Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Which of the following rule is not sufficient to verify the congruency of two triangles
Options
SSS rule
SAS rule
SSA rule
ASA rule
Solution
SSA rule
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
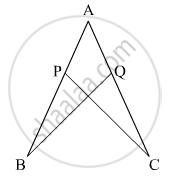
In the given figure, if AB = AC and ∠B = ∠C. Prove that BQ = CP.
ΔPQR and ΔABC is not congruent to ΔRPQ, then which of the following is not true:
In triangles ABC and PQR, if ∠A = ∠R, ∠B = ∠P and AB = RP, then which one of the following congruence conditions applies:
If ΔPQR≅ ΔEFD, then ∠E =
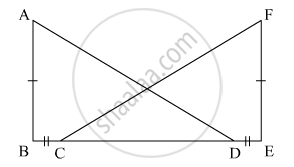
In the given figure, AB ⊥ BE and FE ⊥ BE. If BC = DE and AB = EF, then ΔABD is congruent to
In the following example, a pair of triangles is shown. Equal parts of triangles in each pair are marked with the same sign. Observe the figure and state the test by which the triangle in each pair are congruent.
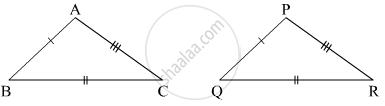
By ______ test
Δ ABC ≅ ΔPQR
In the pair of triangles in the following figure, parts bearing identical marks are congruent. State the test and the correspondence of vertices by the triangle in pairs is congruent.

In the pair of triangles in the following figure, parts bearing identical marks are congruent. State the test and the correspondence of vertices by the triangle in pairs is congruent.

In the following figure, OA = OC and AB = BC.

Prove that: AD = CD
Which of the following pairs of triangles are congruent? Give reasons
ΔABC;(AB = 8cm,BC = 6cm,∠B = 100°);
ΔPQR;(PQ = 8cm,RP = 5cm,∠Q = 100°).
Which of the following pairs of triangles are congruent? Give reasons
ΔABC;(AB = 5cm,BC = 7cm,CA = 9cm);
ΔKLM;(KL = 7cm,LM = 5cm,KM = 9cm).
In a circle with center O. If OM is perpendicular to PQ, prove that PM = QM.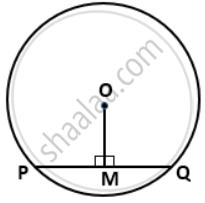
In the figure, ∠CPD = ∠BPD and AD is the bisector of ∠BAC. Prove that ΔCAP ≅ ΔBAP and CP = BP.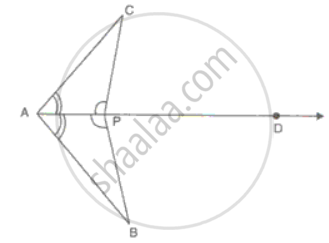
In the figure, RT = TS, ∠1 = 2∠2 and ∠4 = 2∠3. Prove that ΔRBT ≅ ΔSAT.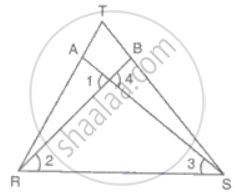
In the figure, AC = AE, AB = AD and ∠BAD = ∠EAC. Prove that BC = DE.
In ΔABC, AB = AC, BM and Cn are perpendiculars on AC and AB respectively. Prove that BM = CN.
If AB = QR, BC = PR and CA = PQ, then ______.
“If two sides and an angle of one triangle are equal to two sides and an angle of another triangle, then the two triangles must be congruent.” Is the statement true? Why?
Without drawing the triangles write all six pairs of equal measures in the following pairs of congruent triangles.
∆ABC ≅ ∆LMN
Without drawing the triangles write all six pairs of equal measures in the following pairs of congruent triangles.
∆YZX ≅ ∆PQR
