Advertisements
Chapters
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 7 chapter 7 - Comparing Quantities NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 7 chapter 7 - Comparing Quantities - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-7_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 7: Comparing Quantities
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 7 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Mathematics [English] Class 7.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 7 7 Comparing Quantities Exercise [Pages 196 - 219]
There are four options, out of which one is correct. write the correct one.
20% of 700 m is ______.
560 m
70 m
210 m
140 m
Gayatri’s income is ₹ 1,60,000 per year. She pays 15% of this as house rent and 10% of the remainder on her child’s education. The money left with her is ______.
₹ 136000
₹ 120000
₹ 122400
₹ 14000
The ratio of Fatima’s income to her savings is 4 : 1. The percentage of money saved by her is ______.
20%
25%
40%
80%
0.07 is equal to ______.
70%
7%
0.7%
0.07%
In a scout camp, 40% of the scouts were from Gujarat State and 20% of these were from Ahmedabad. The percentage of scouts in the camp from Ahmedabad is ______.
25
32.5
8
50
What percent of ₹ 4500 is ₹ 9000?
200
`1/2`
8
50
5.2 is equal to ______.
52%
5.2%
520%
0.52%
The ratio 3:8 is equal to ______.
3.75%
37.5%
0.375%
267%
225% is equal to ______.
9:4
4:9
3:2
2:3
A bicycle is purchased for ₹ 1800 and is sold at a profit of 12%. Its selling price is ______.
₹ 1584
₹ 2016
₹ 1788
₹ 1812
A cricket bat was purchased for ₹ 800 and was sold for ₹ 1600. Then profit earned is ______.
100%
64%
50%
60%
A farmer bought a buffalo for ₹ 44000 and a cow for ₹ 18000. He sold the buffalo at a loss of 5% but made a profit of 10% on the cow. The net result of the transaction is ______.
loss of ₹ 200
profit of ₹ 400
loss of ₹ 400
profit of ₹ 200
If Mohan’s income is 25% more than Raman’s income, then Raman’s income is less than Mohan’s income by ______.
25%
80%
20%
75%
The interest on ₹ 30000 for 3 years at the rate of 15% per annum is ______.
₹ 4500
₹ 9000
₹ 18000
₹ 13500
Amount received on ₹ 3000 for 2 years at the rate of 11% per annum is ______.
₹ 2340
₹ 3660
₹ 4320
₹ 3330
Interest on ₹ 12000 for 1 month at the rate of 10 % per annum is ______.
₹ 1200
₹ 600
₹ 100
₹ 12100
Rajni and Mohini deposited ₹ 3000 and ₹ 4000 in a company at the rate of 10% per annum for 3 years and `2 1/2` years respectively. The difference of the amounts received by them will be ______.
₹ 100
₹ 1000
₹ 900
₹ 1100
If 90% of x is 315 km, then the value of x is ______.
325 km
350 km
405 km
340 km
On selling an article for ₹ 329, a dealer lost 6%. The cost price of the article is ______.
₹ 310.37
₹ 348.74
₹ 335
₹ 350
`(25% "of" 50% "of" 100%)/(25 xx 50)` is equal to ______.
1.1%
0.1%
0.01%
1%
The sum which will earn a simple interest of ₹ 126 in 2 years at 14% per annum is ______.
₹ 394
₹ 395
₹ 450
₹ 540
The per cent that represents the unshaded region in the figure is ______.

75%
50%
40%
60%
The per cent that represents the shaded region in the figure is ______.

