Advertisements
Chapters
▶ 2: Data Handling
3: Square-Square Root and Cube-Cube Root
4: Linear Equation In One Variable
5: Understanding Quadrilaterals and Practical Geometry
6: Visualising Solid Shapes
7: Algebraic Expression, Identities and Factorisation
8: Exponents and Powers
9: Comparing Quantities
10: Direct and Inverse Proportions
11: Mensuration
12: Introduct To Graphs
13: Playing With Numbers
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 chapter 2 - Data Handling NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 chapter 2 - Data Handling - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-8_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 2: Data Handling
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 2 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Mathematics [English] Class 8.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 2 Data Handling Exercise [Pages 42 - 59]
Choose the correct alternative:
The height of a rectangle in a histogram shows the ______.
Width of the class
Upper limit of the class
Lower limit of the class
Frequency of the class
A geometric representation showing the relationship between a whole and its parts is a ______.
Pie chart
Histogram
Bar graph
Pictograph
In a pie chart, the total angle at the centre of the circle is ______.
180°
360°
270°
90°
The range of the data 30, 61, 55, 56, 60, 20, 26, 46, 28, 56 is ______.
26
30
41
61
Which of the following is not a random experiment?
Tossing a coin
Rolling a dice
Choosing a card from a deck of 52 cards
Throwing a stone from a roof of a building
What is the probability of choosing a vowel from the alphabets?
`21/26`
`5/26`
`1/26`
`3/26`
In a school only, 3 out of 5 students can participate in a competition. What is the probability of the students who do not make it to the competition?
0.65
0.4
0.45
0.6
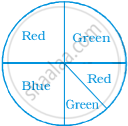
Students of a class voted for their favourite colour and a pie chart was prepared based on the data collected.
Observe the pie chart given below and answer questions based on it.
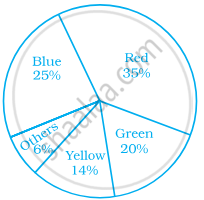
Which colour received `1/5` of the votes?
Red
Blue
Green
Yellow
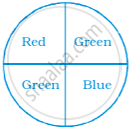
Students of a class voted for their favourite colour and a pie chart was prepared based on the data collected.
Observe the pie chart given below and answer questions based on it.
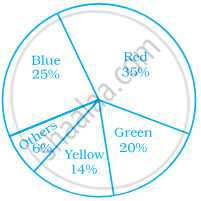
If 400 students voted in all, then how many did vote ‘Others’ colour as their favourite?
6
20
24
40
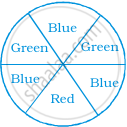
Students of a class voted for their favourite colour and a pie chart was prepared based on the data collected.
Observe the pie chart given below and answer questions based on it.

Which of the following is a reasonable conclusion for the given data?
`1/20`th student voted for blue colour
Green is the least popular colour
The number of students who voted for red colour is two times the number of students who voted for yellow colour
Number of students liking together yellow and green colour is approximately the same as those for red colour
Listed below are the temperature in °C for 10 days.
–6, –8, 0, 3, 2, 0, 1, 5, 4, 4
What is the range of the data?
8
13°C
10°C
12°C
Ram put some buttons on the table. There were 4 blue, 7 red, 3 black and 6 white buttons in all. All of a sudden, a cat jumped on the table and knocked out one button on the floor. What is the probability that the button on the floor is blue?
`7/20`
`3/5`
`1/5`
`1/4`
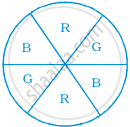
Rahul, Varun and Yash are playing a game of spinning a coloured wheel. Rahul wins if spinner lands on red. Varun wins if spinner lands on blue and Yash wins if it lands on green. Which of the following spinner should be used to make the game fair?
In a frequency distribution with classes 0 – 10, 10 – 20 etc., the size of the class intervals is 10. The lower limit of fourth class is ______.
40
50
20
30
A coin is tossed 200 times and head appeared 120 times. The probability of getting a head in this experiment is ______.
`2/5`
`3/5`
`1/5`
`4/5`
Data collected in a survey shows that 40% of the buyers are interested in buying a particular brand of toothpaste. The central angle of the sector of the pie chart representing this information is ______.
120°
150°
144°
40°
Monthly salary of a person is Rs. 15000. The central angle of the sector representing his expenses on food and house rent on a pie chart is 60°. The amount he spends on food and house rent is ______.
