Advertisements
Advertisements
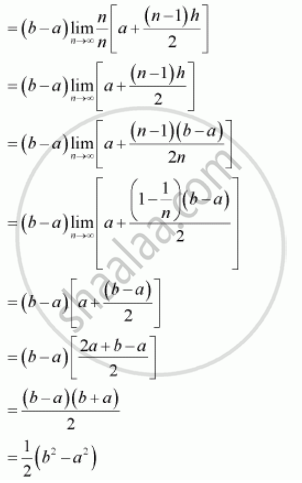
प्रश्न
Evaluate the following definite integrals as limit of sums.
`int_a^b x dx`
उत्तर

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Evaluate `int_1^3(e^(2-3x)+x^2+1)dx` as a limit of sum.
Evaluate the following definite integrals as limit of sums.
`int_2^3 x^2 dx`
Evaluate the following definite integrals as limit of sums `int_(-1)^1 e^x dx`
Evaluate the following definite integrals as limit of sums.
`int_0^4 (x + e^(2x)) dx`
Evaluate the definite integral:
`int_(pi/2)^pi e^x ((1-sinx)/(1-cos x)) dx`
Evaluate the definite integral:
`int_0^(pi/4) (sinx cos x)/(cos^4 x + sin^4 x)`dx
Evaluate the definite integral:
`int_(pi/6)^(pi/3) (sin x + cosx)/sqrt(sin 2x) dx`
Evaluate the definite integral:
`int_0^(pi/4) (sin x + cos x)/(9+16sin 2x) dx`
Evaluate the definite integral:
`int_1^4 [|x - 1|+ |x - 2| + |x -3|]dx`
Prove the following:
`int_0^(pi/2) sin^3 xdx = 2/3`
Prove the following:
`int_0^(pi/4) 2 tan^3 xdx = 1 - log 2`
Prove the following:
`int_0^1sin^(-1) xdx = pi/2 - 1`
\[\int\frac{1}{x} \left( \log x \right)^2 dx\]
\[\int\frac{\sqrt{\tan x}}{\sin x \cos x} dx\]
Using L’Hospital Rule, evaluate: `lim_(x->0) (8^x - 4^x)/(4x
)`
Solve: (x2 – yx2) dy + (y2 + xy2) dx = 0
If f and g are continuous functions in [0, 1] satisfying f(x) = f(a – x) and g(x) + g(a – x) = a, then `int_0^"a" "f"(x) * "g"(x)"d"x` is equal to ______.
Evaluate the following as limit of sum:
`int _0^2 (x^2 + 3) "d"x`
Evaluate the following as limit of sum:
`int_0^2 "e"^x "d"x`
Evaluate the following:
`int_0^2 ("d"x)/("e"^x + "e"^-x)`
Evaluate the following:
`int_0^1 (x"d"x)/sqrt(1 + x^2)`
Evaluate the following:
`int_(pi/3)^(pi/2) sqrt(1 + cosx)/(1 - cos x)^(5/2) "d"x`
The value of `lim_(x -> 0) [(d/(dx) int_0^(x^2) sec^2 xdx),(d/(dx) (x sin x))]` is equal to
If f" = C, C ≠ 0, where C is a constant, then the value of `lim_(x -> 0) (f(x) - 2f (2x) + 3f (3x))/x^2` is
`lim_(x -> 0) (xroot(3)(z^2 - (z - x)^2))/(root(3)(8xz - 4x^2) + root(3)(8xz))^4` is equal to
