Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the adjoining figure, a circle touches all the four sides of a quadrilateral ABCD whose sides are AB=6cm, BC=9cm and CD=8 cm. Find the length of side AD.
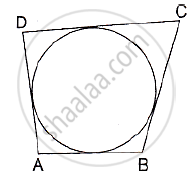
Solution
We know that when a quadrilateral circumscribes a circle then sum of opposites sides is equal to the sum of other opposite sides.
∴ AB + CD = AD+ BC
⇒ 6 + 8 = AD = 9
⇒ AD = 5 cm
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
ABCD is a quadrilateral such that ∠D = 90°. A circle (O, r) touches the sides AB, BC, CD and DA at P,Q,R and If BC = 38 cm, CD = 25 cm and BP = 27 cm, find r.
Two concentric circles are of radii 6.5 cm and 2.5 cm. Find the length of the chord of the larger circle which touches the smaller circle.
Prove that the line segment joining the points of contact of two parallel tangents of a circle, passes through its centre.
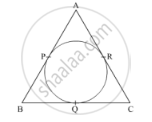
In Fig. 1, the sides AB, BC and CA of a triangle ABC, touch a circle at P, Q and R respectively. If PA = 4 cm, BP = 3 cm and AC = 11 cm, then the length of BC (in cm) is ?
If the area of a circle is equal to sum of the areas of two circles of diameters 10 cm and 24 cm, then the diameter of the larger circle (in cm) is:
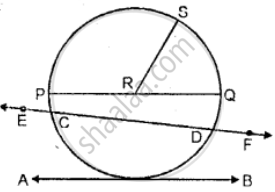
Two concentric circles with center O have A, B, C, D as the points of intersection with the lines L shown in the figure. If AD = 12 cm and BC s = 8 cm, find the lengths of AB, CD, AC and BD.
Use the figure given below to fill in the blank:
______ is a chord of the circle.
Draw circle with the radii given below.
3 cm
In the following figure, BC is a diameter of the circle and ∠BAO = 60º. Then ∠ADC is equal to ______.
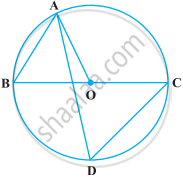
A quadrilateral ABCD is inscribed in a circle such that AB is a diameter and ∠ADC = 130º. Find ∠BAC.
