Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following:
If A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {4, 5, 6} check if the following are relations from A to B. Also write its domain and range
R2 = {(1, 5), (2, 4), (3, 6)}
Solution
A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {4, 5, 6}
∴ A × B = {(1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (3, 4), (3, 5), (3, 6)}
R2 = {(1, 5), (2, 4), (3, 6)}
Since R2 ⊆ A × B
∴ R2 is a relation from A to B.
Domain (R2) = Set of first components of R2
= {1, 2, 3}
Range (R2) = Set of second components of R2
= {4, 5, 6}
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
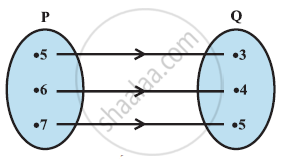
The given figure shows a relationship between the sets P and Q. Write this relation
- in set-builder form.
- in roster form.
What is its domain and range?
Determine the domain and range of the relation R defined by R = {(x, x + 5): x ∈ {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5}}.
Write the relation R = {(x, x3): x is a prime number less than 10} in roster form.
Find the inverse relation R−1 in each of the cases:
(i) R = {(1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 3), (3, 2), (5, 6)}
Let A = [1, 2] and B = [3, 4]. Find the total number of relation from A into B.
Determine the domain and range of the relations:
(ii) \[S = \left\{ \left( a, b \right) : b = \left| a - 1 \right|, a \in Z \text{ and} \left| a \right| \leq 3 \right\}\]
Let A = {a, b}. List all relations on A and find their number.
For the relation R1 defined on R by the rule (a, b) ∈ R1 ⇔ 1 + ab > 0. Prove that: (a, b) ∈ R1 and (b , c) ∈ R1 ⇒ (a, c) ∈ R1 is not true for all a, b, c ∈ R.
Let R be a relation on N × N defined by
(a, b) R (c, d) ⇔ a + d = b + c for all (a, b), (c, d) ∈ N × N
Show that:
(ii) (a, b) R (c, d) ⇒ (c, d) R (a, b) for all (a, b), (c, d) ∈ N × N
Let R be a relation on N × N defined by
(a, b) R (c, d) ⇔ a + d = b + c for all (a, b), (c, d) ∈ N × N
(iii) (a, b) R (c, d) and (c, d) R (e, f) ⇒ (a, b) R (e, f) for all (a, b), (c, d), (e, f) ∈ N × N
If R = {(x, y) : x, y ∈ Z, x2 + y2 ≤ 4} is a relation defined on the set Z of integers, then write domain of R.
If R = [(x, y) : x, y ∈ W, 2x + y = 8], then write the domain and range of R.
Let A = [1, 2, 3], B = [1, 3, 5]. If relation R from A to B is given by = {(1, 3), (2, 5), (3, 3)}, Then R−1 is
Express {(x, y) / x2 + y2 = 100, where x, y ∈ W} as a set of ordered pairs
Write the relation in the Roster Form. State its domain and range
R4 = {(x, y)/y > x + 1, x = 1, 2 and y = 2, 4, 6}
Write the relation in the Roster Form. State its domain and range
R5 = {(x, y)/x + y = 3, x, y∈ {0, 1, 2, 3}
Identify which of if the following relations are reflexive, symmetric, and transitive.
| Relation | Reflexive | Symmetric | Transitive |
| R = {(a, b) : a, b ∈ Z, a – b is an integer} | |||
| R = {(a, b) : a, b ∈ N, a + b is even} | √ | √ | x |
| R = {(a, b) : a, b ∈ N, a divides b} | |||
| R = {(a, b) : a, b ∈ N, a2 – 4ab + 3b2 = 0} | |||
| R = {(a, b) : a is sister of b and a, b ∈ G = Set of girls} | |||
| R = {(a, b) : Line a is perpendicular to line b in a plane} | |||
| R = {(a, b) : a, b ∈ R, a < b} | |||
| R = {(a, b) : a, b ∈ R, a ≤ b3} |
Answer the following:
R = {1, 2, 3} → {1, 2, 3} given by R = {(1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3), (1, 2), (2, 3)} Check if R is reflexive
Answer the following:
R = {1, 2, 3} → {1, 2, 3} given by R = {(1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3), (1, 2), (2, 3)} Check if R is symmentric
Let A = {1, 2, 3, 7} and B = {3, 0, –1, 7}, the following is relation from A to B?
R1 = {(2, 1), (7, 1)}
Let A = {1, 2, 3, 7} and B = {3, 0, –1, 7}, the following is relation from A to B?
R2 = {(–1, 1)}
Let A = {1, 2, 3, 4, …, 45} and R be the relation defined as “is square of ” on A. Write R as a subset of A × A. Also, find the domain and range of R
Multiple Choice Question :
If there are 1024 relation from a set A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} to a set B, then the number of elements in B is
Discuss the following relation for reflexivity, symmetricity and transitivity:
On the set of natural numbers the relation R defined by “xRy if x + 2y = 1”
Let X = {a, b, c, d} and R = {(a, a), (b, b), (a, c)}. Write down the minimum number of ordered pairs to be included to R to make it reflexive
Let X = {a, b, c, d} and R = {(a, a), (b, b), (a, c)}. Write down the minimum number of ordered pairs to be included to R to make it symmetric
Let X = {a, b, c, d} and R = {(a, a), (b, b), (a, c)}. Write down the minimum number of ordered pairs to be included to R to make it equivalence
Let A = {a, b, c} and R = {(a, a), (b, b), (a, c)}. Write down the minimum number of ordered pairs to be included to R to make it symmetric
Let A = {a, b, c} and R = {(a, a), (b, b), (a, c)}. Write down the minimum number of ordered pairs to be included to R to make it transitive
Let P be the set of all triangles in a plane and R be the relation defined on P as aRb if a is similar to b. Prove that R is an equivalence relation
On the set of natural numbers let R be the relation defined by aRb if 2a + 3b = 30. Write down the relation by listing all the pairs. Check whether it is reflexive
On the set of natural numbers let R be the relation defined by aRb if a + b ≤ 6. Write down the relation by listing all the pairs. Check whether it is symmetric
On the set of natural numbers let R be the relation defined by aRb if a + b ≤ 6. Write down the relation by listing all the pairs. Check whether it is transitive
On the set of natural numbers let R be the relation defined by aRb if a + b ≤ 6. Write down the relation by listing all the pairs. Check whether it is equivalence
Find the domain and range of the relation R given by R = {(x, y) : y = `x + 6/x`; where x, y ∈ N and x < 6}.
Is the given relation a function? Give reasons for your answer.
t = {(x, 3) | x is a real number
If R = {(x, y): x, y ∈ Z, x2 + 3y2 ≤ 8} is a relation on the set of integers Z, then the domain of R–1 is ______.
Let N denote the set of all natural numbers. Define two binary relations on N as R1 = {(x, y) ∈ N × N : 2x + y = 10} and R2 = {(x, y) ∈ N × N : x + 2y = 10}. Then ______.
