Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When a sparingly soluble substance like alcohol is dissolved in water, surface tension of water
विकल्प
increases
decreases
remains constant
becomes infinite
उत्तर
Decreases
When / sparingly soluble substances are added surface tension decreases.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Derive Laplace’s law for spherical membrane of bubble due to surface tension.
The surface tension of water at 0°C is 75.5 dyne/cm. Calculate surface tension of water at 25°C.
(α for water = 2.7×10-3/°C)
Derive an expression for excess pressure inside a drop of liquid.
A raindrop of diameter 4 mm is about to fall on the ground. Calculate the pressure inside the raindrop. [Surface tension of water T = 0.072 N/m, atmospheric pressure = 1.013 x 105 N/m2 ]
Draw a neat labelled diagram showing forces acting on the meniscus of water in a capillary tube.
Define the angle of contact.
Explain why The angle of contact of mercury with glass is obtuse, while that of water with glass is acute
Explain why A drop of liquid under no external forces is always spherical in shape
A U-shaped wire is dipped in a soap solution and removed. The thin soap film formed between the wire and the light slider supports a weight of 1.5 × 10–2 N (which includes the small weight of the slider). The length of the slider is 30 cm. What is the surface tension of the film?
Mercury has an angle of contact equal to 140° with soda lime glass. A narrow tube of radius 1.00 mm made of this glass is dipped in a trough containing mercury. By what amount does the mercury dip down in the tube relative to the liquid surface outside? Surface tension of mercury at the temperature of the experiment is 0.465 N m–1. Density of mercury = 13.6 × 103 kg m–3
The total energy of free surface of a liquid drop is 2π times the surface tension of the liquid. What is the diameter of the drop? (Assume all terms in SI unit).
A big drop of radius R is formed from 1000 droplets of water. The radius of a droplet will be _______
A) 10 R
B) R/10
C) R/100
D) R/1000
State any two characteristics of the angle of contact
The contact angle between pure water and pure silver is 90°. If a capillary tube made of silver is dipped at one end in pure water, will the water rise in the capillary?
The contact angle between water and glass is 0°. When water is poured in a glass to the maximum of its capacity, the water surface is convex upward. The angle of contact in such a situation is more than 90°. Explain.
When a glass capillary tube is dipped at one end in water, water rises in the tube. The gravitational potential energy is thus increased. Is it a violation of conservation of energy?
The force of surface tension acts tangentially to the surface whereas the force due to air pressure acts perpendicularly on the surface. How is then the force due to excess pressure inside a bubble balanced by the force due to the surface tension?
A heavy mass is attached to a thin wire and is whirled in a vertical circle. The wire is most likely to break
By a surface of a liquid we mean
When water droplets merge to form a bigger drop
If more air is pushed in a soap bubble, the pressure in it
Which of the following graphs may represent the relation between the capillary rise hand the radius r of the capillary?
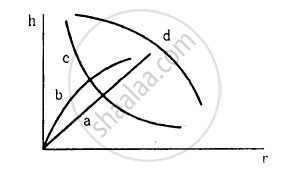
Water rises in a vertical capillary tube up to a length of 10 cm. If the tube is inclined at 45°, the length of water risen in the tube will be
A 20 cm long capillary tube is dipped in water. The water rises up to 8 cm. If the entire arrangement is put in a freely falling elevator, the length of water column in the capillary tube will be
The properties of a surface are different from those of the bulk liquid because the surface molecules
(a) are smaller than other molecules
(b) acquire charge due to collision from air molecules
(c) find different type of molecules in their range of influence
(d) feel a net force in one direction.
The rise of a liquid in a capillary tube depends on
(a) the material
(b) the length
(c) the outer radius
(d) the inner radius of the tube
Find the excess pressure inside (a) a drop of mercury of radius 2 mm (b) a soap bubble of radius 4 mm and (c) an air bubble of radius 4 mm formed inside a tank of water. Surface tension of mercury, soap solution and water are 0.465 N m−1, 0.03 N m−1 and 0.076 N m−1 respectively.
