Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Sales Tax and Value Added Tax
3: Banking
4: Shares and Dividends
5: Linear Inequations (Solving Linear Inequations in One Variable)
6: Quadratic Equation
7: Reflection
8: Ratio and Proportion
9: Factorization
10: Matrices
11: Coordinate Geometry
12: Symmetry
13: Similarity
14: Loci (Locus and its Constructions)
15: Circles
▶ 16: Constructions (Circle)
17: Mensuration
18: Trigonometry
19: Statistics
20: Probability
![ICSE solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 16 - Constructions (Circle) ICSE solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 16 - Constructions (Circle) - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 16: Constructions (Circle)
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 16 of CISCE ICSE for Mathematics [English] Class 10.
ICSE solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 16 Constructions (Circle) Exercise
Take a point O on the plane at the paper. With O as center draw a circle of radius 3 cm. Take a point P on this circle and draw a tangent at P.
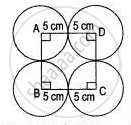
Four equal circles, each of radius 5 cm, touch each other as shown in the figure. Find the area included between them. (Take π= 3.14)
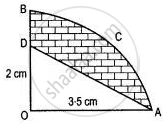
In the figure alongside, OAB is a quadrant of a circle. The radius OA = 3.5 cm and OD = 2 cm. Calculate the area of the shaded 22 portions.
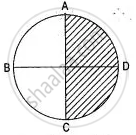
AC and BD are two perpendicular diameter of a circle ABCD. Given that the area of shaded portion is 308 cm2 calculate:
(i) The length of AC and
(ii) The circumference of circle
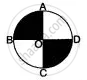
The diagram represents the area swept by wiper of a car. With the dimension given in figure, calculate the shaded swept by the wiper.

AC and BD are two perpendicular diameters of a circle with centre O. If AC = 16 cm, calculate the area and perimeter of the shaded part. (Take π = 3.14).
Draw a circle at a radius of 4 cm. Take a point on it. Without using the centre at the circle, draw a tangent to the circle at point P.
Draw a circle at a radius of 3 cm. Take a point at 5.5 cm from the center at the circle. From point P, draw two tangents to the circle.
Use a ruler and a pair of compasses to construct ΔABC in which BC = 4.2 cm, ∠ ABC = 60°, and AB 5 cm. Construct a circle of radius 2 cm to touch both the arms of ∠ ABC of Δ ABC.
Construct an isosceles triangle ABC such that AB = 6 cm, BC = AC = 4 cm. Bisect ∠C internally and mark a point P on this bisector such that CP = 5 cm. Find the points Q and R which are 5 cm from P and also 5 cm from the line AB.
Draw two lines AB, AC so that ∠ BAC = 40°:
(i) Construct the locus of the center of a circle that touches AB and has a radius of 3.5 cm.
(ii) Construct a circle of radius 35 cm, that touches both AB and AC, and whose center lies within the ∠ BAC.
Draw a circle of radius 3.5 cm. Mark a point P outside the circle at a distance of 6 cm from the centre. Construct two tangents from P to the given circle. Measure and write down the length of one tangent.
Construct a triangle ABC, given that the radius of the circumcircle of triangle ABC is 3.5 cm, ∠ BCA = 45° and ∠ BAC = 60°.
Construct an angle PQR = 45°. Mark a point S on QR such that QS = 4.5 cm. Construct a circle to touch PQ at Q and also to pass through S.
Construct the circumcircle of the ABC when BC = 6 cm, B = 55° and C = 70°.
Using ruler and compass only, construct a triangle ABC such that AB = 5 cm, ABC = 75°, and the radius of the circumcircle of triangle ABC is 3.5 cm. On the same diagram, construct a circle, touching AB at its middle point and also touching the side AC.
(a) Only the ruler and compass may be used in this question. All contraction lines and arcs must be clearly shown and be of sufficient length and clarity to permit assessment.
(i) Construct a ABC, such that AB = AC = 7 cm and BC = 5 cm.
(ii) Construct AD, the perpendicular bisector of BC.
(iii) Draw a circle with center A and radius 3 cm. Let this circle cut AD at P.
(iv) Construct another circle, to touch the circle with center A, externally at P, and pass through B and C.
