Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In figure, if ∠D = ∠C, then it is true that ΔADE ~ ΔACB? Why?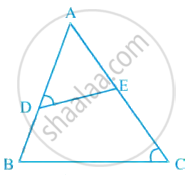
Solution
In ΔADE and ΔACB,
∠A = ∠A ...[Common angle]
∠D = ∠C ...[Given]
ΔADE ~ ΔACB ...[By AAA similarity criterion]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
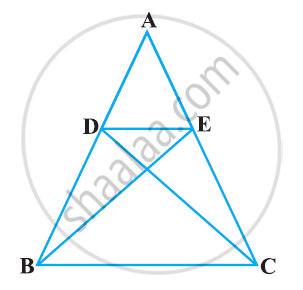
In the following figure, if ΔABE ≅ ΔACD, show that ΔADE ∼ ΔABC.
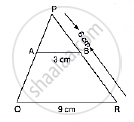
In the following figure, ABC and AMP are two right triangles, right-angled at B and M respectively, prove that:

- ΔABC ~ ΔAMP
- `("CA")/("PA") = ("BC")/("MP")`
In the following figure, AB || QR. Find the length of PB.
The sides of certain triangles are given below. Determine which of them right triangles are.
7cm, 24cm, 25cm
The sides of certain triangles are given below. Determine which of them right triangles are.
1.6cm, 3.8cm, 4cm
In the given figure MN|| BC and AM: MB= 1: 2
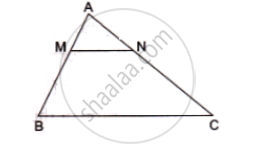
find ` (area(ΔAMN))/(area(ΔABC))`
A 15 metres high tower casts a shadow 24 metres long at a certain time and at the same time, a telephone pole casts a shadow 16 metres long. Find the height of the telephone pole.
In figure, two line segments AC and BD intersect each other at the point P such that PA = 6 cm, PB = 3 cm, PC = 2.5 cm, PD = 5 cm, ∠APB = 50° and ∠CDP = 30°. Then, ∠PBA is equal to ______.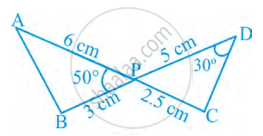
In ΔABC, AP ⊥ BC, BQ ⊥ AC. If AP = 7, BQ = 8 and BC = 12, then find AC.

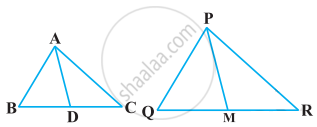
Sides AB and BC and median AD of a triangle ABC are respectively proportional to sides PQ and QR and median PM of ΔPQR show that ΔABC ~ ΔPQR.