36%
64%
27%
48%
Fill in the blanks to make the statements true.
2:3 = ______ %
`18 3/4%` = ______ : ______.
30% of ₹ 360 = ______.
120% of 50 km = ______.
2.5 = ______ %.
`8/5` = ______ %.
A ______ with its denominator 100 is called a percent.
15 kg is ______ % of 50 kg.
Weight of Nikhil increased from 60 kg to 66 kg. Then, the increase in weight is ______ %.
In a class of 50 students, 8 % were absent on one day. The number of students present on that day was ______.
Savitri obtained 440 marks out of 500 in an examination. She secured ______% marks in the examination.
Out of a total deposit of ₹ 1500 in her bank account, Abida withdrew 40% of the deposit. Now the balance in her account is ______.
______ is 50% more than 60.
John sells a bat for ₹ 75 and suffers a loss of ₹ 8. The cost price of the bat is ______.
If the price of sugar is decreased by 20%, then the new price of 3 kg sugar originally costing ₹ 120 will be ______.
Mohini bought a cow for ₹ 9000 and sold it at a loss of ₹ 900. The selling price of the cow is ______.
Devangi buys a chair for ₹ 700 and sells it for ₹ 750. She earns a profit of ______ % in the transaction.
Sonal bought a bed sheet for ₹ 400 and sold it for ₹ 440. Her ______ % is ______.
Nasim bought a pen for ₹ 60 and sold it for ₹54. His ______ % is ______.
Aahuti purchased a house for ₹ 50,59,700 and spent ₹ 40300 on its repairs. To make a profit of 5%, she should sell the house for ₹ ______.
If 20 lemons are bought for ₹ 10 and sold at 5 for three rupees, then ______ in the transaction is ______ %.
Narain bought 120 oranges at ₹ 4 each. He sold 60 % of the oranges at ₹ 5 each and the remaining at ₹ 3.50 each. His ______ is ______ %.
A fruit seller purchased 20 kg of apples at ₹ 50 per kg. Out of these, 5% of the apples were found to be rotten. If he sells the remaining apples at ₹ 60 per kg, then his ______ is ______%.
Interest on ₹ 3000 at 10% per annum for a period of 3 years is ______.
Amount obtained by depositing ₹ 20,000 at 8% per annum for six months is ______.
Interest on ₹ 12500 at 18% per annum for a period of 2 years and 4 months is ______.
25 ml is ______ percent of 5 litres.
If A is increased by 20%, it equals B. If B is decreased by 50%, it equals C. Then ______ % of A is equal to C.
Interest = `(P xx R xx T)/100`, where T is ______ R% is ______ and P is ______.
The difference of interest for 2 years and 3 years on a sum of ₹ 2100 at 8% per annum is ______.
To convert a fraction into a percent, we ______ it by 100.
To convert a decimal into a per cent, we shift the decimal point two places to the ______.
The ______ of interest on a sum of ₹ 2000 at the rate of 6% per annum for `1 1/2` years and 2 years is ₹ 420.
When converted into percentage, the value of 6.5 is ______ than 100%.
Fill in the blanks so that each mark on the number line is labelled with a percent, a fraction and a decimal. Write all fractions in lowest terms.
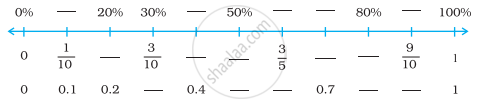
Fill in the blanks so that each mark on the number line is labelled with a percent, a fraction and a decimal. Write all fractions in lowest terms.
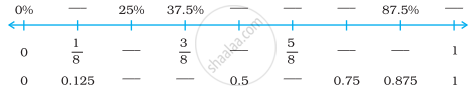
State whether the statements are True or False.
`2/3 = 66 2/3%`.
True
False
When an improper fraction is converted into percentage then the answer can also be less than 100.
True
False
8 hours is 50% of 4 days.
True
False
The interest on ₹ 350 at 5% per annum for 73 days is ₹ 35.
True
False
The simple interest on a sum of ₹ P for T years at R% per annum is given by the formula: Simple Interest = `(T xx P xx R)/100`.
True
False
75% = `4/3`.
True
False
12% of 120 is 100.
True
False
If Ankita obtains 336 marks out of 600, then percentage of marks obtained by her is 33.6.
True
False
0.018 is equivalent to 8%.
True
False
50% of ₹ 50 is ₹ 25.
True
False
250 cm is 4% of 1 km.
True
False
Out of 600 students of a school, 126 go for a picnic. The percentage of students that did not go for the picnic is 75.
True
False
By selling a book for ₹ 50, a shopkeeper suffers a loss of 10%. The cost price of the book is ₹ 60.
True
False
If a chair is bought for ₹ 2000 and is sold at a gain of 10%, then selling price of the chair is ₹ 2010.
True
False
If a bicycle was bought for ₹ 650 and sold for ₹ 585, then the percentage of profit is 10.
True
False
Sushma sold her watch for ₹ 3320 at a gain of ₹ 320. For earning a gain of 10% she should have sold the watch for ₹ 3300.
True
False
Interest on ₹ 1200 for `1 1/2` years at the rate of 15% per annum is ₹ 180.
True
False
Amount received after depositing ₹ 800 for a period of 3 years at the rate of 12% per annum is ₹ 896.
True
False
₹ 6400 were lent to Feroz and Rashmi at 15% per annum for `3 1/2` and 5 years respectively. The difference in the interest paid by them is ₹ 150.
True
False
A vendor purchased 720 lemons at ₹ 120 per hundred.10% of the lemons were found rotten which he sold at ₹ 50 per hundred. If he sells the remaining lemons at ₹ 125 per hundred, then his profit will be 16%.
True
False
Find the value of x if 8% of ₹ x is ₹ 100.
Find the value of x if 32% of x kg is 400 kg.
Find the value of x if 35% of ₹ x is ₹ 280.
Find the value of x if 45% of marks x is 405.
Imagine that a 10 × 10 grid has value 300 and that this value is divided evenly among the small squares. In other words, each small square is worth 3. Use a new grid for each part of this problem, and label each grid “Value: 300.”
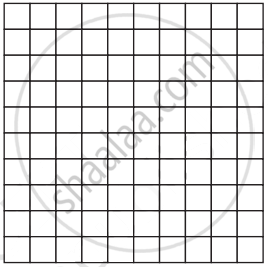
- Shade 25% of the grid. What is 25% of 300? Compare the two answers.
- What is the value of 25 squares?
- Shade 17% of the grid. What is 17% of 300? Compare the two answers
- What is the value of `1/10` of the grid?
- Express `1/6` as a percent.
Express `1/6` as a per cent.
Express `9/40` as a per cent.
Express `1/100` as a per cent.
Express 80% as fraction in its lowest term.
Express `33 1/3%` as a ratio in the lowest term.
Express `16 2/3%` as a ratio in the lowest form.
Express 150% as a ratio in the lowest form.
Sachin and Sanjana are calculating 23% of 800.

