Commerce (English Medium)
Science (English Medium)
Arts (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2016-2017
Date & Time: 24th March 2017, 12:30 pm
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
Out of  which is an example of a benzylic halide?
which is an example of a benzylic halide?
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
What is the effect of adding a catalyst on Activation energy (Ea)
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
What is the effect of catalyst on: Gibbs energy (∆G)
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Write the formula of the compound of iodine which is obtained when conc. HNO3 oxidises I2
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
What type of colloid is formed when a gas is dispersed in a liquid? Give an example
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound:
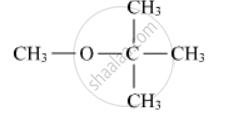
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Draw the structures of the following molecules: XeF4
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Draw the structures of the following: BrF5
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Write the name of the cell which is generally used in transistors. Write the reactions taking place at the anode and the cathode of this cell.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their acid strength:
p-cresol, p-nitrophenol, phenol
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Write the mechanism (using curved arrow notation) of the following reaction:

Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Write the structures of the products when Butan-2-ol reacts with CrO3
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Write the structures of the products when Butan-2-ol reacts with SOCl2
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Using IUPAC norms write the formulae for Potassium trioxalatoaluminate(III)
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Using IUPAC norms write the formulae for Dichloridobis(ethane-1,2-diamine)cobalt(III)
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Calculate the number of unit cells in 8.1 g of aluminium if it crystallizes in a f.c.c. structure. (Atomic mass of Al = 27 g mol–1)
Chapter: [0.01] Solid State
Advertisements
What type of isomerism is shown by the complex [Co(NH3)5(SCN)]2+?
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Why is [NiCl4]2− paramagnetic while [Ni(CN)4]2− is diamagnetic? (Atomic number of Ni = 28)
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Why are low spin tetrahedral complexes rarely observed?
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Write one difference in Multimolecular colloid and Associated colloid
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
Write one difference in Coagulation and Peptization
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Write one difference in Homogeneous catalysis and Heterogeneous catalysis
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
What are the dispersed phase and dispersion medium in milk?
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
Write one similarity between Physisorption and Chemisorption
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
Write the chemical method by which Fe(OH)3 sol is prepared from FeCl3.
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
The cell in which the following reaction occurs:
`2Fe^(3+) (aq) + 2I^(-) (aq) ---> 2Fe^(2+) (aq) + I_2 (s)` has `E_"cell"^@` = 0.236 V at 298 K. Calculate the standard Gibbs energy of the cell reaction. (Given : 1 F = 96,500 C mol−1)
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
How many electrons flow through a metllic wire if a current of 0·5 A is passed for 2 hours? (Given : 1 F = 96,500 C mol−1)
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Based on the nature of intermolecular forces, classify the following solids:
Sodium sulphate, Hydrogen
Chapter: [0.01] Solid State
What happens when CdCl2 is doped with AgCl?
Chapter: [0.01] Solid State
Give reasons:Ferrimagnetic substances show better magnetism than antiferromagnetic substances.
Chapter: [0.01] Solid State
Explain the principle of the method of electrolytic refining of metals. Give one example.
Chapter: [0.06] General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Why does copper obtained in the extraction from copper pyrites have a blistered appearance?
Chapter: [0.06] General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
What is the role of depressants in the froth floatation process?
Chapter: [0.06] General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Write the structures of compounds A, B and C in the following reactions:
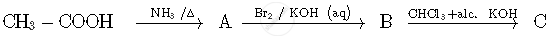
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Write the structures of compounds A, B and C in the following reactions
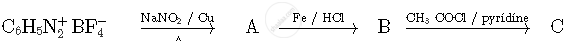
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Give reasons Acetylation of aniline reduces its activation effect.
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Give reasons for the following:
CH3NH2 is more basis than C6H5NH2.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Give reasons Although –NH2 is o/p directing group, yet aniline on nitration gives a significant amount of m-nitroaniline
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Give reasons for the following:
Red phosphorus is less reactive than white phosphorus.
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Give reasons for the following:
Electron gain enthalpies of halogens are largely negative.
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Give reasons for the following: N2O5 is more acidic than N2O3
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Explain the following term with a suitable example:
Cationic detergents
Chapter: [0.16] Chemistry in Everyday Life
What is meant by the term ‘broad spectrum antibiotics’? Explain.
Chapter: [0.16] Chemistry in Everyday Life
Explain Tranquilizers
Chapter: [0.16] Chemistry in Everyday Life
Write the names of monomers used for getting the following polymers:
Teflon
Chapter: [0.15] Polymers
Write the structures of the monomers used for getting the following polymers
Melamine – formaldehyde polymer
Chapter: [0.15] Polymers
Write the name of monomers used for getting the following polymers : Neoprene
Chapter: [0.15] Polymers
Advertisements
Following compounds are given to you :
2-Bromopentane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane
1) Write the compound which is most reactive towards SN2 reaction.
2) Write the compound which is optically active.
3) Write the compound which is most reactive towards β-elimination reaction.
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
A first order reaction takes 20 minutes for 25% decomposition. Calculate the time when 75% of the reaction will be completed.
(Given : log = 2 = 0·3010, log 3 = 0·4771, log 4 = 0·6021)
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
After watching a programme on TV about the presence of carcinogens (cancer causing agents) Potassium bromate and Potassium iodate in bread and other bakery products, Ritu a class XII student decided to aware others about the adverse effects of these carcinogens in foods. She consultanted the school principal and requested him to instruct canteen contractor to stop selling sandwiches, pizza, burgers and other bakery products to the students. Principal took an immediate action and instructed the canteen contractor to replace the bakery products with some proteins and vitamins rich food like fruits, salads, sprouts etc. The decision was welcomed by the parents and students.
After reading the above passage, answer the following questions:
1) What are the values (at least two) displayed by Ritu?
2) Which polysaccharide component of carbohydrates is commonly present in bread?
3) Write the two types of secondary structure of proteins.
4) Give two examples of water soluble vitamins.
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Write the product(s) in the following reactions:

Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Write the product(s) in the following reaction:

Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Write the product(s) in the following reactions:
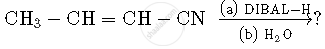
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
Butanal and Butan-2-one
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds: Benzoic acid and Phenol
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Write the equations involved in the following reactions:
Etard reaction
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Write the reaction involved in the Stephen reduction
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
How will you convert the following in not more than two steps:
Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
How will you convert the following in not more than two steps:
Acetophenone to Benzoic acid
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
How will you convert the following in not more than two steps:
Ethanoic acid to 2-Hydroxyethanoic acid
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Give reasons: Transition metals show variable oxidation states.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Account for the following:
Zn, Cd and Hg are soft metals.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Account for the following:
E° value for the Mn3+/Mn2+ couple is highly positive (+1.57 V) as compare to Cr3+/Cr2+.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Write one similarity and one difference between the chemistry of lanthanoid and actinoid elements.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Following are the transition metal ions of 3d series:
Ti4+, V2+, Mn3+, Cr3+
(Atomic numbers: Ti = 22, V = 23, Mn = 25, Cr = 24)
Answer the following:
1) Which ion is most stable in an aqueous solution and why?
2) Which ion is a strong oxidising agent and why?
3) Which ion is colourless and why?
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Complete the following equations:
`2MnO_4^(-)+16H^++5S^(2-)rarr`
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Complete the following equations:
KMnO4 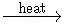
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
A 10% solution (by mass) of sucrose in water has freezing point of 269.15 K. Calculate the freezing point of 10% glucose in water, if freezing point of pure water is 273.15 K
Given : (Molar mass of sucrose = 342 g mol−1)
(Molar mass of glucose = 180 g mol−1)
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Define the term Abnormal molar mass
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
30 g of urea (M = 60 g mol−1) is dissolved in 846 g of water. Calculate the vapour pressure of water for this solution if vapour pressure of pure water at 298 K is 23·8 mm Hg.
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Write two differences between an ideal solution and a non-ideal solution.
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Chemistry with solutions 2016 - 2017
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 -2017 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Chemistry, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Chemistry will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
