Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
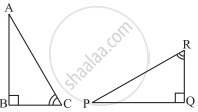
If ΔABC and ΔPQR are to be congruent, name one additional pair of corresponding parts. What criterion did you use?
Solution
BC = QR
ΔABC ≅ ΔPQR (ASA criterion)
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
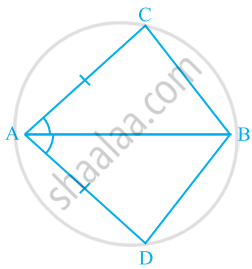
In quadrilateral ACBD, AC = AD and AB bisects ∠A (See the given figure). Show that ΔABC ≅ ΔABD. What can you say about BC and BD?
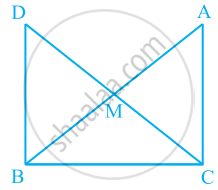
In right triangle ABC, right angled at C, M is the mid-point of hypotenuse AB. C is joined to M and produced to a point D such that DM = CM. Point D is joined to point B (see the given figure). Show that:
- ΔAMC ≅ ΔBMD
- ∠DBC is a right angle.
- ΔDBC ≅ ΔACB
- CM = `1/2` AB
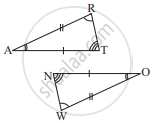
In the figure, the two triangles are congruent.
The corresponding parts are marked. We can write ΔRAT ≅ ?
In two triangles ABC and DEF, it is given that ∠A = ∠D, ∠B = ∠E and ∠C =∠F. Are the two triangles necessarily congruent?
ABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC. BE and CF are its two medians. Show that BE = CF.
If the following pair of the triangle is congruent? state the condition of congruency:
In ΔABC and ΔQRP, AB = QR, ∠B = ∠R and ∠C = P.
The given figure shows a circle with center O. P is mid-point of chord AB.
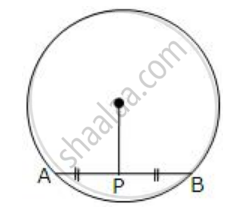
Show that OP is perpendicular to AB.
In a triangle ABC, D is mid-point of BC; AD is produced up to E so that DE = AD.
Prove that :
(i) ΔABD and ΔECD are congruent.
(ii) AB = CE.
(iii) AB is parallel to EC
From the given diagram, in which ABCD is a parallelogram, ABL is a line segment and E is mid-point of BC.
Prove that:
(i) ΔDCE ≅ ΔLBE
(ii) AB = BL.
(iii) AL = 2DC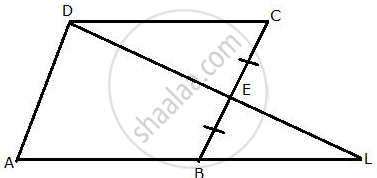
In the figure, given below, triangle ABC is right-angled at B. ABPQ and ACRS are squares. 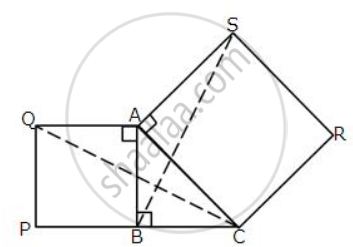
Prove that:
(i) ΔACQ and ΔASB are congruent.
(ii) CQ = BS.
