Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Sales Tax and Value Added Tax
3: Banking
4: Shares and Dividends
5: Linear Inequations (Solving Linear Inequations in One Variable)
6: Quadratic Equation
7: Reflection
8: Ratio and Proportion
9: Factorization
10: Matrices
11: Coordinate Geometry
12: Symmetry
▶ 13: Similarity
14: Loci (Locus and its Constructions)
15: Circles
16: Constructions (Circle)
17: Mensuration
18: Trigonometry
19: Statistics
20: Probability
![ICSE solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 13 - Similarity ICSE solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 13 - Similarity - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 13: Similarity
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 13 of CISCE ICSE for Mathematics [English] Class 10.
ICSE solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 13 Similarity Determine the Following
The model of a building is constructed with scale factor 1:30.
(i) If the height of the model is 80 cm, find the actual height of the building in metres.
(ii) If the actual volume of a tank at the top of the building is 27 m3, find the volume of the tank on the top of the model.
Triangles ABC and DEF are similar.
If area (ΔABC) = 16 cm, area (ΔDEF) = 25 cm2 and BC = 2.3 cm find EF.
Triangles ABC and DEF are similar.
If area (ΔABC) = 9 cm2, area (ΔDEF) = 64 cm2 and DE = 5.1 cm, find AB.
Triangles ABC and DEF are similar.
If AC = 19 cm and DF = 8 cm, find the ratio between the area of two triangles.
Triangles ABC and DEF are similar.
If area (ΔABC) = 36 cm2, area (ΔDEF) = 64 cm2 and DE = 6.2 cm, find AB.
Triangles ABC and DEF are similar.
If area (ΔABC) = 36 cm2, area (ΔDEF) = 64 cm2 and DE = 6.2 cm, find AB.
ICSE solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 13 Similarity Prove the Following
In ΔPQR, L and M are two points on the base QR, such that ∠LPQ = ∠QRP and ∠RPM = ∠RQP.
Prove that : (i) ΔPQL ∼ ΔRPM
(ii) QL. Rm = PL. PM
(iii) PQ2 = QR. QL.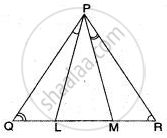
D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively of a Δ ABC such that DE | | BC and divides Δ ABC into two parts, equal in area. Find `"BD"/"AB"`.
Prove that the area of the triangle BCE described on one side BC of a square ABCD as base is one half of the area of similar triangle ACF described on the diagonal AC as base.
In figure ABC and DBC are two triangles on the same base BC. Prove that
`"Area (ΔABC)"/"Area (ΔDBC)" = "AO"/"DO"`.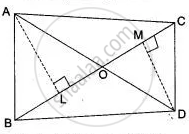
In the adjoining figure, the medians BD and CE of a ∆ABC meet at G. Prove that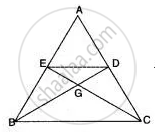
(i) ∆EGD ∼ ∆CGB and
(ii) BG = 2GD for (i) above.
ICSE solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 13 Similarity Figure Based Questions
In the adjoining figure, ΔACB ∼ ∆APQ. If BC = 10 cm, PQ = 5 cm, BA = 6.5 cm and AP = 2.8 cm find the area (∆ACB) : area (∆APQ).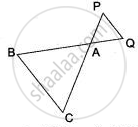
Two isosceles triangle have equal vertical angles and their areas are in the ratio of 36 : 25. Find the ratio between their corresponding heights.
In ΔABC, and E are the mid-points of AB and AC respectively. Find the ratio of the areas of ΔADE and ΔABC.
In the given figure, AB and DE are perpendicular to BC.
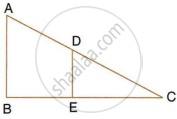
- Prove that ΔABC ∼ ΔDEC
- If AB = 6 cm, DE = 4 cm and AC = 15 cm. Calculate CD.
- Find the ratio of the area of a ΔABC : area of ΔDEC.
In the given figure, ABC is a triangle. DE is parallel to BC and `"AD"/"DB" = (3)/(2)`.
(i) Determine the ratios `"AD"/"AB","DE"/"BC"`.
(ii) Prove that ΔDEF is similar to ΔCBF.
Hence, find `"EF"/"FB"`.
(iii) What is the ratio of the areas of ΔDEF and ΔBFC?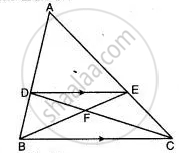
In the adjoining figure ABC is a right angle triangle with ∠BAC = 90°, and AD ⊥ BC.
