Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
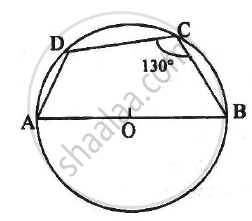
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral in a circle with centre O. If ∠ADC = 130°; find ∠BAC.

उत्तर

Here ∠ACB = 90°
(Angle in a semicircle is right angle)
Also, ∠ABC = 180° – ∠ADC = 180° – 130° = 50°
(Pair of opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary)
By angle sum property of right triangle ACB,
∠BAC = 90° – ∠ABC = 90° – 50° = 40°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the given figure, AB is the diameter of a circle with centre O. ∠BCD = 130o. Find:
1) ∠DAB
2) ∠DBA
In a cyclic quadrilateral ABCD, ∠A : ∠C = 3 : 1 and ∠B : ∠D = 1 : 5; find each angle of the quadrilateral.
In the following figure, ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral in which AD is parallel to BC.
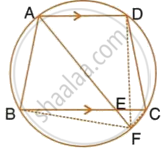
If the bisector of angle A meets BC at point E and the given circle at point F, prove that:
- EF = FC
- BF = DF
In a circle with centre O , chords AB and CD intersets inside the circle at E . Prove that ∠ AOC = ∠ BOD = 2 ∠ AEC.
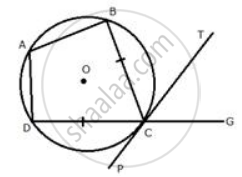
In the figure, ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral with BC = CD. TC is tangent to the circle at point C and DC is produced to point G. If angle BCG=108° and O is the centre of the circle, find: angle DOC
ABCD is a parallelogram. A circle through vertices A and B meets side BC at point P and side AD at point Q. Show that quadrilateral PCDQ is cyclic.
In the figure, ∠DBC = 58°. BD is a diameter of the circle. Calculate : ∠BEC
In the given below figure,
∠ BAD = 65°
∠ ABD = 70°
∠ BDC = 45°
Find: (i) ∠ BCD, (ii) ∠ ADB.
Hence show that AC is a diameter.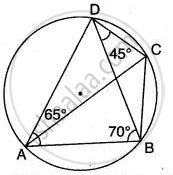
If O is the centre of the circle, find the value of x in each of the following figures
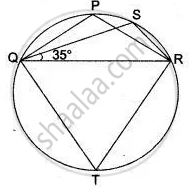
In the figure , Δ PQR is an isosceles triangle with PQ = PR, and m ∠ PQR = 35°. Find m ∠ QSR and ∠ QTR.