Now calculate 52% of 700 using both the ways described above. Which way do you find easier?
Write 0.089 as a percent.
Write 1.56 as a percent.
What is 15% of 20?
What is 800% of 800?
What is 100% of 500?
What percent of 1 hour is 30 minutes?
What percent of 1 day is 1 minute?
What percent of 1 km is 1000 metres?
Find out 8% of 25 kg.
What percent of ₹ 80 is ₹ 100?
45% of the population of a town are men and 40% are women. What is the percentage of children?
The strength of a school is 2000. If 40 % of the students are girls then how many boys are there in the school?
Chalk contains 10% calcium, 3% carbon and 12% oxygen. Find the amount of carbon and calcium (in grams) in `2 1/2` kg of chalk.
800 kg of mortar consists of 55% sand, 33% cement and rest lime. What is the mass of lime in mortar?
In a furniture shop, 24 tables were bought at the rate of ₹ 450 per table. The shopkeeper sold 16 of them at the rate of ₹ 600 per table and the remaining at the rate of 400 per table. Find her gain or loss percent.
Medha deposited 20% of her money in a bank. After spending 20% of the remainder, she has ₹ 4800 left with her. How much did she originally have?
The cost of a flower vase got increased by 12%. If the current cost is ₹ 896, what was its original cost?
Radhika borrowed ₹ 12000 from her friends. Out of which ₹ 4000 were borrowed at 18% and the remaining at 15% rate of interest per annum. What is the total interest after 3 years?
A man travelled 60 km by car and 240 km by train. Find what percent of total journey did he travel by car and what percent by train?
By selling a chair for ₹ 1440, a shopkeeper loses 10%. At what price, did he buy it?
Dhruvika invested money for a period from May 2006 to April 2008 at rate of 12% per annum. If interest received by her is ₹ 1620, find the money invested.
A person wanted to sell a scooter at a loss of 25%. But at the last moment he changed his mind and sold the scooter at a loss of 20%. If the difference in the two SP’s is ₹ 4000, then find the CP of the scooter.
The population of a village is 8000. Out of these, 80% are literate and of these literate people, 40% are women. Find the ratio the number of literate women to the total population?
In an entertainment programme, 250 tickets of ₹ 400 and 500 tickets of ₹ 100 were sold. If the entertainment tax is 40% on ticket of ₹ 400 and 20% on ticket of ₹ 100, find how much entertainment tax was collected from the programme.
Bhavya earns ₹ 50,000 per month and spends 80% of it. Due to pay revision, her monthly income increases by 20% but due to price rise, she has to spend 20% more. Find her new savings.
In an examination, there are three papers each of 100 marks. A candidate obtained 53 marks in the first and 75 marks in the second paper. How many marks must the candidate obtain in the third paper to get an overall of 70 per cent marks?
Health Application
A doctor reports blood pressure in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) as a ratio of systolic blood pressure to diastolic blood pressure (such as 140 over 80). Systolic pressure is measured when the heart beats, and diastolic pressure is measured when it rests. Refer to the table of blood pressure ranges for adults.
| Blood Pressure Ranges | |||
| Normal | Prehypertension | Hypertension (Very High) |
|
| Systolic | Under 120 mm Hg | 120-139 mm Hg | 140 mm Hg and above |
| Diastolic | Under 80 mm Hg | 80-89 mm Hg | 90 mm Hg and above |
Manohar is a healthy 37 years old man whose blood pressure is in the normal category.
- Calculate an approximate ratio of systolic to diastolic blood pressures in the normal range.
- If Manohar’s systolic blood pressure is 102 mm Hg, use the ratio from part (a) to predict his diastolic blood pressure.
- Calculate the ratio of average systolic to average diastolic blood pressure in the prehypertension category.
Science Application:
The king cobra can reach a length of 558 cm. This is only about 60 per cent of the length of the largest reticulated python. Find the length of the largest reticulated python.
Physical Science Application:
Unequal masses will not balance on a fulcrum if they are at equal distance from it; one side will go up and the other side will go down.
Unequal masses will balance when the following proportion is true:
`("mass"1)/("length"2) = ("mass"2)/("length"1)`
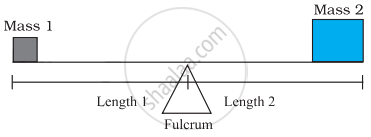
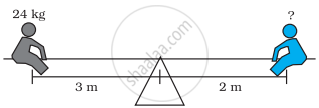
Two children can be balanced on a seesaw when
`("mass"1)/("length"2) = ("mass"2)/("length"1)`. The child on the left and child on the right are balanced. What is the mass of the child on the right?
Life Science Application:
A DNA model was built using the scale 2 cm : 0.0000001 mm. If the model of the DNA chain is 17 cm long, what is the length of the actual chain?
Language Application
Given below is a Mathematical term.

