Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
derive the relation between the change in internal energy (∆U), work is done (W), and heat (Q).
Solution
Relation between the change in internal energy (ΔU), work is done (W), and heat (Q):
- When the amount of heat Q is added to the system and the system does not do any work during the process, its internal energy increases by the amount, ΔU = Q.
- When the system does some work to increase its volume, and no heat is added to it while expanding, the system loses energy to its surrounding,s and its internal energy decreases.
∴ ΔU = –W. - As the internal energy can be changed using both ways, we can consider the total change in the internal energy as,
ΔU = Q – W ….(1)
This is the mathematical statement of the first law of thermodynamics.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain why Air pressure in a car tyre increases during driving.
A steam engine delivers 5.4×108 J of work per minute and services 3.6 × 109 J of heat per minute from its boiler. What is the efficiency of the engine? How much heat is wasted per minute?
A force F is applied on a block of mass M. The block is displaced through a distance d in the direction of the force. What is the work done by the force on the block? Does the internal energy change because of this work?
The final volume of a system is equal to the initial volume in a certain process. Is the work done by the system necessarily zero? Is it necessarily nonzero?
Can work be done by a system without changing its volume?
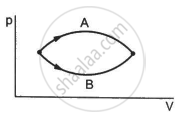
Figure shows two processes A and B on a system. Let ∆Q1 and ∆Q2 be the heat given to the system in processes A and B respectively. Then ____________ .
Consider the following two statements.
(A) If heat is added to a system, its temperature must increase.
(B) If positive work is done by a system in a thermodynamic process, its volume must increase.
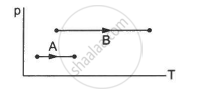
Consider two processes on a system as shown in figure.
The volumes in the initial states are the same in the two processes and the volumes in the final states are also the same. Let ∆W1 and ∆W2 be the work done by the system in the processes A and B respectively.
A gas is contained in a metallic cylinder fitted with a piston. The piston is suddenly moved in to compress the gas and is maintained at this position. As time passes the pressure of the gas in the cylinder ______________ .
In a process on a system, the initial pressure and volume are equal to the final pressure and volume.
(a) The initial temperature must be equal to the final temperature.
(b) The initial internal energy must be equal to the final internal energy.
(c) The net heat given to the system in the process must be zero.
(d) The net work done by the system in the process must be zero.
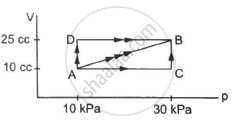
Figure shows three paths through which a gas can be taken from the state A to the state B. Calculate the work done by the gas in each of the three paths.
What is the energy associated with the random, disordered motion of the molecules of a system called as?
Define heat.
What is the internal energy of the system, when the amount of heat Q is added to the system and the system does not do any work during the process?
One gram of water (1 cm3) becomes 1671 cm3 of steam at a pressure of 1 atm. The latent heat of vaporization at this pressure is 2256 J/g. Calculate the external work and the increase in internal energy.
The internal energy of a system is ______
An ideal gas is compressed at a constant temperature. Its internal energy will ____________.
In a thermodynamic system, working substance is ideal gas. Its internal energy is in the form of ______.
When 1 g of water at 0° C and 1 x 105 N/m2 pressure is converted into ice of volume 1.082 cm3, the external work done will be ____________.
Which of the following represents isothermal process?
A person of mass 60 kg wants to lose 5kg by going up and down a 10 m high stairs. Assume he burns twice as much fat while going up than coming down. If 1 kg of fat is burnt on expending 7000 kilo calories, how many times must he go up and down to reduce his weight by 5 kg?
n mole of a perfect gas undergoes a cyclic process ABCA (see figure) consisting of the following processes:
A `→` B: Isothermal expansion at temperature T so that the volume is doubled from V1 to V2 = 2V1 and pressure changes from P1 to P2.
B `→` C: Isobaric compression at pressure P2 to initial volume V1.
C `→` A: Isochoric change leading to change of pressure from P2 to P1.
Total workdone in the complete cycle ABCA is ______.

An expansion process on a diatomic ideal gas (Cv = 5/2 R), has a linear path between the initial and final coordinates on a pV diagram. The coordinates of the initial state are: the pressure is 300 kPa, the volume is 0.08 m3 and the temperature is 390 K. The final pressure is 90 kPa and the final temperature s 320 K. The change in the internal energy of the gas, in SI units, is closest to:
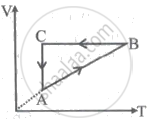
A cyclic process ABCA is shown in the V-T diagram. A process on the P-V diagram is ______.
A steam engine delivers 4.8 x 108 Jof work per minute and services 1.2 x 109 J of heat per minute from its boiler. What is the percentage efficiency of the engine?
What is heat?
A system releases 125 kJ of heat while 104 kJ work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
Explain the change in internal energy of a thermodynamic system (the gas) by heating it.
