Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The electric field in a region is given by `vec"E"` = 5 `hatk`N/C. Calculate the electric flux Through a square of side 10.0 cm in the following cases
- The square is along the XY plane
- The square is along XZ plane
- The normal to the square makes an angle of 45° with the Z axis.
Solution
Given: `vec"E"` = 5 `hatk` N/C, |E| = 5 N/C, l = 10 cm = 10 × 10−2 m = 10−1 m, A = l2 = 10−2m2
To find: Electric flux in three cases (Φ1), (Φ2), (Φ3)
(i) Given the plane of Area is along XY plane. hence the direction of its normal `(vec"dS")` vector will be along Z axis.
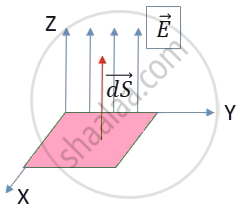
The Angle between `vec"E"` and `"d"vec"S"` is zero i.e. θ = 0°.
∴ Φ = EA cos θ
∴ Φ1 = 5 × 10−2 cos 0
∴ Φ1 = 5 × 10−2 V m
(ii) Plane of Area is along XZ plane. Hence the direction of its normal `(vec"dS")` vector will be along Y axis.
∴ θ = 90°
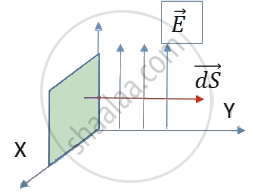
∴ Φ = EA cos θ
∴ Φ2 = 5 × 10−2 cos 90°
∴ Φ2 = 0 V m
(iii) When normal to the square makes an angle of 45° with the Z axis.
∴ θ = 45°
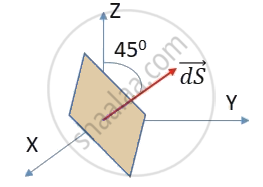
∴ Φ = EA cos θ
∴ Φ3 = 5 × 10−2 cos 45°
∴ Φ3 = 3.5 × 10−2 V m
Electric flux in the above-mentioned cases are 5 × 10−2 V m, 0 V m, and 3.5 × 10−2 V m.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define electric flux.
Find out the outward flux to a point charge +q placed at the centre of a cube of side ‘a’. Why is it found to be independent of the size and shape of the surface enclosing it? Explain.
What is the electric flux through a cube of side 1 cm which encloses an electric dipole?
Given a uniform electric field `vecE=5xx10^3hati`N/C, find the flux of this field through a square of 10 cm on a side whose plane is parallel to the y-z plane. What would be the flux through the same square if the plane makes a 30° angle with the x-axis ?
Consider a uniform electric field E = 3 × 103 `bbhat i` N/C.
- What is the flux of this field through a square of 10 cm on a side whose plane is parallel to the yz plane?
- What is the flux through the same square if the normal to its plane makes a 60° angle with the x-axis?
Careful measurement of the electric field at the surface of a black box indicates that the net outward flux through the surface of the box is 8.0 × 103 N m2/C.
- What is the net charge inside the box?
- If the net outward flux through the surface of the box were zero, could you conclude that there were no charges inside the box? Why or Why not?
A uniformly charged conducting sphere of 2.4 m diameter has a surface charge density of 80.0 μC/m2.
- Find the charge on the sphere.
- What is the total electric flux leaving the surface of the sphere?
Given a uniform electric filed \[\vec{E} = 4 \times {10}^3 \ \hat{i} N/C\]. Find the flux of this field through a square of 5 cm on a side whose plane is parallel to the Y-Z plane. What would be the flux through the same square if the plane makes a 30° angle with the x-axis?
Two charges of magnitudes −2Q and +Q are located at points (a, 0) and (4a, 0) respectively. What is the electric flux due to these charges through a sphere of radius ‘3a’ with its centre at the origin?
Two charges of magnitudes −3Q and + 2Q are located at points (a, 0) and (4a, 0) respectively. What is the electric flux due to these charges through a sphere of radius ‘5a’ with its centre at the origin?
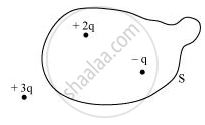
Figure shows three point charges +2q, −q and + 3q. Two charges + 2q and −q are enclosed within a surface ‘S’. What is the electric flux due to this configuration through the surface ‘S’?
A circular ring of radius r made of a non-conducting material is placed with its axis parallel to a uniform electric field. The ring is rotated about a diameter through 180°. Does the flux of the electric field change? If yes, does it decrease or increase?
It is said that any charge given to a conductor comes to its surface. Should all the protons come to the surface? Should all the electrons come to the surface? Should all the free electrons come to the surface?
A charge q is placed at the centre of the open end of a cylindrical vessel (see the figure). The flux of the electric field through the surface of the vessel is ____________ .

Mark the correct options:
Electric charges are distributed in a small volume. The flux of the electric field through a spherical surface of radius 10 cm surrounding the total charge is 25 V m. The flux over a concentric sphere of radius 20 cm will be _____________ .
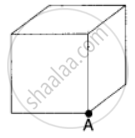
The total flux through the faces of the cube with side of length a if a charge q is placed at corner A of the cube is ______.
A cylinder of radius R and length L is placed in a uniform electric field E parallel to the cylinder axis. The total flux for the surface of the cylinder is given by ______.
Total electric flux coming out of a unit positive charge kept in air is ______.
The electric field intensity due to an infinite cylinder of radius R and having charge q per unit length at a distance rir r(r > R) from its axis is ______.
A point charge q is placed at a distance a/2 directly above the centre of a square of side a. The electric flux through the square is ______.
A charge Qµc is placed at the centre of a cube the flux coming from any surface will be.
A hollow sphere of radius R has a point charge q at its centre. Electric flux emanating from the sphere is X. How will the electric flux change, if at all, when charge q is replaced by an electric dipole?
