Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the given figure, ▢ABCD is a parallelogram. It circumscribes the circle with centre T. Point E, F, G, H are touching points. If AE = 4.5, EB = 5.5, find AD.

उत्तर
ABCD is a parallelogram.
∴ AB = CD .....(1) (Opposite sides of parallelogram are equal)
AD = BC .....(2) (Opposite sides of parallelogram are equal)
Tangent segments drawn from an external point to a circle are congruent.
AE = AH .....(3)
DG = DH .....(4)
BE = BF .....(5)
CG = CF .....(6)
Adding (3), (4), (5) and (6), we get
AE + BE + CG + DG = AH + DH + BF + CF
⇒ AB + CD = AD + BC .....(7)
From (1), (2) and (7), we have
2AB = 2AD
⇒ AB = AD
∴ AD = AB = AE + EB = 4.5 + 5.5 = 10 units
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Prove that a parallelogram circumscribing a circle is a rhombus.
Prove that the tangents drawn at the ends of a diameter of a circle are parallel.
If tangents PA and PB from a point P to a circle with centre O are inclined to each other an angle of 80°, then ∠POA is equal to ______.
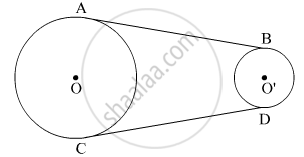
In the figure, AB and CD are common tangents to two circles of unequal radii. Prove that AB = CD.
In the following figure, PQ = QR, ∠RQP = 68°, PC and CQ are tangents to the circle with centre O.

Calculate the values of:
- ∠QOP
- ∠QCP
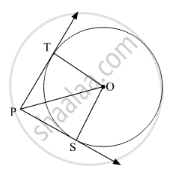
In Fig. 2, from a point P, two tangents PT and PS are drawn to a circle with centre O such that ∠SPT = 120°, Prove that OP = 2PS ?
In the given figure, AD is a diameter. O is the centre of the circle. AD is parallel to BC and ∠CBD = 32°.
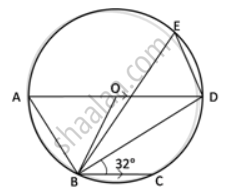
Find: ∠AOB
In the following figure, Q is the centre of a circle and PM, PN are tangent segments to the circle. If ∠MPN = 60°, find ∠MQN.
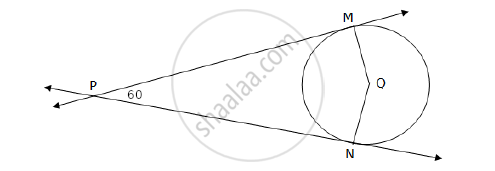
If two tangents inclined at an angle of 60° are drawn to a circle of radius 3 cm the length of each tangent is equal to ______
A tangent is drawn from a point at a distance of 17 cm of circle C(0, r) of radius 8 cm. The length of its tangent is ______
The length of a tangent drawn from a point at a distance of 10 cm of the circle is 8 cm. The radius of the circle is ______
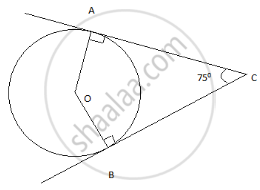
In fig, O is the centre of the circle, CA is tangent at A and CB is tangent at B drawn to the circle. If ∠ACB = 75°, then ∠AOB = ______
The angle between two tangents to a circle may be 0°.
The length of tangent from an external point P on a circle with centre O is always less than OP.
In the given figure, perimeter of ΔPQR is 20 cm. Find the length of tangent PA.

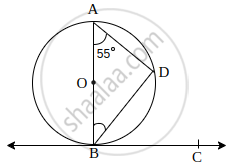
In the given figure, BC is tangent to the circle at point B of circle centred at O. BD is a chord of the circle so that ∠BAD = 55°. Find m∠DBC.
Two concentric circles with centre O are of radii 3 cm and 5 cm. Find the length of chord AB of the larger circle which touches the smaller circle at P.

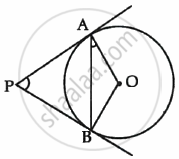
PA and PB are tangents drawn to the circle with centre O as shown in the figure. Prove that ∠APB = 2∠OAB.
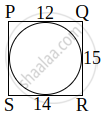
A quadrilateral PQRS is drawn to circumscribe a circle. If PQ = 12 cm, QR = 15 cm and RS = 14 cm, then find the length of SP is ______.