Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw Δ ABC such that, AB = 8 cm, BC = 6 cm and ∠ B = 90°. Draw seg BD
perpendicular to hypotenuse AC. Draw a circle passing through points
B, D, A. Show that line CB is a tangent of the circle.
उत्तर
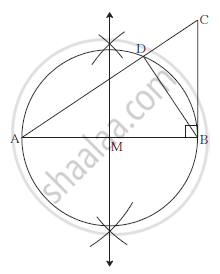
Seg BD ⊥ Seg AC
∴ΔADB is a right angled triangle.
∴ Seg AB is a diameter of the circle passing through the points
A,B and D
∴ Seg MB is a radius of the circle.
∠MBC is a right angle .................(Given)
∴ line CB is a tangent of the circle.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The common point of a tangent to a circle and the circle is called ______.
What is the distance between two parallel tangents of a circle having radius 4.5 cm ? Justify your answer.
Four alternative answers for the following question is given. Choose the correct alternative.
If two circles are touching externally, how many common tangents of them can be drawn?
A chord PQ of a circle is parallel to the tangent drawn at a point R of the circle. Prove that R bisects the arc PRQ.
In following fig., PT is a tangent to the circle at T and PAB is a secant to the same circle. If PB = 9cm and AB = Scm, find PT.
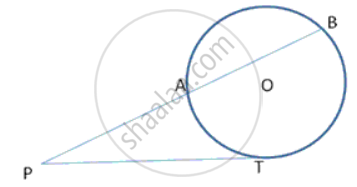
The length of the direct common tangent to two circles of radii 12cm and 4cm is 15cm. calculate the distance between their centres.
PA and PB are tangents from P to the circle with centre O. At M, a tangent is drawn cutting PA at K and PB at N. Prove that KN = AK + BN.
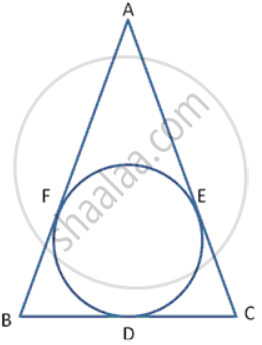
In following figure , the incircle of Δ ABC , touches the sides BC , CA and AB at D , E and F respectively. Show AF + BD + CE = AE + BF + CD
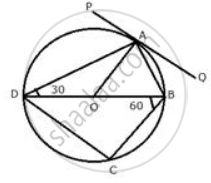
In the following figure, PQ is the tangent to the circle at A, DB is a diameter and O is the centre of the circle. If ∠ ADB = 30° and ∠ CBD = 60° ; calculate : ∠CDB
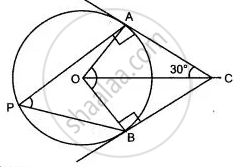
In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle. Tangents at A and B meet at C. If angle ACO = 30°, find: angle AOB
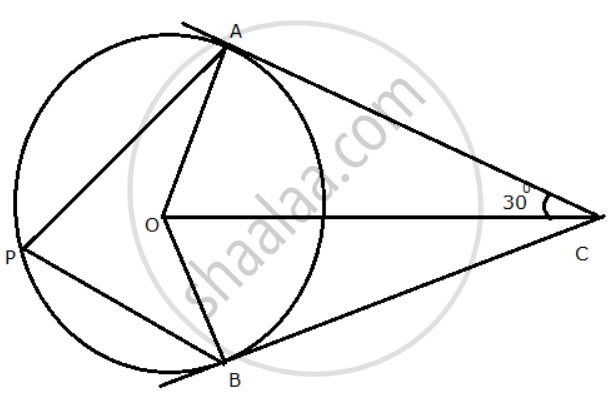
In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle. Tangents at A and B meet at C. If ∠ACO = 30°,
find: (i) ∠ BCO (ii) ∠ AOB (iii) ∠ APB
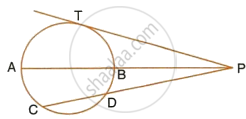
In the given figure, diameter AB and chord CD of a circle meet at P. PT is a tangent to the circle at T. CD = 7.8 cm, PD = 5 cm, PB = 4 cm. Find:
- AB.
- the length of tangent PT.
In Question 5 above, if radii of the two circles are equal, prove that AB = CD.
In figure, O is the centre of a circle of radius 5 cm, T is a point such that OT = 13 cm and OT intersects the circle at E. If AB is the tangent to the circle at E, find the length of AB.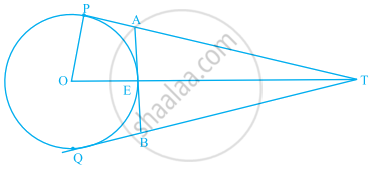
Construct a pair of tangents to a circle of radius 4 cm, which are inclined to each other at an angle of 60°.
If two tangents TL and TM are drawn to a circle with centre C such that ∠LTM = 70°, then find ∠MCT.
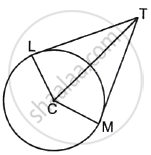
A tangent JK is drawn to a circle with centre C such that CK = 6 cm and ∠CKJ = 60°. Find the length of the tangent JK.

The distance between two tangents parallel to each other of a circle is 13 cm. Find the radius of the circle.
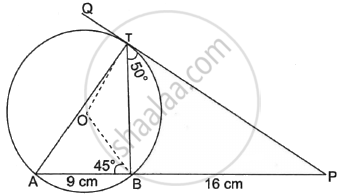
In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle. PQ is a tangent to the circle at T. Chord AB produced meets the tangent at P.
AB = 9 cm, BP = 16 cm, ∠PTB = 50° ∠OBA = 45°
Find:
- Length of PT
- ∠BAT
- ∠BOT
- ∠ABT
In the given diagram an isosceles ΔABC is inscribed in a circle with centre O. PQ is a tangent to the circle at C. OM is perpendicular to chord AC and ∠COM = 65°.
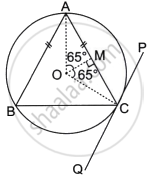
Find:
- ∠ABC
- ∠BAC
- ∠BCQ
