Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In a ∆ABC, ∠A = 90°, AB = 5 cm and AC = 12 cm. If AD ⊥ BC, then AD =
Options
- \[\frac{13}{2}cm\]
- \[\frac{60}{13}cm\]
- \[\frac{13}{60}cm\]
- \[\frac{2\sqrt{15}}{13}cm\]
Solution
Given: In ΔABC, `∠ A = 90^o` AD ⊥ BC, AC = 12cm, and AB = 5cm.
To find: AD
We know that the ratio of areas of two similar triangles is equal to the ratio of squares of their corresponding sides.
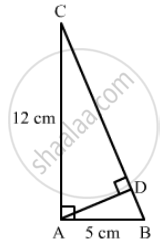
In ∆ACB and ∆ADC,
We got the result as `b`.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In the below figure, If AB || CD, find the value of x.
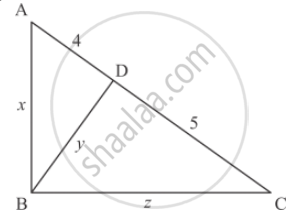
In below Figure, ΔABC is right angled at C and DE ⊥ AB. Prove that ΔABC ~ ΔADE and Hence find the lengths of AE and DE.

In ∆ABC, D and E are points on sides AB and AC respectively such that AD ✕ EC = AE ✕ DB. Prove that DE || BC.
In each of the figures given below, an altitude is drawn to the hypotenuse by a right-angled triangle. The length of different line-segment are marked in each figure. Determine x, y, z in each case.
If the areas of two similar triangles ABC and PQR are in the ratio 9 : 16 and BC = 4.5 cm, what is the length of QR?
If the altitude of two similar triangles are in the ratio 2 : 3, what is the ratio of their areas?
If ∆ABC and ∆DEF are two triangles such tha\[\frac{AB}{DE} = \frac{BC}{EF} = \frac{CA}{FD} = \frac{2}{5}\] , then Area (∆ABC) : Area (∆DEF) =
If ∆ABC is an equilateral triangle such that AD ⊥ BC, then AD2 =
∆ABC ∼ ∆PQR such that ar(∆ABC) = 4 ar(∆PQR). If BC = 12 cm, then QR =
If ABC is an isosceles triangle and D is a point of BC such that AD ⊥ BC, then
