Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Planes are drawn through the points (5, 0, 2) and (3, –2, 5) parallel to the coordinate planes. Find the lengths of the edges of the rectangular parallelepiped so formed.
उत्तर
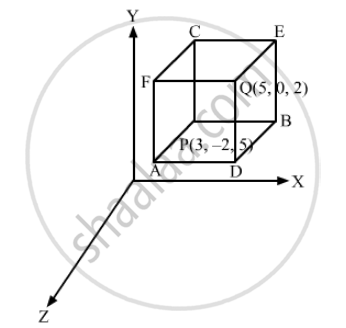
Clearly, PBEC and QDAF are the planes parallel to the yz-plane such that their distances from the yz-plane are 5 and 3, respectively.
\[\therefore\]PA = Distance between planes PBEC and QDAF
= 5\[-\]3
= 2
PB is the distance between planes PAFC and BDQE that are parallel to the zx-plane and are at distances 0 and\[-\]2,respectively, from the zx-plane.
\[\therefore\]PB = 0
\[-\](\[-\]2)
= 2
PC is the distance between parallel planes PBDA and CEQF that are at distances 2 and 5, respectively, from the xy-plane.
\[\therefore\]PC = 2\[-\]5
=\[-\]3
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the octants in which the following points lie:
(1, 2, 3), (4, –2, 3), (4, –2, –5), (4, 2, –5), (–4, 2, –5), (–4, 2, 5),
(–3, –1, 6), (2, –4, –7).
The x-axis and y-axis taken together determine a plane known as_______.
Name the octants in which the following points lie: (5, 2, 3)
Name the octants in which the following points lie:
(7, 4, –3)
Name the octants in which the following points lie:
(–7, 2 – 5)
Find the image of:
(5, 2, –7) in the xy-plane.
Find the image of:
(–5, 0, 3) in the xz-plane.
Find the image of:
(–4, 0, 0) in the xy-plane.
A cube of side 5 has one vertex at the point (1, 0, –1), and the three edges from this vertex are, respectively, parallel to the negative x and y axes and positive z-axis. Find the coordinates of the other vertices of the cube.
Show that the points A(3, 3, 3), B(0, 6, 3), C(1, 7, 7) and D(4, 4, 7) are the vertices of a square.
Find the coordinates of the point which is equidistant from the four points O(0, 0, 0), A(2, 0, 0), B(0, 3, 0) and C(0, 0, 8).
Show that the points (a, b, c), (b, c, a) and (c, a, b) are the vertices of an equilateral triangle.
Verify the following:
(0, 7, –10), (1, 6, –6) and (4, 9, –6) are vertices of an isosceles triangle.
Verify the following:
(0, 7, –10), (1, 6, –6) and (4, 9, –6) are vertices of an isosceles triangle.
Verify the following:
(0, 7, 10), (–1, 6, 6) and (–4, 9, –6) are vertices of a right-angled triangle.
Show that the points A(1, 2, 3), B(–1, –2, –1), C(2, 3, 2) and D(4, 7, 6) are the vertices of a parallelogram ABCD, but not a rectangle.
Show that the plane ax + by + cz + d = 0 divides the line joining the points (x1, y1, z1) and (x2, y2, z2) in the ratio \[- \frac{a x_1 + b y_1 + c z_1 + d}{a x_2 + b y_2 + c z_2 + d}\]
Find the point on x-axis which is equidistant from the points A (3, 2, 2) and B (5, 5, 4).
The coordinates of the foot of the perpendicular drawn from the point P(3, 4, 5) on the yz- plane are
Find the direction cosines of the line passing through the points P(2, 3, 5) and Q(–1, 2, 4).
The x-coordinate of a point on the line joining the points Q(2, 2, 1) and R(5, 1, –2) is 4. Find its z-coordinate.
Find the coordinates of the point where the line through (3, – 4, – 5) and (2, –3, 1) crosses the plane passing through three points (2, 2, 1), (3, 0, 1) and (4, –1, 0)
Find the image of the point (1, 6, 3) in the line `x/1 = (y - 1)/2 = (z - 2)/3`
If a line makes angles `pi/2, 3/4 pi` and `pi/4` with x, y, z axis, respectively, then its direction cosines are ______.
If a line makes angles α, β, γ with the positive directions of the coordinate axes, then the value of sin2α + sin2β + sin2γ is ______.
If a line makes an angle of `pi/4` with each of y and z axis, then the angle which it makes with x-axis is ______.
Find the equation of a plane which bisects perpendicularly the line joining the points A(2, 3, 4) and B(4, 5, 8) at right angles.
Find the angle between the lines whose direction cosines are given by the equations l + m + n = 0, l2 + m2 – n2 = 0
Find the equations of the line passing through the point (3,0,1) and parallel to the planes x + 2y = 0 and 3y – z = 0.
Find the equation of the plane through the points (2, 1, –1) and (–1, 3, 4), and perpendicular to the plane x – 2y + 4z = 10.
Find the equation of the plane which is perpendicular to the plane 5x + 3y + 6z + 8 = 0 and which contains the line of intersection of the planes x + 2y + 3z – 4 = 0 and 2x + y – z + 5 = 0.
Show that the straight lines whose direction cosines are given by 2l + 2m – n = 0 and mn + nl + lm = 0 are at right angles.
The vector equation of the line `(x - 5)/3 = (y + 4)/7 = (z - 6)/2` is ______.
The cartesian equation of the plane `vecr * (hati + hatj - hatk)` is ______.
The unit vector normal to the plane x + 2y +3z – 6 = 0 is `1/sqrt(14)hati + 2/sqrt(14)hatj + 3/sqrt(14)hatk`.
The angle between the line `vecr = (5hati - hatj - 4hatk) + lambda(2hati - hatj + hatk)` and the plane `vec.(3hati - 4hatj - hatk)` + 5 = 0 is `sin^-1(5/(2sqrt(91)))`.
The line `vecr = 2hati - 3hatj - hatk + lambda(hati - hatj + 2hatk)` lies in the plane `vecr.(3hati + hatj - hatk) + 2` = 0.
If the foot of perpendicular drawn from the origin to a plane is (5, – 3, – 2), then the equation of plane is `vecr.(5hati - 3hatj - 2hatk)` = 38.
