Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Let f(x) = x, \[g\left( x \right) = \frac{1}{x}\] and h(x) = f(x) g(x). Then, h(x) = 1
पर्याय
(a) x ∈ R
(b) x ∈ Q
(c) x ∈ R − Q
(d) x ∈ R, x ≠ 0
उत्तर
(d) x ∈ R, x ≠ 0
f(x) = x, \[g\left( x \right) = \frac{1}{x}\] and h(x) = f(x) g(x) Now,
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Let A = {−2, −1, 0, 1, 2} and f : A → Z be a function defined by f(x) = x2 − 2x − 3. Find:
(a) range of f, i.e. f(A).
A function f : R → R is defined by f(x) = x2. Determine (a) range of f, (b) {x : f(x) = 4}, (c) [y: f(y) = −1].
If f : R → R be defined by f(x) = x2 + 1, then find f−1 [17] and f−1 [−3].
If f(x) = x2 − 3x + 4, then find the values of x satisfying the equation f(x) = f(2x + 1).
If f is a real function satisfying \[f\left( x + \frac{1}{x} \right) = x^2 + \frac{1}{x^2}\]
for all x ∈ R − {0}, then write the expression for f(x).
If\[f\left( x \right) = 1 - \frac{1}{x}\] , then write the value of \[f\left( f\left( \frac{1}{x} \right) \right)\]
Write the domain and range of function f(x) given by \[f\left( x \right) = \sqrt{\left[ x \right] - x}\] .
If f(x) = cos (log x), then value of \[f\left( x \right) f\left( 4 \right) - \frac{1}{2} \left\{ f\left( \frac{x}{4} \right) + f\left( 4x \right) \right\}\] is
Let f : R → R be defined by f(x) = 2x + |x|. Then f(2x) + f(−x) − f(x) =
If f : R → R and g : R → R are defined by f(x) = 2x + 3 and g(x) = x2 + 7, then the values of x such that g(f(x)) = 8 are
If f : R → R be given by for all \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{4^x}{4^x + 2}\] x ∈ R, then
The domain of definition of \[f\left( x \right) = \sqrt{x - 3 - 2\sqrt{x - 4}} - \sqrt{x - 3 + 2\sqrt{x - 4}}\] is
Check if the following relation is function:
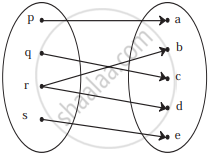
If f(m) = m2 − 3m + 1, find `f(1/2)`
Check if the following relation is a function.
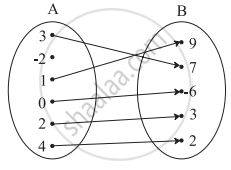
Which sets of ordered pairs represent functions from A = {1, 2, 3, 4} to B = {−1, 0, 1, 2, 3}? Justify.
{(1, 0), (3, 3), (2, −1), (4, 1), (2, 2)}
Check if the relation given by the equation represents y as function of x:
2y + 10 = 0
Find the domain and range of the following function.
f(x) = 7x2 + 4x − 1
Find the domain and range of the follwoing function.
h(x) = `sqrt(x + 5)/(5 + x)`
Check the injectivity and surjectivity of the following function.
f : N → N given by f(x) = x3
Express the following logarithmic equation in exponential form
log10 (0.001) = −3
Express the following logarithmic equation in exponential form
ln e = 1
Solve for x.
log2 + log(x + 3) – log(3x – 5) = log3
Select the correct answer from given alternatives.
If log (5x – 9) – log (x + 3) = log 2 then x = ...............
Answer the following:
Let f : R → R be given by f(x) = x3 + 1 for all x ∈ R. Draw its graph
Answer the following:
For any base show that log (1 + 2 + 3) = log 1 + log 2 + log 3
Answer the following:
Show that, `log ("a"^2/"bc") + log ("b"^2/"ca") + log ("c"^2/"ab")` = 0
Answer the following:
Find the domain of the following function.
f(x) = 5–xPx–1
Answer the following:
Find (f ° g) (x) and (g ° f) (x)
f(x) = `x/(x + 1)`, g(x) = `x/(1 - x)`
The domain of the function f(x) = log3+x (x2 - 1) is ______.
Let f : R → R be defined by
f(x) = `{(3x; x > 2),(2x^2; 1 ≤ x ≤ 2), (4x; x < 1):}`
Then f(-2) + f(1) + f(3) is ______
Find the domain for which the functions f(x) = 2x2 – 1 and g(x) = 1 – 3x are equal.
Find the range of the following functions given by f(x) = 1 + 3 cos2x
(Hint: –1 ≤ cos 2x ≤ 1 ⇒ –3 ≤ 3 cos 2x ≤ 3 ⇒ –2 ≤ 1 + 3cos 2x ≤ 4)
The value of the function f(x) = `(x^2 - 3x + 2)/(x^2 + x - 6)` lies in the interval
The period of the function
f(x) = `(sin 8x cos x - sin 6x cos 3x)/(cos 2x cos x - sin 3x sin 4x)` is ______.
Range of the function f(x) = `x/(1 + x^2)` is ______.
