Advertisements
Chapters
2: Quadratic Equations
3: Arithmetic Progression
4: Financial Planning
5: Probability
6: Statistics
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 1: Linear Equations in Two Variables
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 1 of Maharashtra State Board Balbharati for Algebra (Mathematics 1) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board.
Balbharati solutions for Algebra (Mathematics 1) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board 1 Linear Equations in Two Variables Practice Set 1.1 [Pages 4 - 5]
Complete the following activity to solve the simultaneous equations.
5x + 3y = 9 -----(I)
2x − 3y = 12 ----- (II)
Solve the following simultaneous equation.
3a + 5b = 26; a + 5b = 22
Solve the following simultaneous equation.
x + 7y = 10; 3x – 2y = 7
Solve the following simultaneous equation.
2x – 3y = 9; 2x + y = 13
Solve the following simultaneous equation.
5m – 3n = 19; m – 6n = –7
Solve the following simultaneous equation.
5x + 2y = –3; x + 5y = 4
Solve the following simultaneous equation.
`1/3x + y = 10/3` ; `2x + 1/4y = 11/4`
Solve the following simultaneous equation.
99x + 101y = 499; 101x + 99y = 501
Solve the following simultaneous equation.
49x – 57y = 172; 57x – 49y = 252
Balbharati solutions for Algebra (Mathematics 1) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board 1 Linear Equations in Two Variables Practice Set 1.2 [Page 8]
Complete the following table to draw graph of the equation -
(I) x + y = 3 (II) x – y = 4
x + y = 3
| x | 3 | ||
| y | 5 | 3 | |
| (x, y) | (3, 0) | (0, 3) |
x – y = 4
| x | -1 | 0 | |
| y | 0 | -4 | |
| (x, y) | (0, -4) |
Solve the following simultaneous equations graphically.
x + y = 6 ; x – y = 4
Solve the following simultaneous equations graphically.
x + y = 5; x – y = 3
Solve the following simultaneous equations graphically.
x + y = 0 ; 2x – y = 9
Solve the following simultaneous equation graphically.
3x – y = 2 ; 2x – y = 3
Solve the Following Simultaneous Equation Graphically.
3x – 4y = –7; 5x – 2y = 0
Solve the following simultaneous equations graphically.
2x – 3y = 4 ; 3y – x = 4
Balbharati solutions for Algebra (Mathematics 1) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board 1 Linear Equations in Two Variables Practice Set 1.3 [Page 16]
Fill in the blanks with correct number:
`|(3,2),(4,5)| = 3 xx square - square xx 4 = square - 8 = square`
Find the value of following determinant.
`|(-1,7),(2,4)|`
Find the value of following determinant.
`|(5,3), (-7,0)|`
Find the values of following determinant.
`|(7/3,5/3), (3/2, 1/2)|`
Solve the following simultaneous equations using Cramer’s rule.
3x – 4y = 10 ; 4x + 3y = 5
Solve the following simultaneous equations using Cramer’s rule.
4x + 3y – 4 = 0 ; 6x = 8 – 5y
Solve the following simultaneous equations using Cramer’s rule.
x + 2y = –1 ; 2x – 3y = 12
Solve the following simultaneous equations using Cramer’s rule.
6x – 4y = –12; 8x – 3y = –2
Solve the following simultaneous equations using Cramer’s rule.
4m + 6n = 54; 3m + 2n = 28
Solve the following simultaneous equations using Cramer’s rule.
2x + 3y = 2; x - `y/2 = 1/2`.
Balbharati solutions for Algebra (Mathematics 1) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board 1 Linear Equations in Two Variables Practice Set 1.4 [Page 19]
Solve the following simultaneous equation.
\[ \frac{2}{x} - \frac{3}{y} = 15; \frac{8}{x} + \frac{5}{y} = 77\]
Solve the following simultaneous equations.
`10/("x" + "y") + 2/("x" - "y") = 4; 15/("x" + "y") - 5/("x" - "y") = -2`
Solve the following simultaneous equations.
`27/(x -2) + 31/(y + 3) = 85, 31/(x -2) + 27/(y + 3) = 89`
Solve the following simultaneous equation.