Rs. 5000
Rs. 2500
Rs. 6000
Rs. 9000
The following pie chart gives the distribution of constituents in the human body. The central angle of the sector showing the distribution of protein and other constituents is ______.
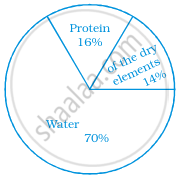
108°
54°
30°
216°
Rohan and Shalu are playing with 5 cards as shown in the figure. What is the probability of Rohan picking a card without seeing, that has the number 2 on it?
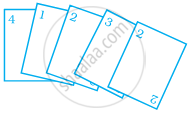
`2/5`
`1/5`
`3/5`
`4/5`
The following pie chart represents the distribution of proteins in parts of a human body. What is the ratio of distribution of proteins in the muscles to that of proteins in the bones?
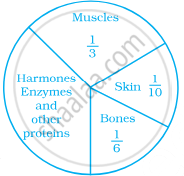
3 : 1
1 : 2
1 : 3
2 : 1
What is the central angle of the sector representing skin and bones together?

36°
60°
90°
96°
What is the central angle of the sector representing hormones enzymes and other proteins?

120°
144°
156°
176°
A coin is tossed 12 times and the outcomes are observed as shown below:
The chance of occurrence of Head is
`1/2`
`5/12`
`7/12`
`5/7`
Total number of outcomes, when a ball is drawn from a bag which contains 3 red, 5 black and 4 blue balls is ______.
8
7
9
12
A graph showing two sets of data simultaneously is known as ______.
Pictograph
Histogram
Pie chart
Double bar graph
Size of the class 150 – 175 is ______.
150
175
25
–25
In a throw of a dice, the probability of getting the number 7 is ______.
`1/2`
`1/6`
1
0
Data represented using circles is known as ______.
Bar graph
Histogram
Pictograph
Pie chart
Tally marks are used to find ______.
Class intervals
Range
Frequency
Upper limit
Upper limit of class interval 75 – 85 is ______.
10
–10
75
85
Numbers 1 to 5 are written on separate slips, i.e one number on one slip and put in a box. Wahida pick a slip from the box without looking at it. What is the probability that the slip bears an odd number?
`1/5`
`2/5`
`3/5`
`4/5`
A glass jar contains 6 red, 5 green, 4 blue and 5 yellow marbles of same size. Hari takes out a marble from the jar at random. What is the probability that the chosen marble is of red colour?
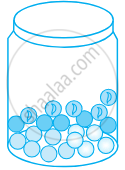
`7/10`
`3/10`
`4/5`
`2/5`
A coin is tossed two times. The number of possible outcomes is ______.
1
2
3
4
A coin is tossed three times. The number of possible outcomes is ______.
3
4
6
8
A diece is tossed two times. The number of possible outcomes is ______.
12
24
36
30
Fill in the blanks:
Data available in an unorganised form is called ______ data.
In the class interval 20 – 30, the lower class limit is ______.
In the class interval 26 – 33, 33 is known as ______.
The range of the data 6, 8, 16, 22, 8, 20, 7, 25 is ______.
A pie chart is used to compare ______ to a whole.
In the experiment of tossing a coin one time, the outcome is either ______ or ______.
When a dice is rolled, the six possible outcomes are ______.
Each outcome or a collection of outcomes in an experiment makes an ______.
An experiment whose outcomes cannot be predicted exactly in advance is called a ______ experiment.
The difference between the upper and lower limit of a class interval is called the ______ of the class interval.
The sixth class interval for a grouped data whose first two class intervals are 10 – 15 and 15 – 20 is ______.
The total number of people surveyed is ______.
The number of people owning books more than 60 is ______.
The number of people owning books less than 40 is ______.
The number of people having books more than 20 and less than 40 is ______.
The number of times a particular observation occurs in a given data is called its ______.
When the number of observations is large, the observations are usually organised in groups of equal width called ______.
The total number of outcomes when a coin is tossed is ______.
The class size of the interval 80 – 85 is ______.
In a histogram ______ are drawn with width equal to a class interval without leaving any gap in between.
When a dice is thrown, outcomes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 are equally ______.
In a histogram, class intervals and frequencies are taken along ______ axis and ______ axis.
In the class intervals 10 – 20, 20 – 30, etc., respectively, 20 lies in the class ______.
State whether the following statement is True or False:
In a pie chart a whole circle is divided into sectors.
