Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If f(x) = loge (1 − x) and g(x) = [x], then determine function:
(i) f + g
उत्तर
Given:
f(x) = loge (1 − x) and g(x) = [x]
Clearly, f(x) = loge (1 − x) is defined for all ( 1 -x) > 0.
⇒ 1 > x
⇒ x < 1
⇒ x ∈ ( -∞, 1)
Thus, domain (f ) = ( - ∞, 1)
Again,
g(x) = [x] is defined for all x ∈ R.
Thus, domain (g) = R
∴ Domain (f) ∩ Domain (g) = ( - ∞, 1) ∩ R = ( -∞, 1)
Hence,
(i ) ( f + g ) : ( -∞, 1) → R is given by ( f + g ) (x) = f (x) + g (x) = loge (1 − x) + [ x ].
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
find: f(1), f(−1), f(0) and f(2).
Let f : R+ → R, where R+ is the set of all positive real numbers, such that f(x) = loge x. Determine
(b) {x : f(x) = −2}
Let f and g be two real functions defined by \[f\left( x \right) = \sqrt{x + 1}\] and \[g\left( x \right) = \sqrt{9 - x^2}\] . Then, describe function:
(i) f + g
If f(x) = loge (1 − x) and g(x) = [x], then determine function:
(iii) \[\frac{f}{g}\]
Write the range of the real function f(x) = |x|.
Write the range of the function f(x) = ex−[x], x ∈ R.
If f(x) = 4x − x2, x ∈ R, then write the value of f(a + 1) −f(a − 1).
Which one of the following is not a function?
If f(x) = cos (log x), then the value of f(x2) f(y2) −
If f(x) = cos (log x), then value of \[f\left( x \right) f\left( 4 \right) - \frac{1}{2} \left\{ f\left( \frac{x}{4} \right) + f\left( 4x \right) \right\}\] is
If \[f\left( x \right) = 64 x^3 + \frac{1}{x^3}\] and α, β are the roots of \[4x + \frac{1}{x} = 3\] . Then,
If f : R → R be given by for all \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{4^x}{4^x + 2}\] x ∈ R, then
Check if the following relation is a function.
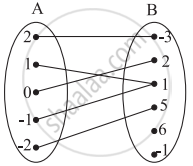
Which sets of ordered pairs represent functions from A = {1, 2, 3, 4} to B = {−1, 0, 1, 2, 3}? Justify.
{(1, 3), (4, 1), (2, 2)}
Find the domain and range of the following function.
f(x) = `root(3)(x + 1)`
Express the following exponential equation in logarithmic form
10−2 = 0.01
Find the domain of f(x) = log10 (x2 − 5x + 6)
Write the following expression as a single logarithm.
`1/3 log (x - 1) + 1/2 log (x)`
Solve for x.
log2 + log(x + 3) – log(3x – 5) = log3
Solve for x.
log2 x + log4 x + log16 x = `21/4`
If `log(( x - y)/4) = logsqrt(x) + log sqrt(y)`, show that (x + y)2 = 20xy
Answer the following:
A function f is defined as : f(x) = 5 – x for 0 ≤ x ≤ 4. Find the value of x such that f(x) = 5
Answer the following:
If f(x) = ax2 + bx + 2 and f(1) = 3, f(4) = 42, find a and b
Answer the following:
Let f : R → R be given by f(x) = x + 5 for all x ∈ R. Draw its graph
Answer the following:
Show that, `log ("a"^2/"bc") + log ("b"^2/"ca") + log ("c"^2/"ab")` = 0
Answer the following:
If a2 + b2 = 7ab, show that, `log(("a" + "b")/3) = 1/2 log "a" + 1/2 log "b"`
A graph representing the function f(x) is given in it is clear that f(9) = 2
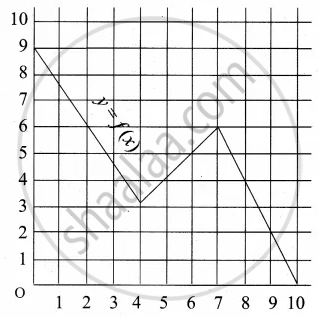
What is the image of 6 under f?
Let f(x) = 2x + 5. If x ≠ 0 then find `(f(x + 2) -"f"(2))/x`
A function f is defined by f(x) = 3 – 2x. Find x such that f(x2) = (f(x))2
The function f and g are defined by f(x) = 6x + 8; g(x) = `(x - 2)/3`
Calculate the value of `"gg" (1/2)`
The domain of the function f(x) = `sqrtx` is ______.
If a function f(x) is given as f(x) = x2 – 6x + 4 for all x ∈ R, then f(–3) = ______.
Let A and B be any two sets such that n(B) = p, n(A) = q then the total number of functions f : A → B is equal to ______.
Find the domain of the following functions given by f(x) = `1/sqrt(1 - cos x)`
Find the domain of the following functions given by f(x) = `1/sqrt(x + |x|)`
If f(x) = `(x - 1)/(x + 1)`, then show that `f(1/x)` = – f(x)
