Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Circles with centres P and Q intersect at points A and B as shown in the figure. CBD is a line segment and EBM is tangent to the circle, with centre Q, at point B. If the circle are congruent; show that CE = BD.
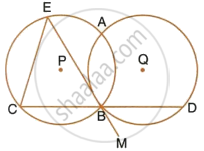
उत्तर
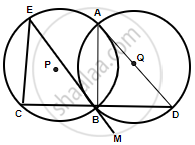
Join AB and AD
EBM is a tangent and BD is a chord.
∠DBM = ∠BAD ...(Angles in alternate segments)
But, ∠DBM = ∠CBE ...(Vertically opposite angles)
∴ ∠BAD = ∠CBE
Since in the same circle or congruent circles, if angles are equal, then chords opposite to them are also equal.
Therefore, CE = BD
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
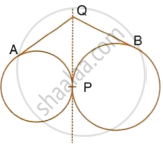
Two circle touch each other externally at point P. Q is a point on the common tangent through P. Prove that the tangents QA and QB are equal.
From the given figure, prove that : AP + BQ + CR = BP + CQ + AR.
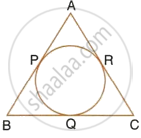
Also show that : AP + BQ + CR = `1/2` × Perimeter of ΔABC.
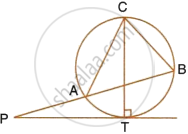
PT is a tangent to the circle at T. If ∠ABC = 70° and ∠ACB = 50°; calculate:
- ∠CBT
- ∠BAT
- ∠APT
If PQ is a tangent to the circle at R; calculate:
- ∠PRS,
- ∠ROT.
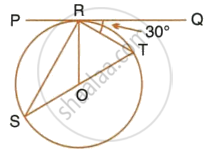
Given O is the centre of the circle and angle TRQ = 30°.
Tangent at P to the circumcircle of triangle PQR is drawn. If the tangent is parallel to side, QR show that ΔPQR is isosceles.
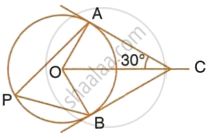
In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle. Tangents at A and B meet at C. If ∠ACO = 30°, find:
- ∠BCO
- ∠AOB
- ∠APB
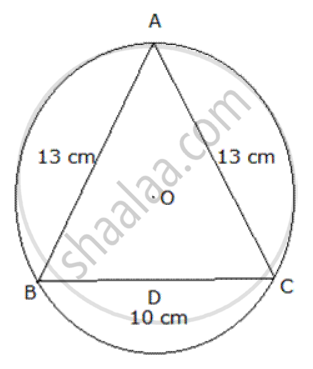
In figure , ABC is an isosceles triangle inscribed in a circle with centre O such that AB = AC = 13 cm and BC = 10 cm .Find the radius of the circle.
In the following figure, PQ and PR are tangents to the circle, with centre O. If ∠ QPR = 60° , calculate:
∠ OQR
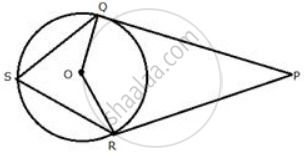
In the given figure, PT touches a circle with centre O at R. Diameter SQ when produced to meet the tangent PT at P. If ∠SPR = x° and ∠QRP = y°; Show that x° + 2y° = 90°
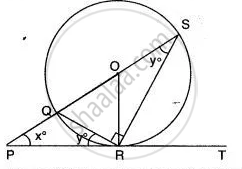
In the joining figure shown XAY is a tangent. If ∠ BDA = 44°, ∠ BXA = 36°.
Calculate: (i) ∠ BAX, (ii) ∠ DAY, (iii) ∠ DAB, (iv) ∠ BCD.