`1/(3x + y) + 1/(3x - y) = 3/4; 1/(2(3x + y)) - 1/(2(3x - y)) = -1/8`
Balbharati solutions for Algebra (Mathematics 1) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board 1 Linear Equations in Two Variables Practice Set 1.5 [Page 26]
Two numbers differ by 3. The sum of twice the smaller number and thrice the greater number is 19. Find the numbers.
Complete the following.

The sum of father’s age and twice the age of his son is 70. If we double the age of the father and add it to the age of his son the sum is 95. Find their present ages.
The denominator of a fraction is 4 more than twice its numerator. Denominator becomes 12 times the numerator, if both the numerator and the denominator are reduced by 6. Find the fraction.
Two types of boxes A, B are to be placed in a truck having a capacity of 10 tons. When 150 boxes of type A and 100 boxes of type B are loaded in the truck, it weighes 10 tons. But when 260 boxes of type A are loaded in the truck, it can still accommodate 40 boxes of type B, so that it is fully loaded. Find the weight of each type of box.
Out of 1900 km, Vishal travelled some distance by bus and some by aeroplane. The bus travels with an average speed of 60 km/hr and the average speed of the aeroplane is 700 km/hr. It takes 5 hours to complete the journey. Find the distance, Vishal travelled by bus.
Balbharati solutions for Algebra (Mathematics 1) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board 1 Linear Equations in Two Variables Problem Set 1 [Pages 27 - 29]
Choose correct alternative for the following question.
To draw graph of 4x + 5y = 19, Find y when x = 1.
4
3
2
-3
Choose correct alternative for the following question.
For simultaneous equations in variables x and y, Dx = 49, Dy = –63, D = 7 then what is x?
7
– 7
`1/7`
`(-1)/7`
Find the value of `|(5,3),(-7,-4)|`.
–1
–41
41
1
Choose correct alternative for the following question.
To solve x + y = 3; 3x – 2y – 4 = 0 by determinant method find D.
5
1
−5
−1
Choose correct alternative for the following question.
ax + by = c and mx + ny = d and an ≠ bm then these simultaneous equations have -
Only one common solution.
No solution.
Infinite number of solutions.
Only two solution.
Complete the following table to draw the graph of 2x – 6y = 3.
| x | -5 | x |
| y | x | 0 |
| (x, y) | (-5, x) | (x, 0) |
Solve the following simultaneous equation graphically.
2x + 3y = 12 ; x – y = 1
Solve the following simultaneous equation graphically.
x – 3y = 1 ; 3x – 2y + 4 = 0
Solve the following simultaneous equation graphically.
5x – 6y + 30 = 0 ; 5x + 4y – 20 = 0
Solve the following simultaneous equation graphically.
3x – y – 2 = 0 ; 2x + y = 8
Solve the following simultaneous equation graphically.
3x + y = 10 ; x – y = 2
Find the value of the following determinant.
Find the value of the following determinant.
`|(5, -2), (-3, 1)|`
Find the value of the following determinant.
Solve the following equations by Cramer’s method.
6x – 3y = –10 ; 3x + 5y – 8 = 0
Solve the following equation by Cramer’s method.
4m – 2n = –4 ; 4m + 3n = 16
Solve the following equations by Cramer’s method.
`3x – 2y = 5/2; 1/3x + 3y = -4/3`
Solve the following equations by Cramer’s method.
7x + 3y = 15; 12y – 5x = 39
Solve the following equation by Cramer’s method.
`("x" + "y" - 8)/2 = ("x" + 2y - 14)/3 = (3"x" - "y")/4`
Solve the following simultaneous equation.
\[\frac{2}{x} + \frac{2}{3y} = \frac{1}{6} ; \frac{3}{x} + \frac{2}{y} = 0\]
Solve the following simultaneous equations.
\[\frac{7}{2x + 1} + \frac{13}{y + 2} = 27 ; \frac{13}{2x + 1} + \frac{7}{y + 2} = 33\]
Solve the following simultaneous equation.
Solve the following simultaneous equations.
Solve the following simultaneous equations.
`1/(2(3x + 4y)) + 1/(5(2x - 3y)) = 1/4; 5/(3x + 4y) - 2/(2x - 3y) = (-3)/2`.
