Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Construct a ΔABC in which CA = 6 cm, AB = 5 cm and ∠BAC = 45°. Then construct a triangle whose sides are `3/5` of the corresponding sides of ΔABC.
उत्तर
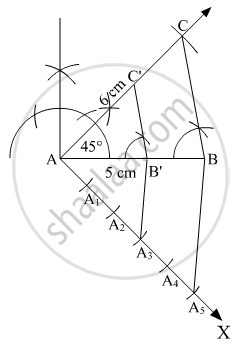
Steps of construction:
1. Draw AB = 5 cm. With A as the centre, draw ∠BAC= 45°. Join BC, ∠ABC is thus formed.
2. Draw AX such that ∠BAX is an acute angle.
3. Cut % equals arcs AA1, A1A2, A2A2, A2A4 and A4A3.
4. Join A3 to B and draw a line through A3 parallel to A3B which meets AB at B
Here, AB' = `3/5` AB
5. Now draw a line through B' parallel to BC which joins AC at C'
Here, BC' = 3/5 BC and AC = `3/5` AC
Thus, AB'C is the required triangle.
संबंधित प्रश्न
In figure, ∠A = ∠CED, prove that ∆CAB ~ ∆CED. Also, find the value of x.
Given `triangle ABC ~ triangle PQR`, if `(AB)/(PQ) = 1/3`, then find `(ar triangle ABC)/(ar triangle PQR)`
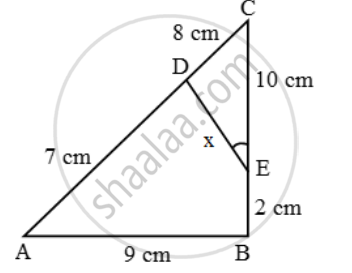
In the given figure, AB and DE are perpendicular to BC.
1) Prove that ΔABC ∼ ΔDEC
2) If AB = 6 cm; DE = 4 cm and AC = 15 cm. Calculate CD.
3) Find the ratio of area of ΔABC: area of ΔDEC
In the given figure ΔABC and ΔAMP are right angled at B and M respectively. Given AC = 10 cm, AP = 15 cm and PM = 12 cm.
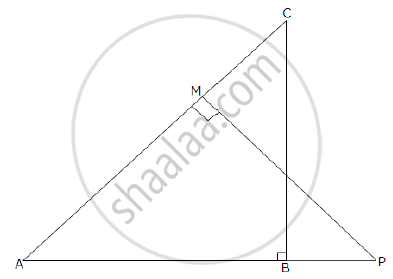
1) Prove ΔABC ~ ΔAMP
2) Find AB and BC.
State, true or false:
Two similar polygons are necessarily congruent.
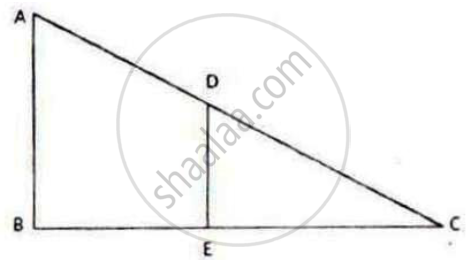
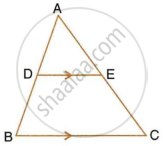
In triangle ABC, DE is parallel to BC; where D and E are the points on AB and AC respectively.
Prove: ∆ADE ~ ∆ABC.
Also, find the length of DE, if AD = 12 cm, BD = 24 cm BC = 8 cm.
The corresponding sides of two similar triangles ABC and DEF are BC = 9.1cm and EF = 6.5cm. If the perimeter of ΔDEF is 25cm, find the perimeter of ΔABC.
In the given figure, ABC is a triangle and PQ is a straight line meeting AB in P and AC in Q. If AP = 1cm, PB = 3cm, AQ = 1.5cm, QC = 4.5cm, prove that area of ΔAPQ is 116 of the area of ΔABC.
