Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State Kohlrausch Law
Solution 1
Kohlrausch Law:
The equivalent conductivity of an electrolyte at infinite dilution is the sum of two values on depending upon the cation and the other upon the anion.
Solution 2
Kohlrausch's law states that at infinite dilution of the solution, each ion of electrolyte migrates independently of its co-ions and contribute independently to the total molar conductivity irrespective of the nature of other ion.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The molar conductivity of cation and anion of salt BA are 180 and 220 mhos respectively. The molar conductivity of salt BA at infinite dilution is_____________ .
(a) 90 mhos.cm2
(b) 110 mhos.cm2.mol-1
(c) 200 mhos.cm2.mol-1
(d) 400 mhos.cm2.mol-1
The conductivity of 0.20 M solution of KCl at 298 K is 0.025 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity.
Conductivity of 0.00241 M acetic acid is 7.896 × 10−5 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity and if `∧_"m"^0` for acetic acid is 390.5 S cm2 mol−1, what is its dissociation constant?
10.0 grams of caustic soda when dissolved in 250 cm3 of water, the resultant gram molarity of solution is _______.
(A) 0.25 M
(B) 0.5 M
(C) 1.0 M
(D) 0.1 M
Write mathematical expression of molar conductivity of the given solution at infinite dilution.
The S.I. unit of cell constant for conductivity cell is __________.
A steady current of 2 amperes was passed through two electrolytic cells X and Y connected in series containing electrolytes FeSO4and ZnSO4 until 2.8g of Fe deposited at the cathode of cell X. How long did the current flow? Calculate the mass of Zn deposited at the cathode of cell Y.
(Molar mass: Fe=56g mol-1,Zn=65.3g mol-1,1F=96500C mol-1)
In the plot of molar conductivity (∧m) vs square root of concentration (c1/2) following curves are obtained for two electrolytes A and B : 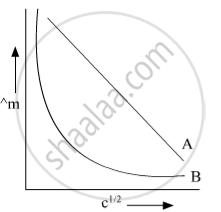
Answer the following:
(i) predict the nature of electrolytes A and B.
(ii) What happens on the extrapolation of ∧m to concentration approaching for electrolytes A and B?
Conductivity always decreases with decrease in concentration both, for weak and strong electrolytes because of the fact that ____________.
Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions states ____________.
Molar conductivity of ionic solution depends on:
(i) temperature.
(ii) distance between electrodes.
(iii) concentration of electrolytes in solution.
(iv) surface area of electrodes.
Solutions of two electrolytes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are diluted. The Λm of ‘B’ increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Justify your answer.
When acidulated water (dil.H2SO4 solution) is electrolysed, will the pH of the solution be affected? Justify your answer.
Why on dilution the m Λm of \[\ce{CH3COOH}\] increases very fast, while that of \[\ce{CH3COONa}\] increases gradually?
Match the items of Column I and Column II on the basis of data given below:
`E_("F"_2//"F"^-)^Θ` = 2.87 V, `"E"_(("Li"^(+))//("Li"^-))^Θ` = − 3.5V, `"E"_(("Au"^(3+))//("Au"))^Θ` = 1.4 V, `"E"_(("Br"_(2))//("Br"^-))^Θ` = 1.09 V
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) F2 | (a) metal is the strongest reducing agent |
| (ii) Li | (b) metal ion which is the weakest oxidising agent |
| (iii) Au3+ | (c) non metal which is the best oxidising agent |
| (iv) Br– | (d) unreactive metal |
| (v) Au | (e) anion that can be oxidised by Au3+ |
| (vi) Li+ | (f) anion which is the weakest reducing agent |
| (vii) F– | (g) metal ion which is an oxidising agent |
Assertion: Λm for weak electrolytes shows a sharp increase when the electrolytic solution is diluted.
Reason: For weak electrolytes degree of dissociation increases with dilution of solution.
Consider figure and answer the question to given below.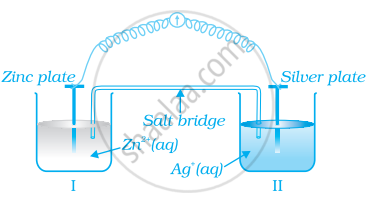
How will the concentration of Zn2+ ions and Ag+ ions be affected after the cell becomes ‘dead’?
An increase in equivalent conductance of a strong electrolyte with dilution is mainly due to :-
The molar conductance of \[\ce{NaCl, HCl}\] and \[\ce{CH3COONa}\] at infinite dilution are 126.45, 426.16 and 91.0 S cm2 mol−1 respectively. The molar conductance of \[\ce{CH3COOH}\] at infinite dilution is. Choose the right option for your answer.
The molar conductance of NaCl, HCl, and CH3COONa at infinite dilution are 126.45, 426.16, and 91.0 S cm2 mol−1 respectively. The molar conductance of CH3COOH at infinite dilution is. Choose the right option for your answer.
Molar conductivity of substance “A” is 5.9 × 103 S/m and “B” is 1 × 10–16 S/m. Which of the two is most likely to be copper metal and why?
Which of the following solutions of KCl will have the highest value of molar conductivity?
Assertion (A): Molar conductivity decreases with increase in concentration.
Reason (R): When concentration approaches zero, the molar conductivity is known as limiting molar conductivity.
The following questions are case-based questions. Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
| Rahul set up an experiment to find the resistance of aqueous KCl solution for different concentrations at 298 K using a conductivity cell connected to a Wheatstone bridge. He fed the Wheatstone bridge with a.c. power in the audio frequency range 550 to 5000 cycles per second. Once the resistance was calculated from the null point, he also calculated the conductivity K and molar conductivity ∧m and recorded his readings in tabular form. |
| S. No. | Conc. (M) |
k S cm−1 | ∧m S cm2 mol−1 |
| 1. | 1.00 | 111.3 × 10−3 | 111.3 |
| 2. | 0.10 | 12.9 × 10−3 | 129.0 |
| 3. | 0.01 | 1.41 × 10−3 | 141.0 |
Answer the following questions:
(a) Why does conductivity decrease with dilution? (1)
(b) If `∧_"m"^0` of KCl is 150.0 S cm2 mol−1, calculate the degree of dissociation of 0.01 M KCI. (1)
(c) If Rahul had used HCl instead of KCl then would you expect the ∧m values to be more or less than those per KCl for a given concentration? Justify. (2)
OR
(c) Amit a classmate of Rahul repeated the same experiment with CH3COOH solution instead of KCl solution. Give one point that would be similar and one that would be different in his observations as compared to Rahul. (2)
The unit of molar conductivity is ______.
The specific conductance of 2.5 × 10-4 M formic acid is 5.25 × 10-5 ohm-1 cm-1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation.
Given `λ°_("H"^+)` = 349.5 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1 and
`λ°_("HCOO"^-) = 50.5 " ohm"^-1 "cm"^2 "mol"^-1`
The resistance of a conductivity cell with a 0.1 M KCl solution is 200 ohm. When the same cell is filled with a 0.02 M NaCl solution, the resistance is 1100 ohm. If the conductivity of 0.1 M KCl solution is 0.0129 ohm-1 cm-1, calculate the cell constant and molar conductivity of 0.02 M NaCl solution.
The solution of two electrolytes A and B are diluted. ^m of B increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Give a reason.
