Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If ∠A and ∠B are acute angles such that sin A = Sin B prove that ∠A = ∠B.
उत्तर
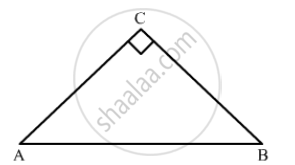
In ΔABC, ∠𝐶 = 90°
sin A = `(BC)/(AB)`and
sin B= `(AC)/(AB)`
As, sin 𝐴 = sin 𝐵
`⇒ (BC)/(AB) = (AC)/(AB)`
⇒ BC= AC
So, ∠𝐴 = ∠𝐵 (𝐴𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 𝑡𝑜 𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒𝑠 𝑎𝑟𝑒 𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑙)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If 3 cot A = 4, Check whether `((1-tan^2 A)/(1+tan^2 A)) = cos^2 "A" - sin^2 "A"` or not.
If A = B = 60°, verify that sin (A − B) = sin A cos B − cos A sin B
In right angled triangle ABC. ∠C = 90°, ∠B = 60°. AB = 15 units. Find remaining angles and sides.
Evaluate:
sin600 cos300 + cos600 sin300
Evaluate:
cos450 cos300 + sin450 sin300
From the following figure, find the values of:
- sin A
- cos A
- cot A
- sec C
- cosec C
- tan C

Given : sin A = `(3)/(5)` , find : (i) tan A (ii) cos A
In the diagram, given below, triangle ABC is right-angled at B and BD is perpendicular to AC.
Find:
(i) cos ∠DBC
(ii) cot ∠DBA

In the figure given below, ABC is an isosceles triangle with BC = 8 cm and AB = AC = 5 cm. Find:
(i) sin B
(ii) tan C
(iii) sin2 B + cos2B
(iv) tan C - cot B
If sin A = `(7)/(25)`, find the value of : `(2"tanA")/"cot A - sin A"`
