Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Identify the gas laws from the following diagram.
| Diagram | Gas laws |
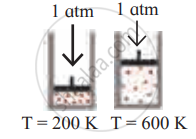 |
______________ |
Solution
| Diagram | Gas laws |
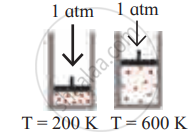 |
Charles’ law |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give reason for the following:
Gases have a lower density compared to solids or liquids.
Answer in one sentence.
A bubble of methane gas rises from the bottom of the North sea. What will happen to the size of the bubble as it rises to the surface?
Convert the following temperature from degree Celcius to kelvin.
−197° C
Convert the following pressure value into Pascals.
10 atmosphere
Convert the following pressure value into Pascals.
107000 Nm−2
Convert −100° C to kelvin
Hot air balloons float in the air because of the low density of the air inside the balloon. Explain this with the help of an appropriate gas law.

Identify the gas laws from the following diagram.
| Diagram | Gas laws |
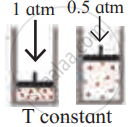 |
______________ |
Identify the gas laws from the following diagram.
| Diagram | Gas laws |
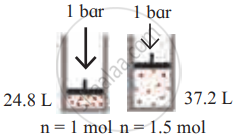 |
______________ |
Write the statement for Charles’ law
With the help of the graph answer the following -

At constant temperature, Identify the law.
Solve the following.
A balloon is inflated with helium gas at room temperature of 25°C and at 1 bar pressure when its initial volume is 2.27L and allowed to rise in the air. As it rises in the air external pressure decreases and the volume of the gas increases till finally, it bursts when external pressure is 0.3bar. What is the limit at which the volume of the balloon can stay inflated?
Solve the following.
A syringe has a volume of 10.0 cm3 at pressure 1 atm. If you plug the end so that no gas can escape and push the plunger down, what must be the final volume to change the pressure to 3.5 atm?

Solve the following.
The volume of a given mass of a gas at 0°C is 2 dm3. Calculate the new volume of the gas at constant pressure when the temperature is decreased by 10°C.
Solve the following.
A hot air balloon has a volume of 2800 m3 at 99°C. What is the volume if the air cools to 80°C?

The temperatures at which real gases obey the ideal gas laws over a wide range of pressure is called __________.
State Boyle's law.
Explain the following observation.
Aerated water bottles are kept under water during summer
Hydrochloric acid is treated with a metal to produce hydrogen gas. Suppose a student carries out this reaction and collects a volume of 154.4 × 10−3 dm3 of a gas at a pressure of 742 mm of Hg at a temperature of 298 K. What mass of hydrogen gas (in mg) did the student collect?
A certain sample of gas has a volume of 0.2 L at one atmosphere pressure and 273.15 K. What is the volume of gas at 273.15°C at same pressure?
Volume of a balloon at 25°C and 1 bar pressure is 2.27 L. If the pressure of the gas in balloon is reduced to 0.227 bar, what is the rise in volume of a gas?
A certain mass of a gas occupies a volume of 2 dm3 at STP. At what temperature the volume of gas becomes double, keeping the pressure constant?
If 2 moles of an ideal gas at 546 K has volume of 44.8 L, then what will be it's pressure? (R = 0.082)
If 300 mL of a gas at 26.85°C is cooled to 6.85°C at constant pressure. What will be the final volume of gas?
