Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In Fig below, Find tan P and cot R. Is tan P = cot R?

उत्तर
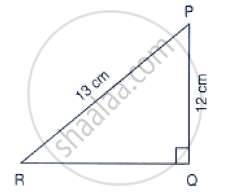
Let x be the adjacent side.
By Pythagoras theorem
𝑃𝑅2 = 𝑃𝑄2 + 𝑅𝑄2
169 = 𝑥2 + 144
𝑥2 = 25
𝑥 = 5
At LP, opposite side = 5
Adjacent side = 12
Hypotenuse = 13
`tan P = (1/12)/5 => 5/12`
At LR, opposite side = 12
Adjacent side = 5
Hypotenuse = 13
`cot R = 1/tan R = 1/(12/5) = 5/12`
`[∵ Tan R = "𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒"/"𝑎𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒"]`
∵ tan P = cot R
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If sin θ = cos (θ – 45°), where θ – 45° are acute angles, find the degree measure of θ
Evaluate:
`cot^2 30^0-2cos^2 30^0-3/4 sec^2 45^0 +1/4 cosec^2 30^0`
In the adjoining figure, ΔABC is right-angled at B and ∠A = 450. If AC = 3`sqrt(2)`cm, find (i) BC, (ii) AB.
If 3x = cosecθ = and `3/x= cottheta` find the value of 3`(x^2-1/x^2)`.
From the following figure, find the values of
(i) cos A
(ii) cosec A
(iii) tan2A - sec2A
(iv) sin C
(v) sec C
(vi) cot2 C - ` 1 / sin^2 "c"`
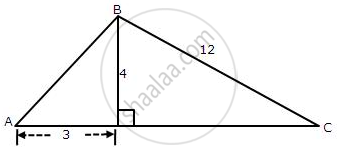
From the following figure, find the values of :
(i) sin A
(ii) sec A
(iii) cos2 A + sin2A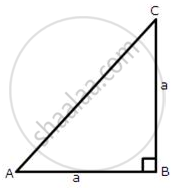
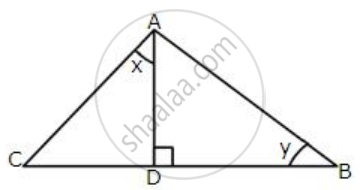
In the following figure:
AD ⊥ BC, AC = 26 CD = 10, BC = 42, ∠DAC = x and ∠B = y.
Find the value of :
(i) cot x
(ii) `1/sin^2 y – 1/tan^2 y`
(iii) `6/cos x – 5/cos y + 8 tan y`.
In rhombus ABCD, diagonals AC and BD intersect each other at point O.
If cosine of angle CAB is 0.6 and OB = 8 cm, find the lengths of the side and the diagonals of the rhombus.
If 5 cos θ = 3, evaluate : `(co secθ – cot θ)/(co secθ + cot θ)`
If cos θ : sin θ = 1 : 2, then find the value of `(8costheta - 2sintheta)/(4costheta + 2sintheta`
