Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the distances of the point P(–4, 3, 5) from the coordinate axes.
उत्तर
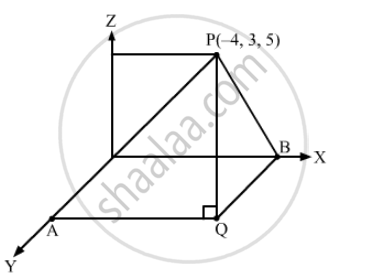
Let PQ be the perpendicular to the xy-plane and QA be perpendicular from Q to the y-axis.
PA will be perpendicular to the x-axis.
Also, QA = \[\left| 3 \right|\]and PQ =\[\left| 5 \right|\]
Now, distance of P from the x-axis:
PB =\[\sqrt{B Q^2 + Q P^2}\]
\[= \sqrt{3^2 + 5^2}\]
\[ = \sqrt{9 + 25} = \sqrt{34}\]
Similarly,
From the right-angled \[∆ PAQ\]distance of P from the y-axis:
PA =\[\sqrt{A Q^2 + Q P^2}\]
\[ = \sqrt{16 + 25} = \sqrt{41}\]
\[ = \sqrt{25} = 5\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the octants in which the following points lie: (5, 2, 3)
Find the image of:
(5, 2, –7) in the xy-plane.
The coordinates of a point are (3, –2, 5). Write down the coordinates of seven points such that the absolute values of their coordinates are the same as those of the coordinates of the given point.
Find the point on y-axis which is equidistant from the points (3, 1, 2) and (5, 5, 2).
Find the points on z-axis which are at a distance \[\sqrt{21}\]from the point (1, 2, 3).
If A(–2, 2, 3) and B(13, –3, 13) are two points.
Find the locus of a point P which moves in such a way the 3PA = 2PB.
Show that the points (a, b, c), (b, c, a) and (c, a, b) are the vertices of an equilateral triangle.
Verify the following:
(0, 7, –10), (1, 6, –6) and (4, 9, –6) are vertices of an isosceles triangle.
Find the locus of the point, the sum of whose distances from the points A(4, 0, 0) and B(–4, 0, 0) is equal to 10.
Show that the points A(1, 2, 3), B(–1, –2, –1), C(2, 3, 2) and D(4, 7, 6) are the vertices of a parallelogram ABCD, but not a rectangle.
Write the distance of the point P(3, 4, 5) from z-axis.
Write the coordinates of the foot of the perpendicular from the point (1, 2, 3) on y-axis.
Write the length of the perpendicular drawn from the point P(3, 5, 12) on x-axis.
Find the ratio in which the line segment joining the points (2, 4,5) and (3, −5, 4) is divided by the yz-plane.
The coordinates of the foot of the perpendicular from a point P(6,7, 8) on x - axis are
The perpendicular distance of the point P (6, 7, 8) from xy - plane is
The length of the perpendicular drawn from the point P (3, 4, 5) on y-axis is
The perpendicular distance of the point P(3, 3,4) from the x-axis is
The length of the perpendicular drawn from the point P(a, b, c) from z-axis is
Find the direction cosines of the line passing through the points P(2, 3, 5) and Q(–1, 2, 4).
If a line makes an angle of 30°, 60°, 90° with the positive direction of x, y, z-axes, respectively, then find its direction cosines.
The x-coordinate of a point on the line joining the points Q(2, 2, 1) and R(5, 1, –2) is 4. Find its z-coordinate.
Find the image of the point having position vector `hati + 3hatj + 4hatk` in the plane `hatr * (2hati - hatj + hatk)` + 3 = 0.
If a line makes angles α, β, γ with the positive directions of the coordinate axes, then the value of sin2α + sin2β + sin2γ is ______.
If a line makes an angle of `pi/4` with each of y and z axis, then the angle which it makes with x-axis is ______.
Find the equation of a plane which bisects perpendicularly the line joining the points A(2, 3, 4) and B(4, 5, 8) at right angles.
If the line drawn from the point (–2, – 1, – 3) meets a plane at right angle at the point (1, – 3, 3), find the equation of the plane
If a variable line in two adjacent positions has direction cosines l, m, n and l + δl, m + δm, n + δn, show that the small angle δθ between the two positions is given by δθ2 = δl2 + δm2 + δn2
Find the length and the foot of perpendicular from the point `(1, 3/2, 2)` to the plane 2x – 2y + 4z + 5 = 0.
The plane ax + by = 0 is rotated about its line of intersection with the plane z = 0 through an angle α. Prove that the equation of the plane in its new position is ax + by `+- (sqrt(a^2 + b^2) tan alpha)z ` = 0
Show that the points `(hati - hatj + 3hatk)` and `3(hati + hatj + hatk)` are equidistant from the plane `vecr * (5hati + 2hatj - 7hatk) + 9` = 0 and lies on opposite side of it.
The plane 2x – 3y + 6z – 11 = 0 makes an angle sin–1(α) with x-axis. The value of α is equal to ______.
The direction cosines of the vector `(2hati + 2hatj - hatk)` are ______.
The intercepts made by the plane 2x – 3y + 5z +4 = 0 on the co-ordinate axis are `-2, 4/3, - 4/5`.
