Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Following the case, state whether the function is one-one, onto, or bijective. Justify your answer.
f : R → R defined by f(x) = 3 − 4x
उत्तर
f: R → R is defined as f(x) = 3 − 4x.
Let `x_1 , x_2 in R " such that " f(x_1) = f(x_2)`
`=> 3 - 4x_1 = 3 - 4x_2`
`=> -4x_1 = -4x_2`
`=> x_1 = x_2`
∴ f is one-one.
f: R → R be given for every y ∈ R (co-domain of f), there exists an element x ∈ R (domain of f) such that
f(x) = y
=> y = 3 - 4x
For any real number (y) in R, there `(3-y)/4` in R such that
`f((3-y)/4)`
= `3 -4 ((3-y)/4)`
= y
∴f is onto.
Hence, f is bijective.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Let A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {4, 5, 6, 7} and let f = {(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)} be a function from A to B. Show that f is one-one.
Following the case, state whether the function is one-one, onto, or bijective. Justify your answer.
f: R → R defined by f(x) = 1 + x2
Give an example of a function which is one-one but not onto ?
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection : f : N → N given by f(x) = x2
If A = {1, 2, 3}, show that a onto function f : A → A must be one-one.
Find gof and fog when f : R → R and g : R → R is defined by f(x) = 2x + 3 and g(x) = x2 + 5 .
Let f be any real function and let g be a function given by g(x) = 2x. Prove that gof = f + f.
Let f be a real function given by f (x)=`sqrt (x-2)`
Find each of the following:
(i) fof
(ii) fofof
(iii) (fofof) (38)
(iv) f2
Also, show that fof ≠ `f^2` .
State with reason whether the following functions have inverse:
h : {2, 3, 4, 5} → {7, 9, 11, 13} with h = {(2, 7), (3, 9), (4, 11), (5, 13)}
Let f : [−1, ∞) → [−1, ∞) be given by f(x) = (x + 1)2 − 1, x ≥ −1. Show that f is invertible. Also, find the set S = {x : f(x) = f−1 (x)}.
If A = {1, 2, 3, 4} and B = {a, b, c, d}, define any four bijections from A to B. Also give their inverse functions.
If f : R → R is given by f(x) = x3, write f−1 (1).
Write whether f : R → R, given by `f(x) = x + sqrtx^2` is one-one, many-one, onto or into.
What is the range of the function
`f (x) = ([x - 1])/(x -1) ?`
If f : R → R is defined by f(x) = 3x + 2, find f (f (x)).
The function \[f : [0, \infty ) \to \text {R given by } f\left( x \right) = \frac{x}{x + 1} is\]
Which of the following functions from
to itself are bijections?
Let
\[f : R - \left\{ n \right\} \to R\]
\[f : R \to R\] is defined by
\[f\left( x \right) = \frac{e^{x^2} - e^{- x^2}}{e^{x^2 + e^{- x^2}}} is\]
A function f from the set of natural numbers to the set of integers defined by
\[f\left( n \right)\begin{cases}\frac{n - 1}{2}, & \text{when n is odd} \\ - \frac{n}{2}, & \text{when n is even}\end{cases}\]
Let \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{1}{1 - x} . \text{Then}, \left\{ f o \left( fof \right) \right\} \left( x \right)\]
The distinct linear functions that map [−1, 1] onto [0, 2] are
If \[f : R \to \left( - 1, 1 \right)\] is defined by
\[f\left( x \right) = \frac{- x|x|}{1 + x^2}, \text{ then } f^{- 1} \left( x \right)\] equals
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
If the set A contains 5 elements and the set B contains 6 elements, then the number of one-one and onto mappings from A to B is
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
Let f : R \[-\] \[\left\{ \frac{3}{5} \right\}\] \[\to\] R be defined by f(x) = \[\frac{3x + 2}{5x - 3}\] Then,
If f(x) = `(x+3)/(4x−5) , "g"(x) = (3+5x)/(4x−1)` then verify that `("fog") (x)` = x.
Let the function f: R → R be defined by f(x) = 4x – 1, ∀ x ∈ R. Then, show that f is one-one.
Are the following set of ordered pairs functions? If so, examine whether the mapping is injective or surjective.
{(x, y): x is a person, y is the mother of x}
Let X = {1, 2, 3}and Y = {4, 5}. Find whether the following subset of X ×Y are function from X to Y or not
k = {(1,4), (2, 5)}
The function f : A → B defined by f(x) = 4x + 7, x ∈ R is ____________.
Let f : R → R be a function defined by f(x) `= ("e"^abs"x" - "e"^-"x")/("e"^"x" + "e"^-"x")` then f(x) is
Raji visited the Exhibition along with her family. The Exhibition had a huge swing, which attracted many children. Raji found that the swing traced the path of a Parabola as given by y = x2.
Answer the following questions using the above information.
- The function f: Z → Z defined by f(x) = x2 is ____________.
If f: R → R given by f(x) =(3 − x3)1/3, find f0f(x)
Let f: R → R defined by f(x) = x4. Choose the correct answer
'If 'f' is a linear function satisfying f[x + f(x)] = x + f(x), then f(5) can be equal to:
Number of integral values of x satisfying the inequality `(3/4)^(6x + 10 - x^2) < 27/64` is ______.
Let f(x) = ax (a > 0) be written as f(x) = f1(x) + f2(x), where f1(x) is an even function and f2(x) is an odd function. Then f1(x + y) + f1(x – y) equals ______.
A function f : [– 4, 4] `rightarrow` [0, 4] is given by f(x) = `sqrt(16 - x^2)`. Show that f is an onto function but not a one-one function. Further, find all possible values of 'a' for which f(a) = `sqrt(7)`.
Write the domain and range (principle value branch) of the following functions:
f(x) = tan–1 x.
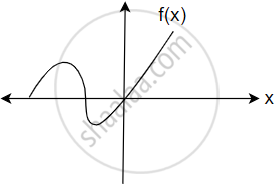
The given function f : R → R is not ‘onto’ function. Give reason.