Find the ratio of consonants to vowels in the term.
Language Application
Given below is a Mathematical term.

Find the ratio of consonants to vowels in the term.
Language Application
Given below is a Mathematical term.

Find the ratio of consonants to vowels in the term.
Language Application
Given below is a Mathematical term.

Find the ratio of consonants to vowels in the term.
Language Application
Given below is a Mathematical term.

Find the ratio of consonants to vowels in the term.
Language Application
Given below is a Mathematical term.

Find the percentage of consonants in the term.
Language Application
Given below is a Mathematical term.

Find the percentage of consonants in the term.
Language Application
Given below is a Mathematical term.

Find the percentage of consonants in the term.
Language Application
Given below is a Mathematical term.

Find the percentage of consonants in the term.
Language Application
Given below is a Mathematical term.

Find the percentage of consonants in the term.
What’s the Error?
An analysis showed that 0.06 per cent of the T-shirts made by one company were defective. A student says this is 6 out of every 100. What is the student’s error?
What’s the Error?
A student said that the ratios `3/4` and `9/16` were proportional. What error did the student make?
What’s the Error?
A clothing store charges ₹ 1024 for 4 T-shirts. A student says that the unit price is ₹ 25.6 per T-shirt. What is the error? What is the correct unit price?
A tea merchant blends two varieties of tea in the ratio of 5:4. The cost of first variety is ₹ 200 per kg and that of second variety is ₹ 300 per kg. If he sells the blended tea at the rate of ₹ 275 per kg, find out the percentage of her profit or loss.
A piece of cloth 5 m long shrinks 10 per cent on washing. How long will the cloth be after washing?
Nancy obtained 426 marks out of 600 and the marks obtained by Rohit are 560 out of 800. Whose performance is better?
A memorial trust donates ₹ 5,00,000 to a school, the interest on which is to be used for awarding 3 scholarships to students obtaining first three positions in the school examination every year. If the donation earns an interest of 12 per cent per annum and the values of the second and third scholarships are ₹ 20,000 and ₹ 15,000 respectively, find out the value of the first scholarship.
Ambika got 99 per cent marks in Mathematics, 76 per cent marks in Hindi, 61 per cent in English, 84 per cent in Science, and 95% in Social Science. If each subject carries 100 marks, then find the percentage of marks obtained by Ambika in the aggregate of all the subjects.
What sum of money lent out at 16 per cent per annum simple interest would produce ₹ 9600 as interest in 2 years?
Harish bought a gas-chullah for ₹ 900 and later sold it to Archana at a profit of 5 per cent. Archana used it for a period of two years and later sold it to Babita at a loss of 20 per cent. For how much did Babita get it?
Match each of the entries in Column I with the appropriate entries in Column II:
Match the entries in Column I with the appropriate entries in Column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) 3:5 | (A) ₹ 54 |
| (ii) 2.5 | (B) ₹ 47 |
| (iii) 100% | (C) ₹ 53 |
| (iv) `2/3` | (D) ₹ 160 |
| (v) `6 1/4%` | (E) 60% |
| (vi) 12.5% | (F) 25% |
| (vii) SP when CP = ₹ 50 and loss = 6 % | (G) `1/16` |
| (viii) SP when CP = ₹ 50 and profit = ₹ 4 | (H) 250% |
| (ix) Profit% when CP = ₹ 40 and SP = ₹ 50 | (I) ₹ 159 |
| (x) Profit% when CP = ₹ 50 and SP = ₹ 60 | (J) `66 2/3%` |
| (xi) Interest when principal = ₹ 800, Rate of interest = 10% per annum nd period = 2 years |
(K) 20% |
| (xii) Amount when principal = ₹ 150, Rate of interest = 6% per annum and period = 1 year |
(L) 0.125 |
| (M) 3:2 | |
| (N) ₹ 164 | |
| (O) 3:3 |
In a debate competition, the judges decide that 20 per cent of the total marks would be given for accent and presentation. 60 per cent of the rest are reserved for the subject matter and the rest are for rebuttal. If this means 8 marks for rebuttal, then find the total marks.
