Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If ∠A and ∠B are acute angles such that sin A = Sin B prove that ∠A = ∠B.
Solution
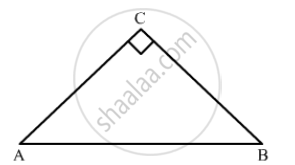
In ΔABC, ∠𝐶 = 90°
sin A = `(BC)/(AB)`and
sin B= `(AC)/(AB)`
As, sin 𝐴 = sin 𝐵
`⇒ (BC)/(AB) = (AC)/(AB)`
⇒ BC= AC
So, ∠𝐴 = ∠𝐵 (𝐴𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 𝑡𝑜 𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒𝑠 𝑎𝑟𝑒 𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑙)
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If 2θ + 45° and 30° − θ are acute angles, find the degree measure of θ satisfying Sin (20 + 45°) = cos (30 - θ°)
If tan θ =`15/ 8 `, find the values of all T-ratios of θ.
If a right ΔABC , right-angled at B, if tan A=1 then verify that 2sin A . cos A = 1
Using the formula, sin A = `sqrt((1-cos 2A)/2) ` find the value of sin 300, it being given that cos 600 = `1/2`
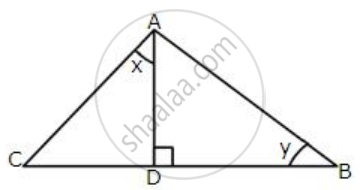
In the following figure:
AD ⊥ BC, AC = 26 CD = 10, BC = 42, ∠DAC = x and ∠B = y.
Find the value of :
(i) cot x
(ii) `1/sin^2 y – 1/tan^2 y`
(iii) `6/cos x – 5/cos y + 8 tan y`.
In ΔABC, ∠B = 90°. If AB = 12units and BC = 5units, find: cos C
If sinA = `(3)/(5)`, find cosA and tanA.
If 8 tanθ = 15, find (i) sinθ, (ii) cotθ, (iii) sin2θ - cot2θ
In the given figure, PQR is a triangle, in which QS ⊥ PR, QS = 3 cm, PS = 4 cm and QR = 12 cm, find the value of: sin P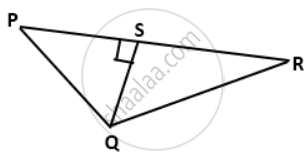
From the given figure, find all the trigonometric ratios of angle B
