Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Which of the following functions form Z to itself are bijections?
Options
\[f\left( x \right) = x^3\]
\[f\left( x \right) = x + 2\]
\[f\left( x \right) = 2x + 1\]
\[f\left( x \right) = x^2 + x\]
Solution
f is not onto because for y = 3∈Co-domain(Z), there is no value of x∈Domain(Z)
\[ x^3 = 3\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \sqrt[3]{3} \not\in Z\]
⇒ f is not onto
So, f is not a bijection
(b) Injectivity:
Let x and y be two elements of the domain (Z), such that
\[x + 2 = y + 2\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = y\]
Surjectivity:
Let y be an element in the co-domain (Z), such that
\[ \Rightarrow y = x + 2\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = y - 2 \in Z \left( Domain \right)\]
So, f is a bijection.
\[ \Rightarrow 4 = 2x + 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2x = 3\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \frac{3}{2} \not\in Z\]
So,f is not a bijection.
\[\]
\[\left( d \right) f\left( 0 \right) = 0^2 + 0 = 0\]
\[and f\left( - 1 \right) = \left( - 1 \right)^2 + \left( - 1 \right) = 1 - 1 = 0\]
⇒ 0 and -1 have the same image.
⇒ f is not one-one.
So,fis not a bijection.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Let f: R → R be the Signum Function defined as
f(x) = `{(1,x>0), (0, x =0),(-1, x< 0):}`
and g: R → R be the Greatest Integer Function given by g(x) = [x], where [x] is greatest integer less than or equal to x. Then does fog and gof coincide in (0, 1]?
Give an example of a function which is not one-one but onto ?
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = 3 − 4x
Let A = [-1, 1]. Then, discuss whether the following functions from A to itself is one-one, onto or bijective : h(x) = x2
Show that if f1 and f2 are one-one maps from R to R, then the product f1 × f2 : R → R defined by (f1 × f2) (x) = f1 (x) f2 (x) need not be one - one.
Let f = {(3, 1), (9, 3), (12, 4)} and g = {(1, 3), (3, 3) (4, 9) (5, 9)}. Show that gof and fog are both defined. Also, find fog and gof.
Let f = {(1, −1), (4, −2), (9, −3), (16, 4)} and g = {(−1, −2), (−2, −4), (−3, −6), (4, 8)}. Show that gof is defined while fog is not defined. Also, find gof.
Verify associativity for the following three mappings : f : N → Z0 (the set of non-zero integers), g : Z0 → Q and h : Q → R given by f(x) = 2x, g(x) = 1/x and h(x) = ex.
Let
f (x) =`{ (1 + x, 0≤ x ≤ 2) , (3 -x , 2 < x ≤ 3):}`
Find fof.
Find f −1 if it exists : f : A → B, where A = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}; B = {0, 1, 9, 25, 49, 81} and f(x) = x2
Let A = R - {3} and B = R - {1}. Consider the function f : A → B defined by f(x) = `(x-2)/(x-3).`Show that f is one-one and onto and hence find f-1.
[CBSE 2012, 2014]
Let f : [−1, ∞) → [−1, ∞) be given by f(x) = (x + 1)2 − 1, x ≥ −1. Show that f is invertible. Also, find the set S = {x : f(x) = f−1 (x)}.
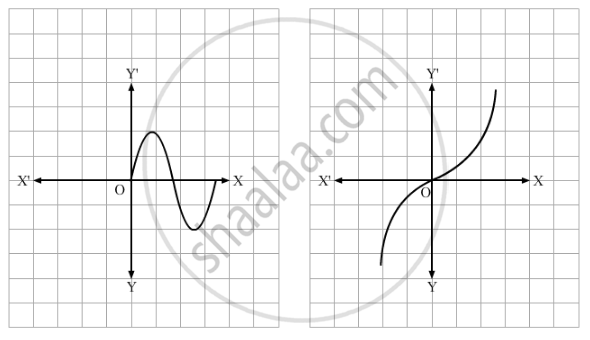
Which of the following graphs represents a one-one function?
