Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A rod of length l slides between two perpendicular lines. Find the locus of the point on the rod which divides it in the ratio 1 : 2.
Solution
Let the two perpendicular lines be the coordinate axes. Let AB be a rod of length l and the coordinates of A and B be (a, 0) and (0, b) respectively.
As the rod AB slides, the values of a and b change. Let P(h, k) be a point on AB.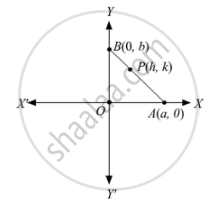
Here, BP:AP = 1:2 .
\[\therefore h = \frac{a + 0}{3}, k = \frac{0 + 2b}{3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = 3h, b = \frac{3k}{2}\] ... (1)
The length of the given rod is l.
\[\therefore AB = l\]
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} = l\]
\[ \Rightarrow a^2 + b^2 = l^2\]
Using equation (1), we get:
\[\Rightarrow 9 h^2 + \left( \frac{3k}{2} \right)^2 = l^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow h^2 + \frac{k^2}{4} = \frac{l^2}{9}\]
Hence, the locus of (h, k) is \[x^2 + \frac{y^2}{4} = \frac{l^2}{9}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The vertices of a triangle ABC are A (0, 0), B (2, −1) and C (9, 2). Find cos B.
The points A (2, 0), B (9, 1), C (11, 6) and D (4, 4) are the vertices of a quadrilateral ABCD. Determine whether ABCD is a rhombus or not.
Find the coordinates of the centre of the circle inscribed in a triangle whose vertices are (−36, 7), (20, 7) and (0, −8).
The base of an equilateral triangle with side 2a lies along the y-axis, such that the mid-point of the base is at the origin. Find the vertices of the triangle.
Find a point on the x-axis, which is equidistant from the points (7, 6) and (3, 4).
Find the locus of a point such that the sum of its distances from (0, 2) and (0, −2) is 6.
Find the locus of a point which is equidistant from (1, 3) and the x-axis.
Find the locus of a point which moves such that its distance from the origin is three times its distance from the x-axis.
A (5, 3), B (3, −2) are two fixed points; find the equation to the locus of a point P which moves so that the area of the triangle PAB is 9 units.
If A (−1, 1) and B (2, 3) are two fixed points, find the locus of a point P, so that the area of ∆PAB = 8 sq. units.
Find the locus of the mid-point of the portion of the line x cos α + y sin α = p which is intercepted between the axes.
What does the equation (a − b) (x2 + y2) −2abx = 0 become if the origin is shifted to the point \[\left( \frac{ab}{a - b}, 0 \right)\] without rotation?
Find what the following equation become when the origin is shifted to the point (1, 1).
x2 − y2 − 2x +2y = 0
Find what the following equation become when the origin is shifted to the point (1, 1).
xy − x − y + 1 = 0
Find what the following equation become when the origin is shifted to the point (1, 1).
xy − y2 − x + y = 0
To what point should the origin be shifted so that the equation x2 + xy − 3x − y + 2 = 0 does not contain any first degree term and constant term?
Verify that the area of the triangle with vertices (2, 3), (5, 7) and (− 3 − 1) remains invariant under the translation of axes when the origin is shifted to the point (−1, 3).
Find what the following equation become when the origin is shifted to the point (1, 1).
x2 + xy − 3y2 − y + 2 = 0
Find what the following equation become when the origin is shifted to the point (1, 1).
xy − y2 − x + y = 0
Find the point to which the origin should be shifted after a translation of axes so that the following equation will have no first degree terms: y2 + x2 − 4x − 8y + 3 = 0
Find the point to which the origin should be shifted after a translation of axes so that the following equation will have no first degree terms: x2 + y2 − 5x + 2y − 5 = 0
Find the point to which the origin should be shifted after a translation of axes so that the following equation will have no first degree terms: x2 − 12x + 4 = 0
Write the coordinates of the orthocentre of the triangle formed by points (8, 0), (4, 6) and (0, 0).
Three vertices of a parallelogram, taken in order, are (−1, −6), (2, −5) and (7, 2). Write the coordinates of its fourth vertex.
Write the coordinates of the circumcentre of a triangle whose centroid and orthocentre are at (3, 3) and (−3, 5), respectively.
Write the coordinates of the in-centre of the triangle with vertices at (0, 0), (5, 0) and (0, 12).
If the points (1, −1), (2, −1) and (4, −3) are the mid-points of the sides of a triangle, then write the coordinates of its centroid.
Write the area of the triangle with vertices at (a, b + c), (b, c + a) and (c, a + b).
