Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A body of mass 1 kg is mafe to oscillate on a spring of force constant 16 N/m. Calculate (a) Angular frequency, (b) Frequency of vibrations.
Solution
Given:
m = 1kg
k= 16N lm
ω = ?
n = ?
Formula:
k=mω2
`therefore ω= sqrt k/m `
` ω = sqrt 16/1`
`therefore ω = 4 rad // s `
`therefore ω = 2 pi n `
`therefore n = ω/(2pi)= 4/ (2xx3.14)= 2/3.14= 0.636 Hz `
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A seconds pendulum is suspended in an elevator moving with constant speed in downward direction. The periodic time (T) of that pendulum is _______.
The periodic time of a linear harmonic oscillator is 2π second, with maximum displacement of 1 cm. If the particle starts from extreme position, find the displacement of the particle after π/3 seconds.
A copper metal cube has each side of length 1 m. The bottom edge of the cube is fixed and tangential force 4.2x108 N is applied to a top surface. Calculate the lateral displacement of the top surface if modulus of rigidity of copper is 14x1010 N/m2.
Which of the following example represent periodic motion?
An arrow released from a bow.
Which of the following example represent (nearly) simple harmonic motion and which represent periodic but not simple harmonic motion?
General vibrations of a polyatomic molecule about its equilibrium position.
Answer in brief:
Derive an expression for the period of motion of a simple pendulum. On which factors does it depend?
The length of the second’s pendulum in a clock is increased to 4 times its initial length. Calculate the number of oscillations completed by the new pendulum in one minute.
A particle executes simple harmonic motion with a frequency v. The frequency with which the kinetic energy oscillates is
A particle executes simple harmonic motion under the restoring force provided by a spring. The time period is T. If the spring is divided in two equal parts and one part is used to continue the simple harmonic motion, the time period will
A particle moves in a circular path with a uniform speed. Its motion is
A particle is fastened at the end of a string and is whirled in a vertical circle with the other end of the string being fixed. The motion of the particle is
A small block of mass m is kept on a bigger block of mass M which is attached to a vertical spring of spring constant k as shown in the figure. The system oscillates vertically. (a) Find the resultant force on the smaller block when it is displaced through a distance x above its equilibrium position. (b) Find the normal force on the smaller block at this position. When is this force smallest in magnitude? (c) What can be the maximum amplitude with which the two blocks may oscillate together?
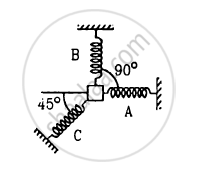
A particle of mass m is attatched to three springs A, B and C of equal force constants kas shown in figure . If the particle is pushed slightly against the spring C and released, find the time period of oscillation.
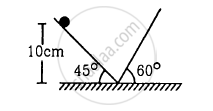
Find the time period of the motion of the particle shown in figure . Neglect the small effect of the bend near the bottom.
A uniform plate of mass M stays horizontally and symmetrically on two wheels rotating in opposite direction in Figure . The separation between the wheels is L. The friction coefficient between each wheel and the plate is μ. Find the time period of oscillation of the plate if it is slightly displaced along its length and released.

The ear-ring of a lady shown in figure has a 3 cm long light suspension wire. (a) Find the time period of small oscillations if the lady is standing on the ground. (b) The lady now sits in a merry-go-round moving at 4 m/s1 in a circle of radius 2 m. Find the time period of small oscillations of the ear-ring.

Find the time period of small oscillations of the following systems. (a) A metre stick suspended through the 20 cm mark. (b) A ring of mass m and radius r suspended through a point on its periphery. (c) A uniform square plate of edge a suspended through a corner. (d) A uniform disc of mass m and radius r suspended through a point r/2 away from the centre.
A uniform disc of radius r is to be suspended through a small hole made in the disc. Find the minimum possible time period of the disc for small oscillations. What should be the distance of the hole from the centre for it to have minimum time period?
The period of oscillation of a body of mass m1 suspended from a light spring is T. When a body of mass m2 is tied to the first body and the system is made to oscillate, the period is 2T. Compare the masses m1 and m2
A 20 cm wide thin circular disc of mass 200 g is suspended to rigid support from a thin metallic string. By holding the rim of the disc, the string is twisted through 60° and released. It now performs angular oscillations of period 1 second. Calculate the maximum restoring torque generated in the string under undamped conditions. (π3 ≈ 31)
The maximum speed of a particle executing S.H.M. is 10 m/s and maximum acceleration is 31.4 m/s2. Its periodic time is ______
A simple pendulum is inside a spacecraft. What will be its periodic time?
Which of the following example represent periodic motion?
A swimmer completing one (return) trip from one bank of a river to the other and back.
Which of the following example represent periodic motion?
A freely suspended bar magnet displaced from its N-S direction and released.
Which of the following example represent periodic motion?
A hydrogen molecule rotating about its center of mass.
Which of the following example represent (nearly) simple harmonic motion and which represent periodic but not simple harmonic motion?
A motion of an oscillating mercury column in a U-tube.
Which of the following example represent (nearly) simple harmonic motion and which represent periodic but not simple harmonic motion?
The motion of a ball bearing inside a smooth curved bowl, when released from a point slightly above the lowermost point.
When two displacements represented by y1 = a sin(ωt) and y2 = b cos(ωt) are superimposed the motion is ______.
A simple pendulum of frequency n falls freely under gravity from a certain height from the ground level. Its frequency of oscillation.
The equation of motion of a particle is x = a cos (αt)2. The motion is ______.
The displacement time graph of a particle executing S.H.M. is shown in figure. Which of the following statement is/are true?
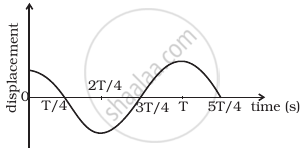
- The force is zero at `t = (T)/4`.
- The acceleration is maximum at `t = (4T)/4`.
- The velocity is maximum at `t = T/4`.
- The P.E. is equal to K.E. of oscillation at `t = T/2`.
What are the two basic characteristics of a simple harmonic motion?
Show that the motion of a particle represented by y = sin ωt – cos ωt is simple harmonic with a period of 2π/ω.
A person normally weighing 50 kg stands on a massless platform which oscillates up and down harmonically at a frequency of 2.0 s–1 and an amplitude 5.0 cm. A weighing machine on the platform gives the persons weight against time.
- Will there be any change in weight of the body, during the oscillation?
- If answer to part (a) is yes, what will be the maximum and minimum reading in the machine and at which position?
The time period of a simple pendulum is T inside a lift when the lift is stationary. If the lift moves upwards with an acceleration `g/2`, the time period of the pendulum will be ______.
When a particle executes Simple Harmonic Motion, the nature of the graph of velocity as a function of displacement will be ______.
A particle performs simple harmonic motion with a period of 2 seconds. The time taken by the particle to cover a displacement equal to half of its amplitude from the mean position is `1/a` s. The value of 'a' to the nearest integer is ______.
