Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
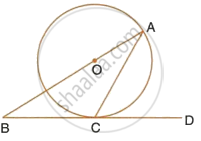
The given figure shows a circle with centre O and BCD is tangent to it at C. Show that : ∠ACD + ∠BAC = 90°.
उत्तर

Join OC.
BCD is the tangent and OC is the radius.
∴ OC ⊥ BD
`=>` ∠OCD = 90°
`=>` ∠OCA + ∠ACD = 90°
But in ΔOCA
OA = OC ...(Radii of same circle)
∴ ∠OCA + ∠OAC
Substituting (i)
∠OAC + ∠ACD = 90°
`=>` ∠BAC + ∠ACD = 90°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
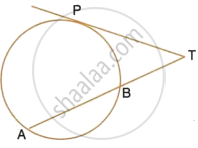
In the given figure, find TP if AT = 16 cm and AB = 12 cm.
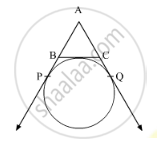
In Figure 1, AP, AQ and BC are tangents to the circle. If AB = 5 cm, AC = 6 cm and BC
= 4 cm, then the length of AP (in cm) is
In the adjoining figure the radius of a circle with centre C is 6 cm, line AB is a tangent at A. Answer the following questions.
(1) What is the measure of ∠CAB ? Why ?
(2) What is the distance of point C from line AB? Why ?
(3) d(A,B) = 6 cm, find d(B,C).
(4) What is the measure of ∠ABC ? Why ? 
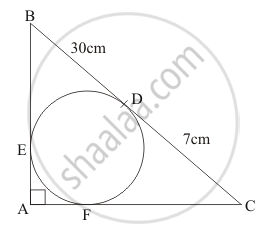
In the given figure, BDC is a tangent to the given circle at point D such that BD = 30 cm and CD = 7 cm. The other tangents BE and CF are drawn respectively from B and C to the circle and meet when produced at A making BAC a right angle triangle. Calculate (ii) radius of the circle.
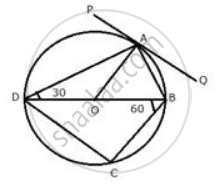
In the following figure, PQ is the tangent to the circle at A, DB is a diameter and O is the centre of the circle. If ∠ ADB = 30° and ∠ CBD = 60° ; calculate ∠ PAD.
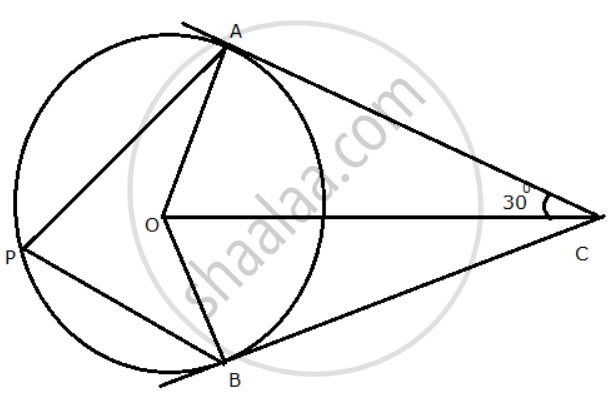
In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle. Tangents at A and B meet at C. If angle ACO = 30°, find: angle AOB
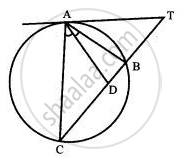
In Fig. TA is a tangent to a circle from the point T and TBC is a secant to the circle. If AD is the bisector of ∠BAC, prove that ΔADT is isosceles.
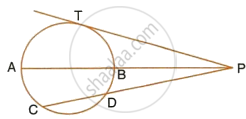
In the given figure, diameter AB and chord CD of a circle meet at P. PT is a tangent to the circle at T. CD = 7.8 cm, PD = 5 cm, PB = 4 cm. Find:
- AB.
- the length of tangent PT.
In figure, M is the centre of the circle and seg KL is a tangent segment. If MK = 12, KL = `6sqrt(3)`, then find
(i) Radius of the circle.
(ii) Measures of ∠K and ∠M.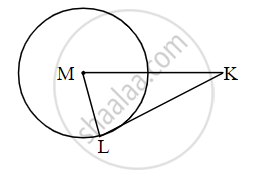
Prove that the tangents drawn at the ends of a chord of a circle make equal angles with the chord.