True
False
The central angle of a sector in a pie chart cannot be more than 180°.
True
False
Sum of all the central angles in a pie chart is 360°.
True
False
In a pie chart two central angles can be of 180°.
True
False
In a pie chart two or more central angles can be equal.
True
False
Getting a prime number on throwing a die is an event.
True
False
Using the following frequency table.
| Marks (obtained out of 10) | 4 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Frequency | 5 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 12 | 9 |
9 students got full marks.
True
False
Using the following frequency table.
| Marks (obtained out of 10) | 4 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Frequency | 5 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 12 | 9 |
The frequency of less than 8 marks is 29.
True
False
Using the following frequency table.
| Marks (obtained out of 10) | 4 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Frequency | 5 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 12 | 9 |
The frequency of more than 8 marks is 21.
True
False
Using the following frequency table.
| Marks (obtained out of 10) | 4 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Frequency | 5 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 12 | 9 |
10 marks the highest frequency.
True
False
If the fifth class interval is 60 – 65, fourth class interval is 55 – 60, then the first-class interval is 45 – 50.
True
False
From the histogram given on the right, we can say that 1500 males above the age of 20 are literate.
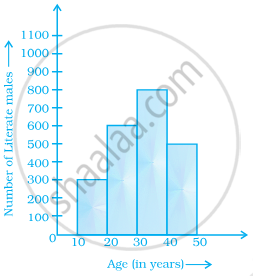
True
False
The class size of the class interval 60 – 68 is 8.
True
False
If a pair of coins is tossed, then the number of outcomes are 2.
True
False
On throwing a dice once, the probability of occurence of an even number is `1/2`.
True
False
On throwing a dice once, the probability of occurence of a composite number is `1/2`.
True
False
From the given pie chart, we can infer that production of Manganese is least in state B.
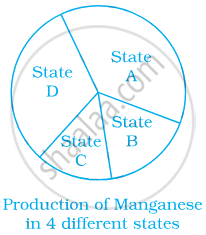
True
False
One or more outcomes of an experiment make an event.
True
False
The probability of getting number 6 in a throw of a dice is `1/6`. Similarly the probability of getting a number 5 is `1/5`.
True
False
The probability of getting a prime number is the same as that of a composite number in a throw of a dice.
True
False
In a throw of a dice, the probability of getting an even number is the same as that of getting an odd number.
True
False
To verify pythagoras theorem is a random experiment.
True
False
The following pictorial representation of data is a histogram.
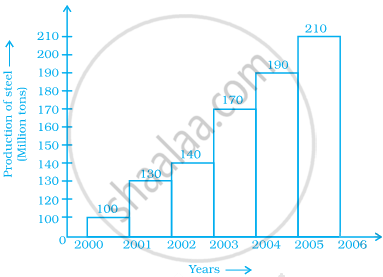
True
False
Given below is a frequency distribution table. Read it and answer the questions that follow:
| Class Interval | Frequency |
| 10 – 20 | 5 |
| 20 – 30 | 10 |
| 30 – 40 | 4 |
| 40 – 50 | 15 |
| 50 – 60 | 12 |
- What is the lower limit of the second class interval?
- What is the upper limit of the last class interval?
- What is the frequency of the third class?
- Which interval has a frequency of 10?
- Which interval has the lowest frequency?
- What is the class size?
The top speeds of thirty different land animals have been organised into a frequency table. Draw a histogram for the given data.
| Maximum Speed (km/h) | Frequency |
| 10 – 20 | 5 |
| 20 – 30 | 5 |
| 30 – 40 | 10 |
| 40 – 50 | 8 |
| 50 – 60 | 0 |
| 60 – 70 | 2 |
Given below is a pie chart showing the time spend by a group of 350 children in different games. Observe it and answer the questions that follow:
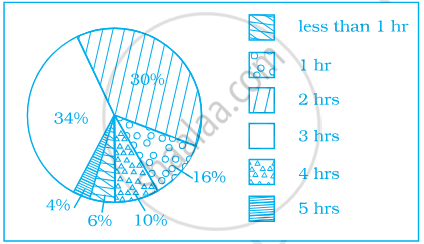
- How many children spend at least one hour in playing games?
- How many children spend more than 2 hours in playing games?
- How many children spend 3 or lesser hours in playing games?
- Which is greater — number of children who spend 2 hours or more per day or number of children who play for less than one hour?