(i) Prove ΔADB ∼ ΔCDA.
(ii) If BD = 18 cm, CD = 8 cm find AD.
(iii) Find the ratio of the area of ΔADB is to area of ΔCDA.
Equilateral triangles are drawn on the sides of a right angled triangle. Show that the area of the triangle on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the areas of triangles on the other two sides.
On a map drawn to scale of 1 : 2,50,000 a rectangular plot of land ABCD has the following measurement AB = 12 cm, BC = 16 cm angles A, B, C, and D are 900 each. Calculate:
(i) The diagonal distance of the plot of land in
(ii) Actual length of diagonal.
On a map drawn to a scale of 1 : 2,50,000; a triangular plot of land has the following measurements : AB = 3 cm, BC = 4 cm and angle ABC = 90°.
Calculate:
- the actual lengths of AB and BC in km.
- the area of the plot in sq. km.
In the adjoining figure. BC is parallel to DE, area of ΔABC = 25 sq cm, area of trapezium BCED = 24 sq cm, DE = 14 cm. Calculate the length of BC.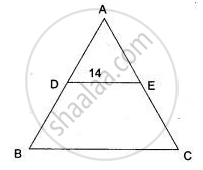
In fig. ABCD is a trapezium in which AB | | DC and AB = 2DC. Determine the ratio between the areas of ΔAOB and ΔCOD.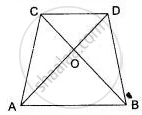
In the given figure ABC is a triangle with ∠EDB = ∠ACB.
(i) Prove that ΔABC ∼ ΔEBD.
(ii) If BE = 6 cm, EC = 4 cm, BD = 5 cm and area of ΔBED = 9 cm2. Calculate the length of AB and area of ΔABC.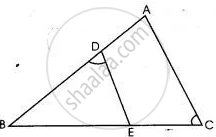
In the figure below, PB and QA are perpendiculars to the line segment AB. If PO = 6 cm, QO = 9 cm and the area of ΔPOB = 120 cm2, find the area of ΔQOA.
In the given figure ABC and CEF are two triangles where BA is parallel to CE and AF: AC = 5: 8.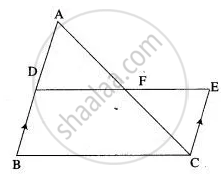
(i) Prove that ΔADF ∼ ΔCEF
(ii) Find AD if CE = 6 cm
(iii) If DF is parallel to BC find area of ΔADF: area of ΔABC.
In the given figure ΔABC and ΔAMP are right angled at B and M respectively.
Given AC = 10 cm, AP = 15 cm and PM = 12 cm.
(i) Prove ΔABC ∼ Δ AMP.
(ii) Find AB and BC.
Triangles ABC and DEF are similar.
If area (ΔABC) = 16 cm2, area (ΔDEF) = 25 cm2 and BC = 2·3 cm find EF.
Triangles ABC and DEF are similar.
If area (ΔABC) = 9 cm2, area (ΔDEF) = 64 cm2 and BC = 5·1 cm find AB.
Triangles ABC and DEF are similar.
If AC = 19 cm and DF = 8 cm, find the ratio between the areas of two triangles.
Triangles ABC and DEF are similar.
If area (ΔABC) = 36 cm2, area (ΔDEf) = 64 cm2 and DE = 6.2 cm, find AB.
In ΔABC, ∠ABC = ∠DAC, AB = 8 cm, AC = 4 cm and AD = 5 cm.
- Prove that ΔACD is similar to ΔBCA.
- Find BC and CD.
- Find area of ΔACD : area of ΔABC.
Solutions for 13: Similarity
![ICSE solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 13 - Similarity ICSE solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 13 - Similarity - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
ICSE solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 13 - Similarity
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 10 CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. ICSE solutions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 10 CISCE 13 (Similarity) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. ICSE textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics [English] Class 10 chapter 13 Similarity are Similarity of Triangles, Axioms of Similarity of Triangles, Conditions for Similarity of Two Triangles: (Sas, Aa Or Aaa and Sss), Basic Proportionality Theorem with Applications, Relation Between the Areas of Two Triangles, Similarity as a Size Transformation, Direct Applications Based on the Above Including Applications to Maps and Models, Areas of Similar Triangles Are Proportional to the Squares on Corresponding Sides.
Using ICSE Mathematics [English] Class 10 solutions Similarity exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in ICSE Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Mathematics [English] Class 10 students prefer ICSE Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 13, Similarity Mathematics [English] Class 10 additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 10 CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
