Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: p-Block Elements - I
3: p-Block Elements - II
4: Transition and Inner Transition Elements
5: Coordination Chemistry
▶ 6: Solid State
7: Chemical Kinetics
8: Ionic Equilibrium
9: Electro Chemistry
10: Surface Chemistry
11: Hydroxy Compounds and Ethers
12: Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids
13: Organic Nitrogen Compounds
14: Biomolecules
15: Chemistry in Everyday Life
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 6 - Solid State Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 6 - Solid State - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-volume-1-and-2-english-class-12-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 6: Solid State
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 6 of Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Samacheer Kalvi for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board.
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board 6 Solid State Evaluation [Pages 197 - 201]
Choose the best answer:
Graphite and diamond are ____________.
covalent and molecular crystals
ionic and covalent crystals
both covalent crystals
both molecular crystals
An ionic compound AxBy crystallizes in fcc type crystal structure with B ions at the centre of each face and A ion occupying corners of the cube. the correct formula of AxBy is
AB
AB3
A3B
A8B6
The ratio of close packed atoms to tetrahedral hole in cubic packing is ____________.
1 : 1
1 : 2
2 : 1
1 : 4
Solid CO2 is an example of ____________.
covalent solid
metallic solid
molecular solid
ionic solid
Assertion: monoclinic sulphur is an example of a monoclinic crystal system
Reason: for a monoclinic system, a ≠ b ≠ c and α = γ = 90°, β ≠ 90°
Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion is true but reason is false.
Both assertion and reason are false.
In calcium fluoride, having the flurite structure the coordination number of Ca2+ ion and F− Ion are ____________.
4 and 2
6 and 6
8 and 4
4 and 8
The number of unit cells in 8 gm of an element X (atomic mass 40) which crystallizes in bcc pattern is (NA is the Avogadro number)
6.023 × 1023
6.023 × 1022
60.23 × 1023
`((6.023 xx 10^23)/(8 xx 40))`
In a solid atom M occupies ccp lattice and `(1/3)` of tetrahedral voids are occupied by atom N. find the formula of solid formed by M and N.
MN
M3N
MN3
M3N2
The ionic radii of A+ and B− are 0.98 × 10−10 m and 1.81 × 10−10 m. the coordination number of each ion in AB is
8
2
6
4
CsCl has bcc arrangement, its unit cell edge length is 400 pm, it's inter atomic distance is
400 pm
800 pm
`sqrt3 xx 100 "pm"`
`((sqrt3)/2) xx 400 "pm"`
A solid compound XY has NaCl structure. if the radius of the cation is 100 pm, the radius of the anion will be
`(100/0.414)`
`(0.732/100)`
100 × 0.414
`(0.414/100)`
The vacant space in bcc lattice unit cell is ____________.
48%
23%
32%
26%
The radius of an atom is 300 pm, if it crystallizes in a face centered cubic lattice, the length of the edge of the unit cell is ____________.
488.5 pm
848.5 pm
884.5 pm
484.5 pm
The fraction of total volume occupied by the atoms in a simple cubic is
`(π/(4sqrt2))`
`(π/6)`
`(π/4)`
`(π/(3sqrt2))`
The yellow colour in NaCl crystal is due to ____________.
excitation of electrons in F centers
reflection of light from Cl− ion on the surface
refraction of light from Na+ ion
all of the above
If ‘a’ stands for the edge length of the cubic system; sc, bcc, and fcc. Then the ratio of radii of spheres in these systems will be respectively.
