Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Form the differential equation of all parabolas whose axis is the X-axis.
उत्तर
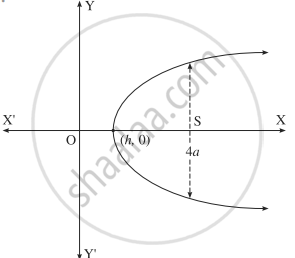
The equation of the parbola whose axis is the X-axis is y2 = 4a(x - h), ....(1)
where a and h are arbitrary constants.
Differentiating (1) w.r.t. x, we get
`"2y"("dy"/"dx") = 4"a"(1 - 0)`
∴ y`"dy"/"dx" = "2a"`
Differentiating again w.r.t. x, we get
`"y" * "d"/"dx"("dy"/"dx") + "dy"/"dx" * "dy"/"dx" = 0`
∴ `"y"("d"^2"y")/"dx"^2 + ("dy"/"dx")^2 = 0`
This is the required D.E.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Obtain the differential equation by eliminating the arbitrary constants from the following equation:
Ax2 + By2 = 1
Obtain the differential equation by eliminating the arbitrary constants from the following equation:
y2 = (x + c)3
Find the differential equation of all circles having radius 9 and centre at point (h, k).
In the following example verify that the given expression is a solution of the corresponding differential equation:
y = `"a" + "b"/"x"; "x" ("d"^2"y")/"dx"^2 + 2 "dy"/"dx" = 0`
Solve the following differential equation:
`"dy"/"dx" = (1 + "y")^2/(1 + "x")^2`
Solve the following differential equation:
`2"e"^("x + 2y") "dx" - 3"dy" = 0`
For the following differential equation find the particular solution satisfying the given condition:
`(e^y + 1) cos x + e^y sin x. dy/dx = 0, "when" x = pi/6,` y = 0
Reduce the following differential equation to the variable separable form and hence solve:
`cos^2 ("x - 2y") = 1 - 2 "dy"/"dx"`
Solve the following differential equation:
(x2 + y2)dx - 2xy dy = 0
Choose the correct option from the given alternatives:
The differential equation of y = `"c"^2 + "c"/"x"` is
The integrating factor of linear differential equation `x dy/dx + 2y = x^2 log x` is ______.
Choose the correct option from the given alternatives:
The solution of the differential equation `"dy"/"dx" = sec "x" - "y" tan "x"`
Choose the correct option from the given alternatives:
`"x"^2/"a"^2 - "y"^2/"b"^2 = 1` is a solution of
In the following example verify that the given function is a solution of the differential equation.
`"x"^2 + "y"^2 = "r"^2; "x" "dy"/"dx" + "r" sqrt(1 + ("dy"/"dx")^2) = "y"`
In the following example verify that the given function is a solution of the differential equation.
`"xy" = "ae"^"x" + "be"^-"x" + "x"^2; "x" ("d"^2"y")/"dx"^2 + 2 "dy"/"dx" + "x"^2 = "xy" + 2`
Obtain the differential equation by eliminating the arbitrary constants from the following equation:
(y - a)2 = b(x + 4)
Solve the following differential equation:
`"dy"/"dx" = "x"^2"y" + "y"`
Find the particular solution of the following differential equation:
(x + y)dy + (x - y)dx = 0; when x = 1 = y
Find the particular solution of the following differential equation:
y(1 + log x) = (log xx) `"dy"/"dx"`, when y(e) = e2
Select and write the correct alternative from the given option for the question
Solution of the equation `x ("d"y)/("d"x)` = y log y is
Select and write the correct alternative from the given option for the question
The solution of `("d"y)/("d"x)` = 1 is
Form the differential equation of family of standard circle
Find the differential equation from the relation x2 + 4y2 = 4b2
Find the differential equation of the family of all non-vertical lines in a plane
Find the differential equation of the family of all non-horizontal lines in a plane
Find the differential equation corresponding to the family of curves represented by the equation y = Ae8x + Be –8x, where A and B are arbitrary constants
Choose the correct alternative:
The slope at any point of a curve y = f(x) is given by `("d"y)/("d"x) - 3x^2` and it passes through (-1, 1). Then the equation of the curve is
The rate of disintegration of a radio active element at time t is proportional to its mass, at the time. Then the time during which the original mass of 1.5 gm. Will disintegrate into its mass of 0.5 gm. is proportional to ______.
Form the differential equation of all lines which makes intercept 3 on x-axis.
The differential equation whose solution is (x – h)2 + (y – k)2 = a2 is (where a is a constant) ______.
The differential equation representing the family of ellipse having foci either on the x-axis or on the y-axis centre at the origin and passing through the point (0, 3) is ______.
The differential equation of the family of circles touching Y-axis at the origin is ______.
The differential equation for a2y = log x + b, is ______.
Solve the differential equation
cos2(x – 2y) = `1 - 2dy/dx`
