded area under the curve in figure (b). - From figures (a) and (b) we can conclude that the work done is more when the system follows path ACB than the work done by the system along the path ADB.
Thus, the work done by a system in a thermodynamic process depends not only on the initial and the final states but also on the intermediate states, i.e., on the paths along which the change takes place.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give an example of some familiar process in which heat is added to an object, without changing its temperature.
Answer in brief.
Why should a Carnot cycle have two isothermal two adiabatic processes?
An ideal gas is taken through an isothermal process. If it does 2000 J of work on its environment, how much heat is added to it?
Draw a p-V diagram showing negative work with varying pressure.
State the assumptions made for thermodynamic processes.
Differentiate between the reversible and irreversible processes.
3 mole of a gas at temperature 400 K expands isothermally from an initial volume of 4 litres to a final volume of 8 litres. Find the work done by the gas. (R = 8.31 J mol-1 K-1)
Explain the thermodynamics of the isochoric process.
Explain thermodynamics of the adiabatic process.
When food is cooked in a vessel by keeping the lid closed, after some time the steam pushes the lid outward. By considering the steam as a thermodynamic system, then in the cooking process
When you exercise in the morning, by considering your body as a thermodynamic system, which of the following is true?
The V-T diagram of an ideal gas which goes through a reversible cycle A→B→C→D is shown below. (Processes D→A and B→C are adiabatic)
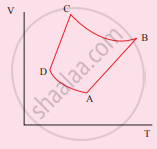
The corresponding PV diagram for the process is (all figures are schematic)
In an isochoric process, we have ____________.
Give the equation of state for an isothermal process.
Apply first law for an adiabatic process.
What is meant by a reversible and irreversible processes?
Among the amount of heat absorbed and the amount of work done by a system, ______
An ideal gas is made to go from a state A to stale B in the given two different ways (see figure) (i) an isobaric and then an isochoric process and (ii) an isochoric and then an isobaric process. The work done by gas in the two processes are W1 and W2 respectively. Then,

An ideal gas A and a real gas B have their volumes increased from V to 2V under isothermal conditions. The increase in internal energy ____________.
An ideal gas is compressed to half its initial volume by means of several processes. Which of the process results in the maximum work done on the gas?
We consider a thermodynamic system. If `Delta"U"` represents the increase in its internal energy and W the work done by the system, which of the following statements is true?
The work done on the system in changing the state of a gas adiabatically from equilibrium state A to equilibrium state B is 22.4 J. If the gas is taken from state A to B through another process in which the net heat absorbed by the system is 15.5 cal, then the net work done by the system in the latter case is ______.
( l cal = 4.2 J)
In the figure shown here, the work done in the process ACBA is ______.
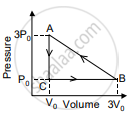
Explain the thermodynamic process.
When an inflated ballon is suddenly burst, why is the emerging air slightly cooled?
Explain how can a gas be expanded at constant temperature.
In a cyclic process, if ΔU = internal energy, W = work done, Q = Heat supplied then ______.
