Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the given figure, AB = DB and AC = DC. Find the values of x and y.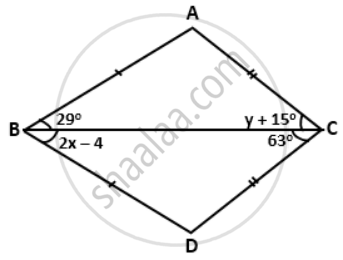
Solution

In ΔABC and ΔDBC
AB = DB ....[given]
AC = DC ....[given]
BC = BC ....[common]
∴ By Side-Side-Side criterion of congruence,
ΔABC ≅ ΔDBC
∴ ∠ACB =∠DBC ....[c.p.c.t]
⇒ y + 15° = 63°
⇒ y = 63° - 15°
⇒ y = 48°
Now, ∠ABC = ∠DBC ....[c.p.c.t]
⇒ 29° = 2x - 4°
⇒ 2x = 29° + 4°
⇒ 2x = 33°
⇒ x = `(33°)/(2)`
⇒ x = 16.5°
Hence, x = 16.5° and y = 48°.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If ΔDEF ≅ ΔBCA, write the part(s) of ΔBCA that correspond to ∠F
Find the measure of each angle of an equilateral triangle.
In a ΔABC, if AB = AC and BC is produced to D such that ∠ACD = 100°, then ∠A =
If ABC and DEF are two triangles such that ΔABC \[\cong\] ΔFDE and AB = 5cm, ∠B = 40°
Which of the following pairs of triangles are congruent? Give reasons
ΔABC;(AB = 5cm,BC = 7cm,CA = 9cm);
ΔKLM;(KL = 7cm,LM = 5cm,KM = 9cm).
In the figure, ∠CPD = ∠BPD and AD is the bisector of ∠BAC. Prove that ΔCAP ≅ ΔBAP and CP = BP.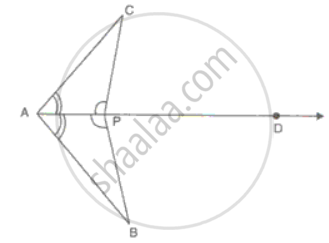
In ΔABC, AB = AC and the bisectors of angles B and C intersect at point O.Prove that BO = CO and the ray AO is the bisector of angle BAC.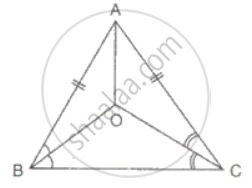
In the figure, RT = TS, ∠1 = 2∠2 and ∠4 = 2∠3. Prove that ΔRBT ≅ ΔSAT.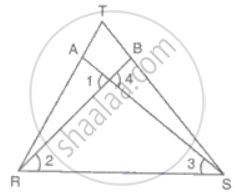
In ΔABC, X and Y are two points on AB and AC such that AX = AY. If AB = AC, prove that CX = BY.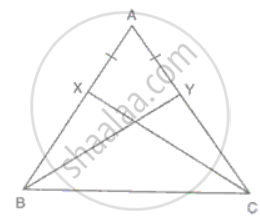
In the figure, AC = AE, AB = AD and ∠BAD = ∠EAC. Prove that BC = DE.