If f : C → C is defined by f(x) = x4, write f−1 (1).
If f : R → R is defined by f(x) = x2, find f−1 (−25).
The function \[f : [0, \infty ) \to \text {R given by } f\left( x \right) = \frac{x}{x + 1} is\]
A function f from the set of natural numbers to integers defined by
`{([n-1]/2," when n is odd" is ),(-n/2,when n is even ) :}`
Which of the following functions from
to itself are bijections?
Let
\[f : R - \left\{ n \right\} \to R\]
Let \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{1}{1 - x} . \text{Then}, \left\{ f o \left( fof \right) \right\} \left( x \right)\]
Let \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{\alpha x}{x + 1}, x \neq - 1\] Then, for what value of α is \[f \left( f\left( x \right) \right) = x?\]
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
Let f : R→ R be defined as, f(x) = \[\begin{cases}2x, if x > 3 \\ x^2 , if 1 < x \leq 3 \\ 3x, if x \leq 1\end{cases}\]
Then, find f( \[-\]1) + f(2) + f(4)
Let A = ℝ − {3}, B = ℝ − {1}. Let f : A → B be defined by \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{x - 2}{x - 3}, \forall x \in A\] Show that f is bijective. Also, find
(i) x, if f−1(x) = 4
(ii) f−1(7)
If f(x) = `(x+3)/(4x−5) , "g"(x) = (3+5x)/(4x−1)` then verify that `("fog") (x)` = x.
Let A be a finite set. Then, each injective function from A into itself is not surjective.
Let D be the domain of the real valued function f defined by f(x) = `sqrt(25 - x^2)`. Then, write D
Are the following set of ordered pairs functions? If so, examine whether the mapping is injective or surjective.
{(x, y): x is a person, y is the mother of x}
Let the function f: R → R be defined by f(x) = cosx, ∀ x ∈ R. Show that f is neither one-one nor onto
Let f: R – `{3/5}` → R be defined by f(x) = `(3x + 2)/(5x - 3)`. Then ______.
Let A = R – {3}, B = R – {1}. Let f : A → B be defined by `"f"("x") = ("x" - 2)/("x" - 3)` Then, ____________.
Let f : R → R, g : R → R be two functions such that f(x) = 2x – 3, g(x) = x3 + 5. The function (fog)-1 (x) is equal to ____________.
Let R be a relation on the set L of lines defined by l1 R l2 if l1 is perpendicular to l2, then relation R is ____________.
Raji visited the Exhibition along with her family. The Exhibition had a huge swing, which attracted many children. Raji found that the swing traced the path of a Parabola as given by y = x2.
Answer the following questions using the above information.
- Let f: R → R be defined by f(x) = x2 is:
Prove that the function f is surjective, where f: N → N such that `f(n) = {{:((n + 1)/2",", if "n is odd"),(n/2",", if "n is even"):}` Is the function injective? Justify your answer.
The domain of the function `cos^-1((2sin^-1(1/(4x^2-1)))/π)` is ______.
Let [x] denote the greatest integer ≤ x, where x ∈ R. If the domain of the real valued function f(x) = `sqrt((|[x]| - 2)/(|[x]| - 3)` is (–∞, a) ∪ [b, c) ∪ [4, ∞), a < b < c, then the value of a + b + c is ______.
Let f(1, 3) `rightarrow` R be a function defined by f(x) = `(x[x])/(1 + x^2)`, where [x] denotes the greatest integer ≤ x, Then the range of f is ______.
Let A = {1, 2, 3, ..., 10} and f : A `rightarrow` A be defined as
f(k) = `{{:(k + 1, if k "is odd"),( k, if k "is even"):}`.
Then the number of possible functions g : A `rightarrow` A such that gof = f is ______.
