Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If P(–5, –3), Q(–4, –6), R(2, –3) and S(1, 2) are the vertices of a quadrilateral PQRS, find its area.
Solution

The vertices of the quadrilateral PQRS are P(−5, −3), Q(−4, −6), R(2, −3) and S(1, 2).
Join QS to form two triangles, namely, ΔPQS and ΔRSQ.
Area of quadrilateral PQRS = Area of ΔPQS + Area of ΔRSQ
We know
Area of triangle having vertices (x1, y1), (x2, y2) and (x3, y3) = `1/2`[x1(y2−y3)+x2(y3−y1)+x3(y1−y2)]
Now,
Area of △PQS = `1/2`[−5(−6−2)+(−4)(2+3)+1(−3+6)]
=`1/2`[−5(−8)+(−4)(5)+1(3)]
=`1/2`(40−20+3)
=`23/2`square units
Area of ∆RSQ= `1/2`[2(2+6)+1(−6+3)+(−4)(−3−2)]
=`1/2`[2(8)+1(−3)+(−4)(−5)]
=`1/2`(16−3+20)
=`33/2` square units
Area of quadrilateral PQRS = Area of ΔPQS + Area of ΔRSQ
`=23/2+33/2`
`=56/2`
=28 square units
Thus, the area of quadrilateral PQRS is 28 square units.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Prove that the points (2a, 4a), (2a, 6a) and `(2a + sqrt3a, 5a)` are the vertices of an equilateral triangle.
Find the value of x for which points A(x, 2), B(-3, -4) and C(7, -5) are collinear.
Using integration, find the area of the triangle whose vertices are (2, 3), (3, 5) and (4, 4).
In ∆PQR, PR = 8 cm, QR = 4 cm and PL = 5 cm. 
Find:
(i) the area of the ∆PQR
(ii) QM.
If the sides of a triangle are 3 cm, 4 cm and 5 cm, then the area is
If Δ = `|(1, x, x^2),(1, y, y^2),(1, z, z^2)|`, Δ1 = `|(1, 1, 1),(yz, zx, xy),(x, y, z)|`, then prove that ∆ + ∆1 = 0.
The area of a triangle with vertices A(3, 0), B(7, 0) and C(8, 4) is ______.
The points A(2, 9), B(a, 5) and C(5, 5) are the vertices of a triangle ABC right angled at B. Find the values of a and hence the area of ∆ABC.
Ratio of the area of ∆WXY to the area of ∆WZY is 3:4 in the given figure. If the area of ∆WXZ is 56 cm2 and WY = 8 cm, find the lengths of XY and YZ.
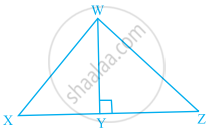
In the given figure, triangle AEC is right-angled at E, B is a point on EC, BD is the altitude of triangle ABC, AC = 25 cm, BC = 7 cm and AE = 15 cm. Find the area of triangle ABC and the length of DB.