Using ruler and compass construct a cyclic quadrilateral ABCD in which AC = 4 cm, ∠ ABC = 60°, AB 1.5 cm and AD = 2 cm. Also, write the steps of construction.
Construct a triangle whose sides are 4.4 cm, 5.2 cm, and 7.1 cm. Construct its circumcircle. Write also the steps of construction.
Draw a circle of radius 3 cm. Construct a square about the circle.
Draw a circle of radius 2.5 cm and circumscribe a regular hexagon about it.
Construct the rhombus ABCD whose diagonals AC and BD are of lengths 8 cm and 6 cm respectively. Construct the inscribed circle of the rhombus. Measure its radius.
Draw an isosceles triangle with sides 6 cm, 4 cm, and 6 cm. Construct the incircle of the triangle. Also, write the steps of construction.
Use ruler and compasses only for this question:
(i) Construct A ABC, where AB = 3.5 cm, BC = 6 cm and ∠ ABC = 60°.
(ii) Construct the locus of points inside the triangle which are equidistant from BA and BC.
(iii) Construct the locus of points inside the triangle which are equidistant from B and C.
(iv) Mark the point P which is equidistant from AB, BC, and also equidistant from B and C. Measure and record the length of PB.
Construct a Δ ABC with BC = 6.5 cm, AB = 5.5 cm, AC = 5 cm. Construct the incircle of the triangle. Measure and record the radius of the incircle.
Draw a circle of radius 4 cm. Take a point P outside the circle without using the center at the circle. Draw two tangents to the circle from point P.
Use a ruler and compass only for this question to construct the cyclic quadrilateral ABCD in which AB = 5 cm, BC = 8 cm, ∠ ABC =
Ruler and compasses only may be used in this question. All constructions lines and arcs must be clearly shown, and the be sufficient length and clarity to permit assessment:
(i) Construct a triangle ABC, in which AB = 9 cm, BC = 10 cm and angle ABC = 45°.
(ii) Draw a circle, with center A and radius 2.5 cm. Let it meet AB at D.
(iii) Construct a circle to touch the circle with center A externally at D and also to touch the line BC.
(i) Construct a triangle ABC, in which AB = 5.0 cm, BC = 3.5 cm and ∠ ABC =
( Use a pair of compasses and ruler only.)
(ii) Construct a circle to touch AB at B and it pass though C.
The center O of a circle of a radius 1.3 cm is at a distance of 3.8 cm from a given straight line AB. Draw a circle to touch the given straight line AB at a point P so that OP = 4.7 cm and to touch the given circle externally.
Using a ruler and compasses only:
(i) Construct a triangle ABC with the following data: AB = 3.5 cm, BC = 6 cm and ∠ ABC = 120°.
(ii) In the same diagram, draw a circle with BC as diameter. Find a point P on the circumference of the circle which is equidistant from AB and BC.
(iii) Measure ∠ BCP.
Draw a circle of radius 3 cm and construct a tangent to it from an external point without using the center.
Construct a ΔABC with base BC = 3.5 cm, vertical angle ∠ BAC = 45°, and median through the vertex A is 3.5 cm. Write also the steps of construction.
Solutions for 16: Constructions (Circle)
![ICSE solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 16 - Constructions (Circle) ICSE solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 16 - Constructions (Circle) - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
ICSE solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 16 - Constructions (Circle)
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 10 CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. ICSE solutions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 10 CISCE 16 (Constructions (Circle)) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. ICSE textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 16 Constructions (Circle) are Circumscribing and Inscribing a Circle on a Regular Hexagon, Circumscribing and Inscribing a Circle on a Triangle, Construction of Tangents to a Circle, Circumscribing and Inscribing Circle on a Quadrilateral, Circumference of a Circle, Surface Area of a Right Circular Cone, Circle - Direct Application Problems Including Inner and Outer Area, Volume of a Cylinder, Volume of a Combination of Solids, Surface Area of a Sphere, Surface Area of Cylinder, Circumference of a Circle, Surface Area of a Sphere, Surface Area of a Right Circular Cone.
Using ICSE Mathematics [English] Class 10 solutions Constructions (Circle) exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in ICSE Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Mathematics [English] Class 10 students prefer ICSE Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 16, Constructions (Circle) Mathematics [English] Class 10 additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 10 CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
