Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the diagram, given below, triangle ABC is right-angled at B and BD is perpendicular to AC.
Find:
(i) cos ∠DBC
(ii) cot ∠DBA

उत्तर १
Consider the given figure :
Since the triangle is a right-angled triangle, so using Pythagorean Theorem
AC2 = 52 + 122
AC2 = 25 + 144 + 169
AC = 13
In ΔCBD and ΔCBA, the ∠C is common to both the triangles, ∠CDB = ∠CBA = 90° so therefore ∠CBD = ∠CAB.
Therefore ΔCBD and ΔCBA are similar triangles according to AAA Rule
So
`"AC"/"BC" = "AB"/"BD"`
`(13)/(5) = ( 12)/"BD"`
`"BD = (60)/(13)`
(i) cos ∠DBC = `"base"/"hypotenuse" = "BD"/"BC" = (60/13)/(5) =(12)/(13)`
(ii) cot ∠DBA =`"base"/"perpendicular" = "BD"/"AB" = (60/13)/(12) =(5)/(13)`
उत्तर २
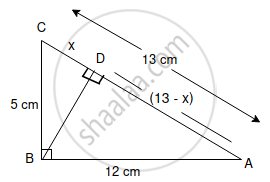
Since the triangle ABC is a right-angled triangle, so using Pythagorean Theorem,
AC2 = BC2 + AB2
AC2 = 52 + 122
AC2 = 25 + 144
AC2 = 169
AC2 = `sqrt169`
AC = 13
In ΔDBC, using Pythagorean Theorem,
BC2 = CD2 + BD2
(5)2 = x2 + BD2
25 - x2 = BD2
BD2 = 25 - x2 ...(i)
In ΔDBA, using Pythagorean Theorem,
BA2 = DA2 + BD2
(12)2 = (13 - x)2 + BD2
144 = (13 - x)2 + BD2
144 = 169 + x2 - 26x + BD2
144 - 169 - x2 + 26x = BD2
BD2 = - 25 - x2 + 26x ...(ii)
From equation (i) and (ii)
25 - x2 = - 25 - x2 + 26x
25 + 25 = 26x
x = `50/26`
x = `25/13`
In ΔBDC,
BC = 5 ; CD = `25/13`
BD2 = 25 - x2
= 25 - `(25/13)^2`
= 25 - `625/169`
= 25 `(1 - 25/169)`
= `25 ((169 - 25)/169)`
BD = `sqrt(25 (144/169))`
BD = `(5 xx 12)/13`
BD = `60/13`
In ΔDBA,
AB = 12; BD = `60/13`
AD = 13 - x
= `13 - 25/13 = (169 - 25)/13 = 144/13`
(i) cos ∠DBC = `"Base"/"hypotenuse" = (60/13)/5 = 60/65 = 12/13`
(ii) cot ∠DBA `= "Base"/"perpendicular" = (60/13)/(144/13) = 60/144 = 10/24 " i.e.," 5/13`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If θ = 30° verify `tan 2 theta = (2 tan theta)/(1 - tan^2 theta)`
If Sec 4A = cosec (A – 20°) where 4A is an acute angle, find the value of A.
In a right-angled triangle, it is given that A is an acute angle and tan A = `(5) /(12)`.
find the value of :
(i) cos A
(ii) sin A
(iii) ` (cosA+sinA)/(cosA– sin A)`
If cot θ= 1; find the value of: 5 tan2 θ+ 2 sin2 θ- 3
If sin A + cosec A = 2;
Find the value of sin2 A + cosec2 A.
Given : 17 cos θ = 15;
Find the value of: tan θ + 2 secθ .
Given q tan A = p, find the value of:
`("p" sin "A" – "q" cos "A")/("p" sin "A" + "q" cos "A")`.
From the given figure, find the values of sec B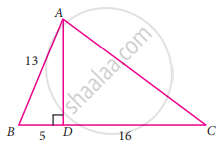
From the given figure, find the values of cosec C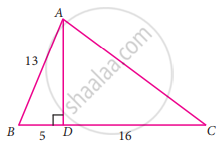
If 3 cot A = 2, then find the value of `(4sin"A" - 3cos"A")/(2sin"A" + 3cos"A")`
