Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In a photo diode, the conductive increases when the material is exposed to light. It is found that the conductivity changes only if the wavelength is less than 620 nm. What is the band gap?
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
उत्तर
Conductivity of any material increases when the number of free charge carriers in the material increases. When a photo diode is exposed to light, additional electron hole pairs are created in the diode; thus, its conductivity increases. So to change the conductivity of a photo diode, the minimum energy of the incident radiation should be equal to the band gap of the material.
In other words,
Band gap = Energy of the incident radiation
\[\Rightarrow E = \frac{hc}{\lambda}\]
\[ \Rightarrow E = \frac{1242 \text{ eV - nm}}{620 \text{ nm }} = 2.0eV\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(i) Explain with the help of a diagram the formation of depletion region and barrier potential in a pn junction.
With the help of neat labelled circuit diagram explain the working of half wave rectifier using semiconductor diode. Draw the input and output waveforms.
When a forward bias is applied to a p-n junction, it ______.
Draw a labelled diagram of a full wave rectifier. Show how output voltage varies with time if the input voltage is a sinusoidal voltage.
The power delivered in the plate circular of a diode is 1.0 W when the plate voltage is 36 V. Find the power delivered if the plate voltage is increased to 49 V. Assume Langmuir-Child equation to hold.
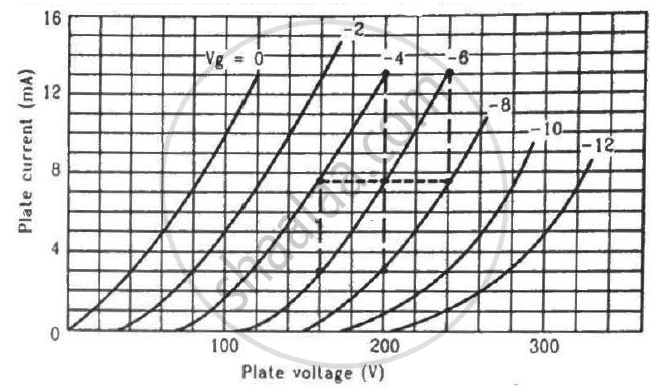
Find the values of rp, µ and gm of a triode operating at plate voltage 200 V and grid voltage −6. The plate characteristics are shown in the figure.
Answer the following question.
Why photodiodes are required to operate in reverse bias? Explain.
Of the diodes shown in the following diagrams, which one is reverse biased?
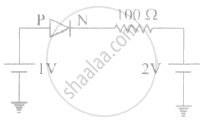
The current through an ideal PN-junction shown in the following circuit diagram will be:
The nature of binding for a crystal with alternate and evenly spaced positive and negatively ions is
In forward bias width of potential barrier in a p + n junction diode
The breakdown in a reverse biased p–n junction diode is more likely to occur due to ______.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is small.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is large.
- strong electric field in a depletion region if the doping concentration is small.
- strong electric field in the depletion region if the doping concentration is large.
Can the potential barrier across a p-n junction be measured by simply connecting a voltmeter across the junction?
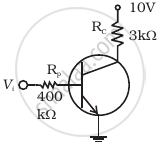
In the circuit shown in figure, when the input voltage of the base resistance is 10 V, Vbe is zero and Vce is also zero. Find the values of Ib, Ic and β.
Consider a box with three terminals on top of it as shown in figure (a):
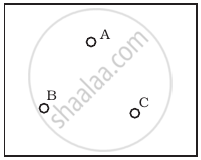 (a) |
Three components namely, two germanium diodes and one resistor are connected across these three terminals in some arrangement. A student performs an experiment in which any two of these three terminals are connected in the circuit shown in figure (b).
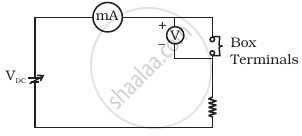 (b) |
The student obtains graphs of current-voltage characteristics for unknown combination of components between the two terminals connected in the circuit. The graphs are
(i) when A is positive and B is negative
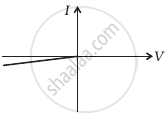 (c) |
(ii) when A is negative and B is positive
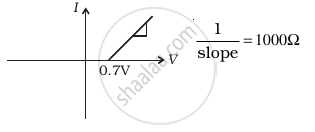 (d) |
(iii) When B is negative and C is positive
|
(e) |
(iv) When B is positive and C is negative
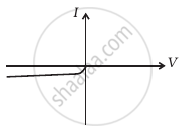 (f) |
(v) When A is positive and C is negative
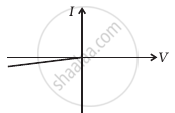 (g) |
(vi) When A is negative and C is positive
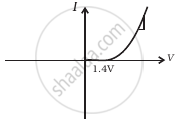 (h) |
From these graphs of current-voltage characteristics shown in figure (c) to (h), determine the arrangement of components between A, B and C.
A semiconductor device is connected in series with a battery, an ammeter and a resistor. A current flows in the circuit. If. the polarity of the battery is reversed, the current in the circuit almost becomes zero. The device is a/an ______.
Describe briefly the following term:
minority carrier injection in forward biasing.
What is meant by forward biasing of a semiconductor diode?
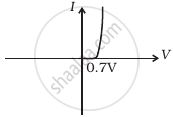
Draw a labelled characteristic curve (l-V graph) for a semiconductor diode during forward bias.