Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The intercept cut off by a line from y-axis is twice than that from x-axis, and the line passes through the point (1, 2). The equation of the line is ______.
विकल्प
2x + y = 4
2x + y + 4 = 0
2x – y = 4
2x – y + 4 = 0
उत्तर
The intercept cut off by a line from y-axis is twice than that from x-axis, and the line passes through the point (1, 2). The equation of the line is 2x + y = 4.
Explanation:
Let the line make intercept ‘a’ on x-axis.
Then, it makes intercept ‘2a’ on y-axis.
Therefore, the equation of the line is given by
`x/a + y/(2a)` = 1
It passes through (1, 2), so, we have
`1/a + 2/(2a)` = 1 or a = 2
Therefore, the required equation of the line is given by
`x/2 + y/4` = 1 or 2x + y = 4
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the slope of a line, which passes through the origin, and the mid-point of the line segment joining the points P (0, –4) and B (8, 0).
Without using the Pythagoras theorem, show that the points (4, 4), (3, 5) and (–1, –1) are the vertices of a right angled triangle.
Find the slope of the line, which makes an angle of 30° with the positive direction of y-axis measured anticlockwise.
Find the value of x for which the points (x, –1), (2, 1) and (4, 5) are collinear.
Find the angle between the x-axis and the line joining the points (3, –1) and (4, –2).
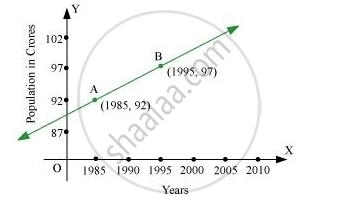
Consider the given population and year graph. Find the slope of the line AB and using it, find what will be the population in the year 2010?
Find the slope of the lines which make the following angle with the positive direction of x-axis:
\[\frac{3\pi}{4}\]
Find the slope of the lines which make the following angle with the positive direction of x-axis: \[\frac{\pi}{3}\]
What can be said regarding a line if its slope is zero ?
What can be said regarding a line if its slope is positive ?
Show that the line joining (2, −3) and (−5, 1) is parallel to the line joining (7, −1) and (0, 3).
If three points A (h, 0), P (a, b) and B (0, k) lie on a line, show that: \[\frac{a}{h} + \frac{b}{k} = 1\].
Show that the perpendicular bisectors of the sides of a triangle are concurrent.
Find the equations of the altitudes of a ∆ ABC whose vertices are A (1, 4), B (−3, 2) and C (−5, −3).
If the image of the point (2, 1) with respect to a line mirror is (5, 2), find the equation of the mirror.
Find the equation of the right bisector of the line segment joining the points (3, 4) and (−1, 2).
Find the angles between the following pair of straight lines:
3x + y + 12 = 0 and x + 2y − 1 = 0
Show that the tangent of an angle between the lines \[\frac{x}{a} + \frac{y}{b} = 1 \text { and } \frac{x}{a} - \frac{y}{b} = 1\text { is } \frac{2ab}{a^2 - b^2}\].
If two opposite vertices of a square are (1, 2) and (5, 8), find the coordinates of its other two vertices and the equations of its sides.
If x + y = k is normal to y2 = 12x, then k is ______.
If one diagonal of a square is along the line 8x – 15y = 0 and one of its vertex is at (1, 2), then find the equation of sides of the square passing through this vertex.
Find the angle between the lines y = `(2 - sqrt(3)) (x + 5)` and y = `(2 + sqrt(3))(x - 7)`
If the equation of the base of an equilateral triangle is x + y = 2 and the vertex is (2, – 1), then find the length of the side of the triangle.
If p is the length of perpendicular from the origin on the line `x/a + y/b` = 1 and a2, p2, b2 are in A.P, then show that a4 + b4 = 0.
If the vertices of a triangle have integral coordinates, then the triangle can not be equilateral.
The points A(– 2, 1), B(0, 5), C(– 1, 2) are collinear.
The line `x/a + y/b` = 1 moves in such a way that `1/a^2 + 1/b^2 = 1/c^2`, where c is a constant. The locus of the foot of the perpendicular from the origin on the given line is x2 + y2 = c2.