The pie chart on the right shows the result of a survey carried out to find the modes of travel used by the children to go to school. Study the pie chart and answer the questions that follow.
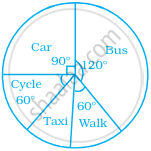
- What is the most common mode of transport?
- What fraction of children travel by car?
- If 18 children travel by car, how many children took part in the survey?
- How many children use taxi to travel to school?
- By which two modes of transport are equal number of children travelling?
A dice is rolled once. What is the probability that the number on top will be odd
A dice is rolled once. What is the probability that the number on top will be greater than 5
A dice is rolled once. What is the probability that the number on top will be a multiple of 3
A dice is rolled once. What is the probability that the number on top will be less than 1
A dice is rolled once. What is the probability that the number on top will be a factor of 36
A dice is rolled once. What is the probability that the number on top will be a factor of 6
Classify the following statements under appropriate headings.
- Getting the sum of angles of a triangle as 180°.
- India winning a cricket match against Pakistan.
- Sun setting in the evening.
- Getting 7 when a die is thrown.
- Sun rising from the west.
- Winning a racing competition by you.
| Certain to happen | Impossible to happen | May or may not happen |
Study the pie chart given below depicting the marks scored by a student in an examination out of 540. Find the marks obtained by him in each subject.
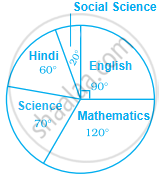
Ritwik draws a ball from a bag that contains white and yellow balls. The probability of choosing a white ball is `2/9`. If the total number of balls in the bag is 36, find the number of yellow balls.
Look at the histogram below and answer the questions that follow.
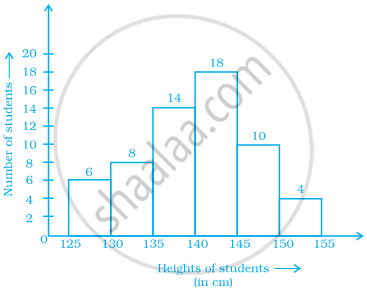
- How many students have height more than or equal to 135 cm but less than 150 cm?
- Which class interval has the least number of students?
- What is the class size?
- How many students have height less than 140 cm?
Following are the number of members in 25 families of a village:
6, 8, 7, 7, 6, 5, 3, 2, 5, 6, 8, 7, 7, 4, 3, 6, 6, 6, 7, 5, 4, 3, 3, 2, 5.
Prepare a frequency distribution table for the data using class intervals 0 – 2, 2 – 4, etc.
Draw a histogram to represent the frequency distribution in question 91.
The marks obtained (out of 20) by 30 students of a class in a test are as follows:
14, 16, 15, 11, 15, 14, 13, 16, 8, 10, 7, 11, 18, 15, 14, 19, 20, 7, 10, 13, 12, 14, 15, 13, 16, 17, 14, 11, 10, 20.
Prepare a frequency distribution table for the above data using class intervals of equal width in which one class interval is 4 – 8 (excluding 8 and including 4).
Prepare a histogram from the frequency distribution table obtained in question 93.
The weights (in kg) of 30 students of a class are:
39, 38, 36, 38, 40, 42, 43, 44, 33, 33, 31, 45, 46, 38, 37, 31, 30, 39, 41, 41, 46, 36, 35, 34, 39, 43, 32, 37, 29, 26.
Prepare a frequency distribution table using one class interval as (30 – 35), 35 not included.
- Which class has the least frequency?
- Which class has the maximum frequency?
Shoes of the following brands are sold in Nov. 2007 at a shoe store. Construct a pie chart for the data.
| Brand | Number of pair of shoes sold |
| A | 130 |
| B | 120 |
| C | 90 |
| D | 40 |
| E | 20 |
The following pie chart depicts the expenditure of a state government under different heads.
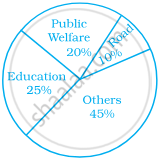
- If the total spending is 10 crores, how much money was spent on roads?
- How many times is the amount of money spent on education compared to the amount spent on roads?
- What fraction of the total expenditure is spent on both roads and public welfare together?
The following data represents the different number of animals in a zoo. Prepare a pie chart for the given data.
| Animals | Number of animals |
| Deer | 42 |
| Elephant | 15 |
| Giraffe | 26 |
| Reptiles | 24 |
| Tiger | 13 |
Playing cards from a pack of cards the following cards are kept face down: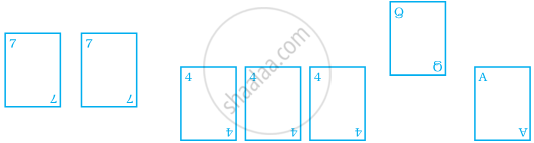
Suhail wins if he picks up a face card. Find the probability of Suhail winning?