Divide ₹ 10000 in two parts so that the simple interest on the first part for 4 years at 12 per cent per annum may be equal to the simple interest on the second part for 4.5 years at 16 per cent per annum.
₹ 9000 becomes ₹ 18000 at simple interest in 8 years. Find the rate per cent per annum.
In how many years will the simple interest on a certain sum be 4.05 times the principal at 13.5 per cent per annum?
The simple interest on a certain sum for 8 years at 12 per cent per annum is ₹ 3120 more than the simple interest on the same sum for 5 years at 14 per cent per annum. Find the sum.
The simple interest on a certain sum for 2.5 years at 12 per cent per annum is ₹ 300 less than the simple interest on the same sum for 4.5 years at 8 per cent per annum. Find the sum.
Designing a Healthy Diet
When you design your healthy diet, you want to make sure that you meet the dietary requirements to help you grow into a healthy adult. As you plan your menu, follow the following guidelines
- Calculate your ideal weight as per your height from the table given at the end of this question.
- An active child should eat around 55.11 calories for each kilogram desired weight.
- 55 per cent of calories should come from carbohydrates. There are 4 calories in each gram of carbohydrates.
- 15 per cent of your calories should come from proteins. There are 4 calories in each gram of proteins.
- 30 per cent of your calories may come from fats. There are 9 calories in each gram of fat.
Following is an example to design your own healthy diet.
Example
- Ideal weight = 40 kg.
- The number of calories needed = 40 × 55.11 = 2204.4
- Calories that should come from carbohydrates = 2204.4 × 0.55 = 1212.42 calories.
Therefore, required quantity of carbohydrates = `1212.42/4` = 303.105 g = 300 g. (approx) - Calories that should come from proteins = 2204.4 × 0.15 = 330.66 calories.
Therefore, required quantity of protein = `330.66/4` g = 82.66 g. - Calories that may come from fat = 2204.4 × 0.3 = 661.3 calories.
Therefore, required quantity of fat = `661.3/9` g = 73.47 g.
Answer the Given Questions
- Your ideal desired weight is ______ kg.
- The quantity of calories you need to eat is ______.
- The quantity of protein needed is ______ g.
- The quantity of fat required is ______ g.
- The quantity of carbohydrates required is ______ g.
| Ideal Height and Weight Proportion | |||||
| Men | Women | ||||
| Feet | cm | Kilograms | Feet | cm | Kilograms |
| 5’ | 152 | 48 | 4’7” | 140 | 34 |
| 5’1” | 155 | 51 | 4’8” | 142 | 36 |
| 5’2” | 157 | 54 | 4’9” | 145 | 39 |
| 5’3” | 160 | 56 | 4’1” | 147 | 41 |
| 5’4” | 163 | 59 | 4’11” | 150 | 43 |
| 5’5” | 165 | 62 | 5’ | 152 | 45 |
| 5’6” | 168 | 65 | 5’1” | 155 | 48 |
| 5’7” | 170 | 67 | 5’2” | 157 | 50 |
| 5’8” | 173 | 70 | 5’3” | 160 | 52 |
| 5’9” | 175 | 73 | 5’4” | 163 | 55 |
| 5’10” | 178 | 75 | 5’5” | 165 | 57 |
| 5’11” | 180 | 78 | 5’6” | 168 | 59 |
| 6’ | 183 | 81 | 5’7” | 170 | 61 |
| 6’1” | 185 | 84 | 5’8” | 173 | 64 |
| 6’2” | 188 | 86 | 5’9” | 175 | 66 |
| 6’3” | 191 | 89 | 5’10” | 178 | 68 |
| 6’4” | 193 | 92 | 5’11” | 180 | 70 |
150 students are studying English, Maths or both. 62 per cent of students study English and 68 per cent are studying Maths. How many students are studying both?
Earth Science:
The table lists the world’s 10 largest deserts.
| Largest Deserts in the World | |
| Desert | Area (km2) |
| Sahara (Africa) | 8,800,000 |
| Gobi (Asia | 1,300,000 |
| Australian Desert (Australia) | 1,250,000 |
| Arabian Desert (Asia) | 850,000 |
| Kalahari Desert (Africa) | 580,000 |
| Chihuahuan Desert (North America) | 370,000 |
| Takla Makan Desert (Asia) | 320,000 |
| Kara Kum (Asia) | 310,000 |
| Namib Desert (Africa) | 310,000 |
| Thar Desert (Asia) | 260,000 |
- What are the mean, median and mode of the areas listed?
- How many times the size of the Gobi Desert is the Namib Desert?
- What percentage of the deserts listed are in Asia?
- What percentage of the total area of the deserts listed is in Asia?
Geography Application:
Earth’s total land area is about 148428950 km2. The land area of Asia is about 30 per cent of this total. What is the approximate land area of Asia to the nearest square km?

