Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A rectangular brick is kept on a table with a part of its length projecting out. It remains at rest if the length projected is slightly less than half the total length but it falls down if the length projected is slightly more than half the total length. Give reason.
उत्तर
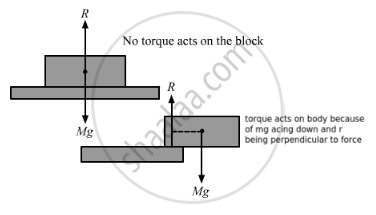
The centre of mass (CM) of a rectangular block lies in the middle of the block . When the block is projected less than half of its length (CM being over the table), no net force acts on it . Thus, no net torque acts upon the body . But if the block is projected more than half of its length outside the table (CM being outside the table), gravitational force acts along the CM of the block . This force produces a moment along the edge of the table . This rotates the block, and as a result, it falls down.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain why friction is necessary to make the disc in Figure roll in the direction indicated
(a) Give the direction of frictional force at B, and the sense of frictional torque, before perfect rolling begins.
(b) What is the force of friction after perfect rolling begins?
The torque of the weight of any body about any vertical axis is zero. If it always correct?
If several forces act on a particle, the total torque on the particle may be obtained by first finding the resultant force and then taking torque of this resultant. Prove this. Is this result valid for the forces acting on different particles of a body in such a way that their lines of action intersect at a common point?
A ladder is resting with one end on a vertical wall and the other end on a horizontal floor. If it more likely to slip when a man stands near the bottom or near the top?
Equal torques act on the disc A and B of the previous problem, initially both being at rest. At a later instant, the linear speeds of a point on the rim of A and another point on the rim of B are \[\nu_A\] and \[\nu_B\] respectively. We have
The density of a rod gradually decreases from one end to the other. It is pivoted at an end so that it can move about a vertical axis though the pivot. A horizontal force F is applied on the free end in a direction perpendicular to the rod. The quantities, that do not depend on which end of the rod is pivoted, are ________________ .
When a force of 6⋅0 N is exerted at 30° to a wrench at a distance of 8 cm from the nut it is just able to loosen the nut. What force F would be sufficient to loosen it if it acts perpendicularly to the wrench at 16 cm from the nut?

A 6⋅5 m long ladder rests against a vertical wall reaching a height of 6⋅0 m. A 60 kg man stands half way up the ladder.
- Find the torque of the force exerted by the man on the ladder about the upper end of the ladder.
- Assuming the weight of the ladder to be negligible as compared to the man and assuming the wall to be smooth, find the force exerted by the ground on the ladder.
A particle is moving with a constant velocity along a line parallel to the positive X-axis. The magnitude of its angular momentum with respect to the origin is, ______
Two discs of the same moment of inertia rotating about their regular axis passing through centre and perpendicular to the plane of the disc with angular velocities ω1 and ω2. They are brought in to contact face to face coinciding with the axis of rotation. The expression for loss of energy during this process is, ______
State conservation of angular momentum.
Choose the correct alternatives:
- For a general rotational motion, angular momentum L and angular velocity ω need not be parallel.
- For a rotational motion about a fixed axis, angular momentum L and angular velocity ω are always parallel.
- For a general translational motion , momentum p and velocity v are always parallel.
- For a general translational motion, acceleration a and velocity v are always parallel.
The net external torque on a system of particles about an axis is zero. Which of the following are compatible with it?
- The forces may be acting radially from a point on the axis.
- The forces may be acting on the axis of rotation.
- The forces may be acting parallel to the axis of rotation.
- The torque caused by some forces may be equal and opposite to that caused by other forces.
A door is hinged at one end and is free to rotate about a vertical axis (Figure). Does its weight cause any torque about this axis? Give reason for your answer.
Two discs of moments of inertia I1 and I2 about their respective axes (normal to the disc and passing through the centre), and rotating with angular speed ω2 and ω2 are brought into contact face to face with their axes of rotation coincident.
- Does the law of conservation of angular momentum apply to the situation? why?
- Find the angular speed of the two-disc system.
- Calculate the loss in kinetic energy of the system in the process.
- Account for this loss.
A spherical shell of 1 kg mass and radius R is rolling with angular speed ω on horizontal plane (as shown in figure). The magnitude of angular momentum of the shell about the origin O is `a/3 R^2` ω. The value of a will be:
The position vector of 1 kg object is `vecr = (3hati - hatj)` m and its velocity `vecv = (3hati + hatk)` ms-1. The magnitude of its angular momentum is `sqrtx` Nm where x is ______.
A solid sphere is rotating in free space. If the radius of the sphere is increased while keeping the mass the same, which one of the following will not be affected?