Playing cards now the following cards are added to the above cards: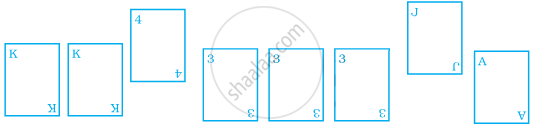
What is the probability of Suhail winning now? Reshma wins if she picks up a 4. What is the probability of Reshma winning?
[Queen, King and Jack cards are called face cards.]
Construct a frequency distribution table for the following weights (in grams) of 35 mangoes, using the equal class intervals, one of them is 40 – 45 (45 not included).
30, 40, 45, 32, 43, 50, 55, 62, 70, 70, 61, 62, 53, 52, 50, 42, 35, 37, 53, 55, 65, 70, 73, 74, 45, 46, 58, 59, 60, 62, 74, 34, 35, 70, 68.
- How many classes are there in the frequency distribution table?
- Which weight group has the highest frequency?
Complete the following table:
| Weights (in kg.) |
Tally Marks | Frequency (Number of persons) |
| 40 – 50 | `\cancel(bb|bb|bb|bb|) \cancel(bb|bb|bb|bb|) bb|bb|` | |
| 50 – 60 | `\cancel(bb|bb|bb|bb|) \cancel(bb|bb|bb|bb|) bb|bb|bb|bb|` | |
| 60 – 70 | `\cancel(bb|bb|bb|bb|) bb|` | |
| 70 – 80 | `bb|bb|` | |
| 80 – 90 | `bb|` |
Find the total number of persons whose weights are given in the above table.
Draw a histogram for the following data.
| Class interval | 10 – 15 | 15 – 20 | 20 – 25 | 25 – 30 | 30 – 35 | 35 – 40 |
| Frequency | 30 | 98 | 80 | 58 | 29 | 50 |
In a hypothetical sample of 20 people the amounts of money with them were found to be as follows:
114, 108, 100, 98, 101, 109, 117, 119, 126, 131, 136, 143, 156, 169, 182, 195, 207, 219, 235, 118.
Draw the histogram of the frequency distribution (taking one of the class intervals as 50 − 100).
The below histogram shows the number of literate females in the age group of 10 to 40 years in a town.
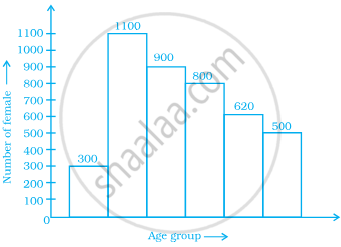
- Write the classes assuming all the classes are of equal width.
- What is the classes width?
- In which age group are literate females the least?
- In which age group is the number of literate females the highest?
The following histogram shows the frequency distribution of teaching experiences of 30 teachers in various schools:

- What is the class width?
- How many teachers are having the maximum teaching experience and how many have the least teaching experience?
- How many teachers have teaching experience of 10 to 20 years?
In a district, the number of branches of different banks is given below:
| Bank | State Bank of India |
Bank of Baroda |
Punjab National Bank |
Canara Bank |
| Number of Branches | 30 | 17 | 15 | 10 |
Draw a pie chart for this data.
For the development of basic infrastructure in a district, a project of Rs 108 crore approved by Development Bank is as follows:
| Item Head | Road | Electricity | Drinking water | Sewerage |
| Amount In crore (Rs.) |
43.2 | 16.2 | 27.00 | 21.6 |
Draw a pie chart for this data.
In the time table of a school, periods allotted per week to different teaching subjects are given below:
| Subject | Hindi | English | Maths | Science | Social Science |
Computer | Sanskrit |
| Periods Allotted |
7 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 4 | 3 |
Draw a pie chart for this data.
A survey was carried out to find the favourite beverage preferred by a certain group of young people. The following pie chart shows the findings of this survey.
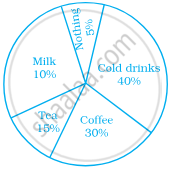
From this pie chart answer the following:
- Which type of beverage is liked by the maximum number of people.
- If 45 people like tea, how many people were surveyed?
