Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If ∠A and ∠B are acute angles such that tan A= Tan B then prove that ∠A = ∠B
उत्तर
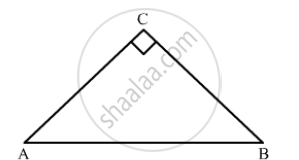
In ΔABC, ∠𝐶 = 90°
Tan A = `(BC)/(AC)` and
Tan B = `(AC)/(BC)`
As, tan 𝐴 = tan 𝐵
`⇒ (BC)/(AC) = (AC)/(BC)`
`⇒ BC^2 = AC^2`
⇒ BC=AC
So, ∠𝐴 = ∠𝐵 (𝐴𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 𝑡𝑜 𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒𝑠 𝑎𝑟𝑒 𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑙)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If 3cos θ – 4sin = 2cos θ + sin θ Find tan θ.
If θ is a positive acute angle such that sec θ = cosec 60°, find 2 cos2 θ – 1
sin20° = cos ______°
If cos A = `(1)/(2)` and sin B = `(1)/(sqrt2)`, find the value of: `(tan"A" – tan"B")/(1+tan"A" tan"B")`.
Are angles A and B from the same triangle? Explain.
If 3 cos A = 4 sin A, find the value of :
(i) cos A(ii) 3 - cot2 A + cosec2A.
In rhombus ABCD, diagonals AC and BD intersect each other at point O.
If cosine of angle CAB is 0.6 and OB = 8 cm, find the lengths of the side and the diagonals of the rhombus.
If 5 cos θ = 3, evaluate : `(co secθ – cot θ)/(co secθ + cot θ)`
In each of the following, one trigonometric ratio is given. Find the values of the other trigonometric.
cos A = `(7)/(25)`
If cos A = `(2x)/(1 + x^2)`, then find the values of sin A and tan A in terms of x
Assertion (A): For 0 < 0 ≤ 90°, cosec θ – cot θ and cosec θ + cot θ are reciprocal of each other.
Reason (R): cot2 θ – cosec2 θ = 1.