Solve the following word problem.
A two-digit number and the number with digits interchanged add up to 143. In the given number the digit in unit’s place is 3 more than the digit in the ten’s place. Find the original number.
Let the digit in unit’s place is x
and that in the ten’s place is y
∴ the number = `square` y + x
The number obtained by interchanging the digits is `square` x + y
According to the first condition two digit number + the number obtained by interchanging the digits = 143
∴ 10y + x + `square` = 143
∴ `square` x + `square` y = 143
x + y = `square` ........(I)
From the second condition,
digit in unit’s place = digit in the ten’s place + 3
∴ x = `square` + 3
∴ x − y = 3 ........(II)
Adding equations (I) and (II)
2x = `square`
x = 8
Putting this value of x in equation (I)
x + y = 13
8 + `square` = 13
∴ y = `square`
The original number is 10 y + x
= `square` + 8
= 58
Kantabai bought \[1\frac{1}{2}\] kg tea and 5 kg sugar from a shop. She paid ₹ 50 as return fare for rickshaw. Total expense was ₹ 700. Then she realised that by ordering online the goods can be bought with free home delivery at the same price. So next month she placed the order online for 2 kg tea and 7 kg sugar. She paid ₹ 880 for that. Find the rate of sugar and tea per kg.
Solve the following word problem.
To find number of notes that Anushka had, complete the following activity.
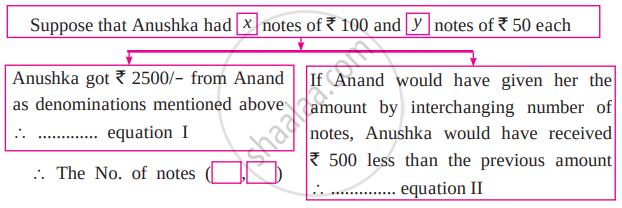
Solve the Following Word Problem.
Sum of the present ages of Manish and Savita is 31. Manish’s age 3 years ago was 4 times the age of Savita. Find their present ages.
Solve the Following Word Problem.
In a factory the ratio of salary of skilled and unskilled workers is 5 : 3. Total salary of one day of both of them is Rs 720. Find daily wages of skilled and unskilled workers.
Solve the Following Word Problem.
Places A and B are 30 km apart and they are on a st raight road. Hamid travels from A to B on bike. At the same time Joseph starts from B on bike, travels towards A. They meet each other after 20 minutes. If Joseph would have started from B at the same time but in the opposite direction (instead of towards A) Hamid would have caught him after 3 hours. Find the speed of Hamid and Joseph.
Solutions for 1: Linear Equations in Two Variables
Balbharati solutions for Algebra (Mathematics 1) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 1 - Linear Equations in Two Variables
Shaalaa.com has the Maharashtra State Board Mathematics Algebra (Mathematics 1) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board Maharashtra State Board solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Balbharati solutions for Mathematics Algebra (Mathematics 1) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board Maharashtra State Board 1 (Linear Equations in Two Variables) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Balbharati textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Algebra (Mathematics 1) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 1 Linear Equations in Two Variables are Substitution Method, Cross - Multiplication Method, Equations Reducible to a Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables, Simple Situational Problems, Determinant of Order Two, Graphical Method, Introduction to linear equations in two variables, Simultaneous method, Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables, Methods of solving linear equations in two variables, Determinant method, Simultaneous method, Application of simultaneous equations, Simultaneous method.
Using Balbharati Algebra (Mathematics 1) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board solutions Linear Equations in Two Variables exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Balbharati Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Maharashtra State Board Algebra (Mathematics 1) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board students prefer Balbharati Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 1, Linear Equations in Two Variables Algebra (Mathematics 1) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board additional questions for Mathematics Algebra (Mathematics 1) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board Maharashtra State Board, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
![Balbharati solutions for Algebra (Mathematics 1) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 1 - Linear Equations in Two Variables Balbharati solutions for Algebra (Mathematics 1) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 1 - Linear Equations in Two Variables - Shaalaa.com](/images/algebra-mathematics-1-english-10-standard-ssc-maharashtra-state-board_6:3c1a2739ef74455990da08f3e1b1d605.png)