The following data represents the approximate percentage of water in various oceans. Prepare a pie chart for the given data.
| Pacific | 40% |
| Atlantic | 30% |
| Indian | 20% |
| Others | 10% |
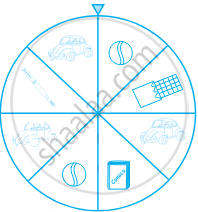
At a Birthday Party, the children spin a wheel to get a gift. Find the probability of getting a ball
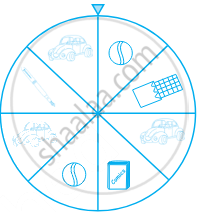
At a Birthday Party, the children spin a wheel to get a gift. Find the probability of getting a toy car
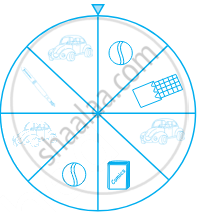
At a Birthday Party, the children spin a wheel to get a gift. Find the probability of any toy except a chocolate
Sonia picks up a card from the given cards.
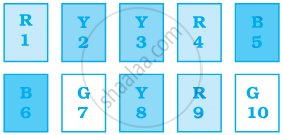
Calculate the probability of getting an odd number
Sonia picks up a card from the given cards.
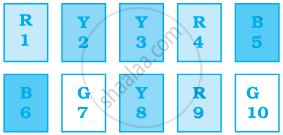
Calculate the probability of getting a Y card
Sonia picks up a card from the given cards.

Calculate the probability of getting a G card
Sonia picks up a card from the given cards.
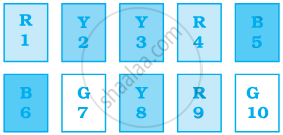
Calculate the probability of getting B card bearing number > 7
Identify which symbol should appear in each sector.
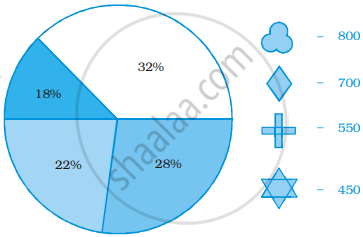
Identify which symbol should appear in each sector.
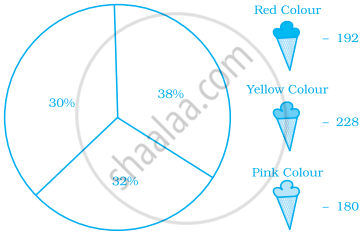
A financial counselor gave a client this pie chart describing how to budget his income. If the client brings home Rs. 50,000 each month, how much should he spend in each category?
- Housing
- Food (including eating out)
- Car loan and Maintenance
- Utilities
- Phone
- Clothing
- Entertainment
Following is a pie chart showing the amount spent in rupees (in thousands) by a company on various modes of advertising for a product.
Now answer the following questions.
- Which type of media advertising is the greatest amount of the total?
- Which type of media advertising is the least amount of the total?
- What percent of the total advertising amount is spent on direct mail campaigns?
- What percent of the advertising amount is spent on newspaper and magazine advertisements?
- What media types do you think are included in miscellaneous? Why aren’t those media types given their own category?
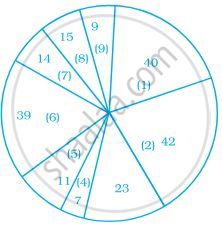
- Television
- Newspapers
- Magazines
- Radio
- Business papers
- Direct mail
- Yellow pages
- Outdoor
- Miscellaneous
Solutions for 2: Data Handling
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 chapter 2 - Data Handling NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 chapter 2 - Data Handling - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-8_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 chapter 2 - Data Handling
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 8 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 8 CBSE 2 (Data Handling) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics [English] Class 8 chapter 2 Data Handling are Graphical Representation of Data as Histograms, Organisation of Data, Concept of Data Handling, Drawing a Bar Graph, Drawing a Double Bar Graph, Interpretation of a Double Bar Graph, Frequency Distribution Table, Concept of Pie Graph (Or a Circle-graph), Interpretation of Pie Diagram, Chance and Probability - Chance, Interpretation of a Pictograph, Interpretation of Bar Graphs, Basic Ideas of Probability.
Using NCERT Exemplar Mathematics [English] Class 8 solutions Data Handling exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Mathematics [English] Class 8 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 2, Data Handling Mathematics [English] Class 8 additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 8 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.