A barometer is constructed with its tube having radius 1.0 mm. Assume that the surface of mercury in the tube is spherical in shape. If the atmospheric pressure is equal to 76 cm of mercury, what will be the height raised in the barometer tube? The contact angle of mercury with glass = 135° and surface tension of mercury = 0.465 N m−1. Density of mercury = 13600 kg m−3.
A drop of mercury of radius 2 mm is split into 8 identical droplets. Find the increase in surface energy. Surface tension of mercury = 0.465 J m−2.
Find the force exerted by the water on a 2 m2 plane surface of a large stone placed at the bottom of a sea 500 m deep. Does the force depend on the orientation of the surface?
A cubical block of ice floating in water has to support a metal piece weighing 0.5 kg. Water can be the minimum edge of the block so that it does not sink in water? Specific gravity of ice = 0.9.
A hollow spherical body of inner and outer radii 6 cm and 8 cm respectively floats half-submerged in water. Find the density of the material of the sphere.
A solid sphere of radius 5 cm floats in water. If a maximum load of 0.1 kg can be put on it without wetting the load, find the specific gravity of the material of the sphere.
Define surface tension
Explain the phenomena of surface tension on the basis of molecular theory.
How does surface tension help a plant?
Explain elasticity using intermolecular forces.
Mention the S.I unit and dimension of surface tension.
Obtain an expression for the excess of pressure inside a
- liquid drop
- liquid bubble
- air bubble
Obtain an expression for the surface tension of a liquid by the capillary rise method.
Water rises in a capillary tube of radius r upto a height h. The mass of water in a capillary is m. The mass of water that will rise in a capillary of radius `"r"/4` will be ______.
Two small drops of mercury each of radius 'R' coalesce to form a large single drop. The ratio of the total surface energies before and after the change is ____________.
A large number of liquid drops each of radius 'r' coalesce to form a big drop of radius 'R'. The energy released in the process in converted into kinetic energy of the big drop. The speed of the big drop is ______. (T = surface tension of liquid, p = density of liquid)
Soap solution is used for cleaning dirty clothes because ______.
This model of the atmosphere works for relatively small distances. Identify the underlying assumption that limits the model.
Surface tension is exhibited by liquids due to force of attraction between molecules of the liquid. The surface tension decreases with increase in temperature and vanishes at boiling point. Given that the latent heat of vaporisation for water Lv = 540 k cal kg–1, the mechanical equivalent of heat J = 4.2 J cal–1, density of water ρw = 103 kg l–1, Avagadro’s No NA = 6.0 × 1026 k mole–1 and the molecular weight of water MA = 18 kg for 1 k mole.
- Estimate the energy required for one molecule of water to evaporate.
- Show that the inter–molecular distance for water is `d = [M_A/N_A xx 1/ρ_w]^(1/3)` and find its value.
- 1 g of water in the vapor state at 1 atm occupies 1601 cm3. Estimate the intermolecular distance at boiling point, in the vapour state.
- During vaporisation a molecule overcomes a force F, assumed constant, to go from an inter-molecular distance d to d ′. Estimate the value of F.
- Calculate F/d, which is a measure of the surface tension.
A hot air balloon is a sphere of radius 8 m. The air inside is at a temperature of 60°C. How large a mass can the balloon lift when the outside temperature is 20°C? (Assume air is an ideal gas, R = 8.314 J mole–1K–1, 1 atm. = 1.013 × 105 Pa; the membrane tension is 5 Nm–1.)
Eight droplets of water each of radius 0.2 mm coalesce into a single drop. Find the decrease in the surface area.
A liquid drop of density ρ is floating half immersed in a liquid of density d. The diameter of the liquid drop is ______.
(ρ > d, g = acceleration due to gravity, T = surface tension)
A spherical liquid drop of radius R is divided into eight equal droplets. If surface tension is T, then the work done in this process will be ______.
The surface tension of boiling water is ______.
