Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In ΔABC right angled at B, AB = 24 cm, BC = 7 m. Determine:
sin A, cos A
उत्तर
ΔABC is right angled at B
AB = 24 cm, BC = 7 cm
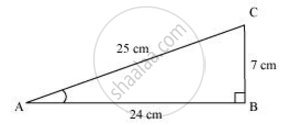
Let ‘x’ be the hypotenuse,
By applying Pythagoras
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
x2 = 242 + 72
x2 = 576 + 49
x2 = 625
x = 25
For Sin A, Cos A
At ∠A, opposite side = 7
adjacent side = 24
hypotenuse = 25
sin A = `"opposite side"/"hypotenuse" =("BC")/("AC") = 7/25`
cos A = `"adjacent side"/"hypotenuse" = ("AB")/("AC") = 24/25`
संबंधित प्रश्न
State whether the following are true or false. Justify your answer.
sec A = `12/5` for some value of angle A.
State whether the following are true or false. Justify your answer.
sin θ = `4/3`, for some angle θ.
In the following, trigonometric ratios are given. Find the values of the other trigonometric ratios.
`sin theta = sqrt3/2`
In the following, trigonometric ratios are given. Find the values of the other trigonometric ratios.
`sec theta = 13/5`
In the following, one of the six trigonometric ratios is given. Find the values of the other trigonometric ratios.
`cos theta = 12/2`
If 3 cot θ = 2, find the value of `(4sin theta - 3 cos theta)/(2 sin theta + 6cos theta)`.
If `cos theta = 12/13`, show that `sin theta (1 - tan theta) = 35/156`
If `tan theta = 1/sqrt7` `(cosec^2 theta - sec^2 theta)/(cosec^2 theta + sec^2 theta) = 3/4`
Evaluate the Following
(cos 0° + sin 45° + sin 30°)(sin 90° − cos 45° + cos 60°)
Evaluate the Following:
`tan 45^@/(cosec 30^@) + sec 60^@/cot 45^@ - (5 sin 90^@)/(2 cos 0^@)`
3 sin² 20° – 2 tan² 45° + 3 sin² 70° is equal to ______.
If sin 2A = `1/2` tan² 45° where A is an acute angle, then the value of A is ______.
If cos A = `4/5`, then the value of tan A is ______.
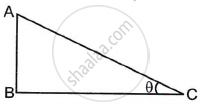
In ΔABC, ∠ABC = 90° and ∠ACB = θ. Then write the ratios of sin θ and tan θ from the figure.
Prove that sec θ + tan θ = `cos θ/(1 - sin θ)`.
Proof: L.H.S. = sec θ + tan θ
= `1/square + square/square`
= `square/square` ......`(∵ sec θ = 1/square, tan θ = square/square)`
= `((1 + sin θ) square)/(cos θ square)` ......[Multiplying `square` with the numerator and denominator]
= `(1^2 - square)/(cos θ square)`
= `square/(cos θ square)`
= `cos θ/(1 - sin θ)` = R.H.S.
∴ L.H.S. = R.H.S.
∴ sec θ + tan θ = `cos θ/(1 - sin θ)`
Prove that: cot θ + tan θ = cosec θ·sec θ
Proof: L.H.S. = cot θ + tan θ
= `square/square + square/square` ......`[∵ cot θ = square/square, tan θ = square/square]`
= `(square + square)/(square xx square)` .....`[∵ square + square = 1]`
= `1/(square xx square)`
= `1/square xx 1/square`
= cosec θ·sec θ ......`[∵ "cosec" θ = 1/square, sec θ = 1/square]`
= R.H.S.
∴ L.H.S. = R.H.S.
∴ cot θ + tan θ = cosec·sec θ
If cos(α + β) = `(3/5)`, sin(α – β) = `5/13` and 0 < α, β < `π/4`, then tan (2α) is equal to ______.
The maximum value of the expression 5cosα + 12sinα – 8 is equal to ______.
Evaluate 2 sec2 θ + 3 cosec2 θ – 2 sin θ cos θ if θ = 45°.