State the AA-similarity criterion
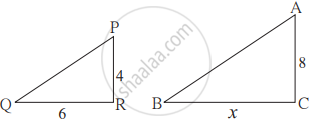
As shown in figure, two poles of height 8 m and 4 m are perpendicular to the ground. If the length of shadow of smaller pole due to sunlight is 6 m then how long will be the shadow of the bigger pole at the same time?

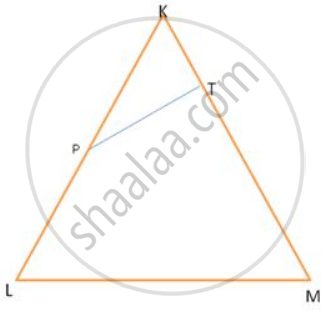
O is any point in the interior of ΔABC. Bisectors of ∠AOB, ∠BOC and ∠AOC intersect side AB, side BC, side AC in
F, D and E respectively.
Prove that
BF × AE × CD = AF × CE × BD
Prove that the area of Δ BCE described on one side BC of a square ABCD is one half the area of the similar Δ ACF described on the diagonal AC.
Figure shows Δ KLM , P an T on KL and KM respectively such that∠ KLM =∠ KTP.
If `"KL"/"KT" = 9/5` , find `("Ar" triangle "KLM")/("Ar" triangle "KTP")`.
A model of a ship is made with a scale factor of 1 : 500. Find
The deck area of the model, if the deck area of the ship is 1500000 m2
The scale of a map is 1 : 200000. A plot of land of area 20km2 is to be represented on the map. Find:
The area in km2 that can be represented by 1 cm2
The scale of a map is 1 : 200000. A plot of land of area 20km2 is to be represented on the map. Find
The area on the map that represents the plot of land.
In the following figure, point D divides AB in the ratio 3 : 5. Find :
- `(AE)/(EC)`
- `(AD)/(AB)`
- `(AE)/(AC)`
Also, if: - DE = 2.4 cm, find the length of BC.
- BC = 4.8 cm, find the length of DE.
If ΔABC ~ ΔDEF, then writes the corresponding congruent angles and also write the ratio of corresponding sides.
If ΔPQR, AB is drawn parallel to QR. If PQ = 9cm, PR = 6cm and PB = 4.cm, find the length of AP.
Find the scale factor in each of the following and state the type of size transformation:
Image length = 6cm, Actual length = 4cm.
Find the scale factor in each of the following and state the type of size transformation:
Model area = 75cm2, Actual area = 3cm2
A map is drawn to scale of 1:20000. Find: The area of the lake on the map which has an actual area of 12km2
In the adjacent figure, ∆ABC is right angled at C and DE ⊥ AB. Prove that ∆ABC ~ ∆ADE and hence find the lengths of AE and DE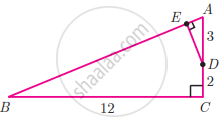
If ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF such that area of ∆ABC is 9 cm2 and the area of ∆DEF is 16 cm2 and BC = 2.1 cm. Find the length of EF.
D is the mid point of side BC and AE ⊥ BC. If BC = a, AC = b, AB = c, ED = x, AD = p and AE = h, prove that c2 = `"p"^2 - "a"x + "a"^2/4`
In the given figure, if ΔEAT ~ ΔBUN, find the measure of all angles.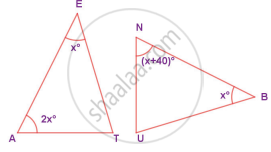
Observe the figure and complete the following activity
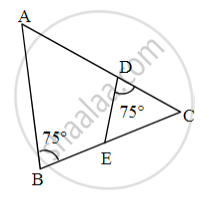
In fig, ∠B = 75°, ∠D = 75°
∠B ≅ [ ______ ] ...[each of 75°]
∠C ≅ ∠C ...[ ______ ]
ΔABC ~ Δ [ ______ ] ...[ ______ similarity test]
In triangle ABC point D is on side BC (B−D−C) such that ∠BAC = ∠ADC then prove that CA2 = CB × CD
If ΔABC ∼ ΔDEF and ∠A = 48°, then ∠D = ______.