The pieces of Tangrams have been rearranged to make the given shape.
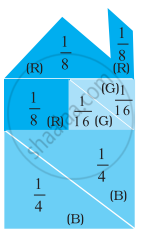
By observing the given shape, answer the following questions:
- What percentage of total has been coloured?
- Red (R) = ______
- Blue (B) = ______
- Green (G) = ______
- Check that the sum of all the percentages calculated above should be 100.
- If we rearrange the same pieces to form some other shape, will the percentage of colours change?
Solutions for 7: Comparing Quantities
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 7 chapter 7 - Comparing Quantities NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 7 chapter 7 - Comparing Quantities - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-7_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 7 chapter 7 - Comparing Quantities
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 7 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 7 CBSE 7 (Comparing Quantities) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics [English] Class 7 chapter 7 Comparing Quantities are Concept of Equivalent Ratios, Conversion between Percentage and Fraction, Converting Decimals to Percentage, Interpreting Percentages, Converting Percentages to “How Many”, Ratios to Percents, Increase Or Decrease as Percent, Basic Concepts of Profit and Loss, Estimation in Percentages, Concept of Proportion, Basic Concept of Percentage, Converting Percentages to Decimals, Profit or Loss as a Percentage, Calculation of Interest, Conversion between Percentage and Fraction, Concept of Ratio, Concept of Unitary Method.
Using NCERT Exemplar Mathematics [English] Class 7 solutions Comparing Quantities exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Mathematics [English] Class 7 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 7, Comparing Quantities Mathematics [English] Class 7 additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 7 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
