Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Let f : R → R be defined as `f (x) = (2x - 3)/4.` write fo f-1 (1) .
Solution
\[Let f^{- 1} \left( x \right) = y . . . \left( 1 \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow f\left( y \right) = x\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{2y - 3}{4} = x\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2y - 3 = 4x\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2y = 4x + 3\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \frac{4x + 3}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow f^{- 1} \left( x \right) = \frac{4x + 3}{2} [\text{ from}\left( 1 \right)]\]
\[ \Rightarrow f^{- 1} \left( x \right) = \frac{4x + 3}{2}\]
\[ \therefore \left( fo f^{- 1} \right)\left( 1 \right) = f\left( \frac{4\left( 1 \right) + 3}{2} \right) = f\left( \frac{7}{2} \right) = \frac{2\left( \frac{7}{2} \right) - 3}{4} = \frac{7 - 3}{4} = \frac{4}{4} = 1\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Let A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {4, 5, 6, 7} and let f = {(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)} be a function from A to B. Show that f is one-one.
Let f: R → R be defined as f(x) = 10x + 7. Find the function g: R → R such that g o f = f o g = 1R.
Give examples of two functions f: N → Z and g: Z → Z such that g o f is injective but gis not injective.
(Hint: Consider f(x) = x and g(x) =|x|)
Given examples of two functions f: N → N and g: N → N such that gof is onto but f is not onto.
(Hint: Consider f(x) = x + 1 and `g(x) = {(x-1, ifx >1),(1, if x = 1):}`
Find the number of all onto functions from the set {1, 2, 3, …, n} to itself.
Let S = {a, b, c} and T = {1, 2, 3}. Find F−1 of the following functions F from S to T, if it exists.
F = {(a, 2), (b, 1), (c, 1)}
Which of the following functions from A to B are one-one and onto?
f1 = {(1, 3), (2, 5), (3, 7)} ; A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {3, 5, 7}
Which of the following functions from A to B are one-one and onto ?
f3 = {(a, x), (b, x), (c, z), (d, z)} ; A = {a, b, c, d,}, B = {x, y, z}.
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = |x|
Let A = [-1, 1]. Then, discuss whether the following function from A to itself is one-one, onto or bijective : `f (x) = x/2`
Let A = [-1, 1]. Then, discuss whether the following function from A to itself is one-one, onto or bijective : g(x) = |x|
If A = {1, 2, 3}, show that a onto function f : A → A must be one-one.
Give examples of two one-one functions f1 and f2 from R to R, such that f1 + f2 : R → R. defined by (f1 + f2) (x) = f1 (x) + f2 (x) is not one-one.
Give examples of two surjective functions f1 and f2 from Z to Z such that f1 + f2 is not surjective.
Let A = R - {3} and B = R - {1}. Consider the function f : A → B defined by f(x) = `(x-2)/(x-3).`Show that f is one-one and onto and hence find f-1.
[CBSE 2012, 2014]
Consider the function f : R+ → [-9 , ∞ ]given by f(x) = 5x2 + 6x - 9. Prove that f is invertible with f -1 (y) = `(sqrt(54 + 5y) -3)/5` [CBSE 2015]
If f : R → (−1, 1) defined by `f (x) = (10^x- 10^-x)/(10^x + 10 ^-x)` is invertible, find f−1.
Let A = {x &epsis; R | −1 ≤ x ≤ 1} and let f : A → A, g : A → A be two functions defined by f(x) = x2 and g(x) = sin (π x/2). Show that g−1 exists but f−1 does not exist. Also, find g−1.
If A = {1, 2, 3} and B = {a, b}, write the total number of functions from A to B.
Let C denote the set of all complex numbers. A function f : C → C is defined by f(x) = x3. Write f−1(1).
If f : R → R is defined by f(x) = x2, find f−1 (−25).
Write the domain of the real function
`f (x) = sqrt([x] - x) .`
What is the range of the function
`f (x) = ([x - 1])/(x -1) ?`
Write the domain of the real function f defined by f(x) = `sqrt (25 -x^2)` [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
Let
f : R → R be given by
\[f\left( x \right) = \left[ x^2 \right] + \left[ x + 1 \right] - 3\]
where [x] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x. Then, f(x) is
(d) one-one and onto
A function f from the set of natural numbers to integers defined by
`{([n-1]/2," when n is odd" is ),(-n/2,when n is even ) :}`
The function f : [-1/2, 1/2, 1/2] → [-π /2,π/2], defined by f (x) = `sin^-1` (3x - `4x^3`), is
\[f : Z \to Z\] be given by
` f (x) = {(x/2, ", if x is even" ) ,(0 , ", if x is odd "):}`
Then, f is
If \[f : R \to R is given by f\left( x \right) = 3x - 5, then f^{- 1} \left( x \right)\]
Which function is used to check whether a character is alphanumeric or not?
For sets A, B and C, let f: A → B, g: B → C be functions such that g o f is injective. Then both f and g are injective functions.
Let g(x) = x2 – 4x – 5, then ____________.
The domain of the function `"f"("x") = 1/(sqrt ({"sin x"} + {"sin" ( pi + "x")}))` where {.} denotes fractional part, is
A general election of Lok Sabha is a gigantic exercise. About 911 million people were eligible to vote and voter turnout was about 67%, the highest ever

Let I be the set of all citizens of India who were eligible to exercise their voting right in the general election held in 2019. A relation ‘R’ is defined on I as follows:
R = {(V1, V2) ∶ V1, V2 ∈ I and both use their voting right in the general election - 2019}
- Three friends F1, F2, and F3 exercised their voting right in general election-2019, then which of the following is true?
An organization conducted a bike race under 2 different categories-boys and girls. Totally there were 250 participants. Among all of them finally, three from Category 1 and two from Category 2 were selected for the final race. Ravi forms two sets B and G with these participants for his college project. Let B = {b1,b2,b3} G={g1,g2} where B represents the set of boys selected and G the set of girls who were selected for the final race.
Ravi decides to explore these sets for various types of relations and functions.
- Let R: B → G be defined by R = { (b1,g1), (b2,g2),(b3,g1)}, then R is ____________.
The solution set of the inequation log1/3(x2 + x + 1) + 1 > 0 is ______.
Let f: R→R be a polynomial function satisfying f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) + 3xy(x + y) –1 ∀ x, y ∈ R and f'(0) = 1, then `lim_(x→∞)(f(2x))/(f(x)` is equal to ______.
Let f(x) be a polynomial of degree 3 such that f(k) = `-2/k` for k = 2, 3, 4, 5. Then the value of 52 – 10f(10) is equal to ______.
For x ∈ R, x ≠ 0, let f0(x) = `1/(1 - x)` and fn+1 (x) = f0(fn(x)), n = 0, 1, 2, .... Then the value of `f_100(3) + f_1(2/3) + f_2(3/2)` is equal to ______.
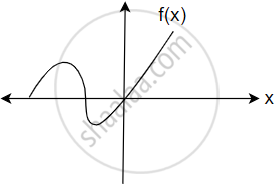
The given function f : R → R is not ‘onto’ function. Give reason.