`(1/2 "a" : sqrt3/2 "a" : sqrt2/2 "a")`
`(sqrt1 "a" : sqrt3 "a" : sqrt2 "a")`
`(1/2 "a" : sqrt3/4 "a" : 1/(2sqrt2) "a")`
`(1/2 "a" : sqrt3 "a" : 1/sqrt2 "a")`
If ‘a’ is the length of the side of the cube, the distance between the body centered atom and one corner atom in the cube will be
`(2/sqrt3) "a"`
`(4/sqrt3) "a"`
`(sqrt3/4) "a"`
`(sqrt3/2) "a"`
Potassium has a bcc structure with nearest neighbor distance 4.52 A0. its atomic weight is 39. its density will be
915 kg m−3
2142 kg m−3
452 kg m−3
390 kg m−3
Schottky defect in a crystal is observed when
unequal number of anions and cations are missing from the lattice
equal number of cations and anions are missing from the lattice
an ion leaves its normal site and occupies an interstitial site
no ion is missing from its lattice
The cation leaves its normal position in the crystal and moves to some interstitial position, the defect in the crystal is known as ____________.
Schottky defect
F center
Frenkel defect
Non-stoichiometric defect
Assertion: due to Frenkel defect, density of the crystalline solid decreases.
Reason: in Frenkel defect cation and anion leaves the crystal.
Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion is true but reason is false.
Both assertion and reason are false.
The crystal with a metal deficiency defect is ____________.
NaCl
FeO
ZnO
KCl
A two-dimensional solid pattern formed by two different atoms X and Y is shown below. The black and white squares represent atoms X and Y respectively. the simplest formula for the compound based on the unit cell from the pattern is
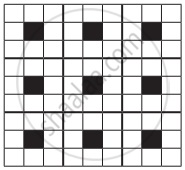
XY8
X4Y9
XY2
XY4
Answer the following questions:
Define unit cell.
Give any three characteristics of ionic crystals.
Differentiate crystalline solids and amorphous solids.
Classify the following solid.
P4
Classify the following solid.
Brass
Classify the following solid.
Diamond
Classify the following solid.
NaCl
Classify the following solid.
Iodine
Explain briefly seven types of unit cells.
Distinguish between hexagonal close packing and cubic close packing.
Distinguish tetrahedral and octahedral voids.
What are point defects?
Explain Schottky defect.
Write short note on metal excess and metal deficiency defect with an example.
Calculate the number of atoms in a fcc unit cell.
Explain AAAA and ABABA and ABCABC type of three dimensional packing with the help of neat diagram.
Why ionic crystals are hard and brittle?
Calculate the percentage efficiency of packing in the case of body centered cubic crystal.
What is the two dimensional coordination number of a molecule in square close packed layer?
What is meant by the term “coordination number”?
What is the coordination number of atoms in a bcc structure?
An element has bcc structure with a cell edge of 288 pm. the density of the element is 7.2 g cm−3. how many atoms are present in 208 g of the element.
Aluminium crystallizes in a cubic close packed structure. Its metallic radius is 125 pm. calculate the edge length of the unit cell.
If NaCl is doped with 10−2 mol percentage of strontium chloride, what is the concentration of cation vacancy?
KF crystallizes in fcc structure like sodium chloride. calculate the distance between K+ and F− in KF.
(Given: density of KF is 2.48 g cm−3)
An atom crystallizes in fcc crystal lattice and has a density of 10 g cm−3 with unit cell edge length of 100 pm. calculate the number of atoms present in 1 g of crystal.
Atoms X and Y form bcc crystalline structure. Atom X is present at the corners of the cube and Y is at the centre of the cube. What is the formula of the compound?
Sodium metal crystallizes in bcc structure with the edge length of the unit cell 4.3 × 10−8 cm. calculate the radius of a sodium atom.
Write a note on Frenkel defect.
Solutions for 6: Solid State
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 6 - Solid State Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 6 - Solid State - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-volume-1-and-2-english-class-12-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 6 - Solid State
Shaalaa.com has the Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Mathematics Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education 6 (Solid State) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Samacheer Kalvi textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 6 Solid State are General Characteristics of Solids, Classification of Solids, Classification of Crystalline Solids, Crystal Lattices and Unit Cells, Primitive and Non-primitive Unit Cell, Packing in Crystals, Imperfection in Solids.
Using Samacheer Kalvi Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board solutions Solid State exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Samacheer Kalvi Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board students prefer Samacheer Kalvi Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 6, Solid State Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board additional questions for Mathematics Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
