Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Water rises to a height 3.2 cm in a glass capillary tube. Find the height to which the same water will rise in another glass capillary having half area of cross section.
उत्तर
`h_1` = 3.2cm, `A_2 = (A_1)/2`
As, `h α 1/r`
`therefore h_1r_1 = h_2r_2`
`pir_2^2 = (pir_1^2)/2`
`=> r_2 = (r_1)/sqrt2`
`therefore h_2 = (3.2 xx r_1)/(r_1//sqrt2) = 3.2 xx sqrt2`
Hence, `h_2 = 4.525` cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a neat labelled diagram showing forces acting on the meniscus of water in a capillary tube.
Define the angle of contact.
The surface tension of water at 0ºc is 75·5 dyne/cm. Find surface tension of water at 25°C. [ α for water = 0·0021/°C ]
Fill in the blanks using the word(s) from the list appended with each statement
Surface tension of liquids generally . . . with temperatures (increases / decreases)
A U-shaped wire is dipped in a soap solution and removed. The thin soap film formed between the wire and the light slider supports a weight of 1.5 × 10–2 N (which includes the small weight of the slider). The length of the slider is 30 cm. What is the surface tension of the film?
Define surface tension and surface energy.
In a conical pendulum, a string of length 120 cm is fixed at rigid support and carries a mass
of 150 g at its free end. If the mass is revolved in a horizontal circle of radius 0.2 m around a
vertical axis, calculate tension in the string (g = 9.8 m/s2)
State any two characteristics of the angle of contact
When a sparingly soluble substance like alcohol is dissolved in water, surface tension of water
The free surface of a liquid resting in an inertial frame is horizontal. Does the normal to the free surface pass through the centre of the earth? Think separately if the liquid is (a) at the equator (b) at a pole (c) somewhere else.
The contact angle between pure water and pure silver is 90°. If a capillary tube made of silver is dipped at one end in pure water, will the water rise in the capillary?
A uniform vertical tube of circular cross section contains a liquid. The contact angle is 90°. Consider a diameter of the tube lying in the surface of the liquid. The surface to the right of this diameter pulls the surface on the left of it. What keeps the surface on the left in equilibrium?
When a glass capillary tube is dipped at one end in water, water rises in the tube. The gravitational potential energy is thus increased. Is it a violation of conservation of energy?
If a mosquito is dipped into water and released, it is not able to fly till it is dry again. Explain
The force of surface tension acts tangentially to the surface whereas the force due to air pressure acts perpendicularly on the surface. How is then the force due to excess pressure inside a bubble balanced by the force due to the surface tension?
If water in one flask and castor oil in other are violently shaken and kept on a table, which will come to rest earlier?
Air is pushed into a soap bubble of radius r to double its radius. If the surface tension of the soap solution in S, the work done in the process is
If two soap bubbles of different radii are connected by a tube,
The excess pressure inside a soap bubble is twice the excess pressure inside a second soap bubble. The volume of the first bubble is n times the volume of the second where n is
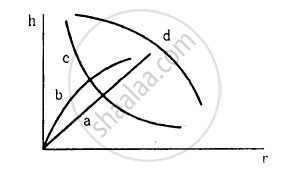
Which of the following graphs may represent the relation between the capillary rise hand the radius r of the capillary?
The properties of a surface are different from those of the bulk liquid because the surface molecules
(a) are smaller than other molecules
(b) acquire charge due to collision from air molecules
(c) find different type of molecules in their range of influence
(d) feel a net force in one direction.
The rise of a liquid in a capillary tube depends on
(a) the material
(b) the length
(c) the outer radius
(d) the inner radius of the tube
Find the excess pressure inside (a) a drop of mercury of radius 2 mm (b) a soap bubble of radius 4 mm and (c) an air bubble of radius 4 mm formed inside a tank of water. Surface tension of mercury, soap solution and water are 0.465 N m−1, 0.03 N m−1 and 0.076 N m−1 respectively.
A capillary tube of radius 0.50 mm is dipped vertically in a pot of water. Find the difference between the pressure of the water in the tube 5.0 cm below the surface and the atmospheric pressure. Surface tension of water = 0.075 N m−1.
Find the surface energy of water kept in a cylindrical vessel of radius 6.0 cm. Surface tension of water = 0.075 J m−2.
The lower end of a capillary tube of radius 1 mm is dipped vertically into mercury. (a) Find the depression of mercury column in the capillary. (b) If the length dipped inside is half the answer of part (a), find the angle made by the mercury surface at the end of the capillary with the vertical. Surface tension of mercury = 0.465 N m−1 and the contact angle of mercury with glass −135 °.
Two large glass plates are placed vertically and parallel to each other inside a tank of water with separation between the plates equal to 1 mm. Find the rise of water in the space between the plates. Surface tension of water = 0.075 Nm−1.
A wire forming a loop is dipped into soap solution and taken out so that a film of soap solution is formed. A loop of 6.28 cm long thread is gently put on the film and the film is pricked with a needle inside the loop. The thread loop takes the shape of a circle. Find the tension the the thread. Surface tension of soap solution = 0.030 N m−1.
Explain the capillary action.
Derive an expression for capillary rise for a liquid having a concave meniscus.
A drop of mercury of radius 0.2 cm is broken into 8 droplets of the same size. Find the work done if the surface tension of mercury is 435.5 dyn/cm.
The water droplets are spherical in free fall due to ______
What will be the shape of the liquid meniscus for the obtuse angle of contact?
Two soap bubbles have a radius in the ratio of 2:3. Compare the works done in blowing these bubbles.
Explain the phenomena of surface tension on the basis of molecular theory.
Obtain an expression for the capillary rise or fall using the forces method.
Numerical Problem.
A stone weighs 500 N. Calculate the pressure exerted by it if it makes contact with a surface of area 25 cm2.
Describe an experiment to prove that friction depends on the nature of a surface.
Explain elasticity using intermolecular forces.
The surface tension of the two liquids is respectively 20 and 60 dyne cm-1. The liquids drop from the ends of two tubes of the same radius. The ratio of the weights of the two drops is ______
A square frame of each side L is dipped in a soap solution and taken out. The force acting on the film formed is _____.
(T = surface tension of soap solution).
The excess of pressure, due to surface tension, on a spherical liquid drop of radius 'R' is proportional to ______.
A large number of liquid drops each of radius 'r' coalesce to form a big drop of radius 'R'. The energy released in the process in converted into kinetic energy of the big drop. The speed of the big drop is ______. (T = surface tension of liquid, p = density of liquid)
Under isothermal conditions, two soap bubbles of radii 'r1' and 'r2' coalesce to form a big drop. The radius of the big drop is ______.
The wear and tear in the machine part is due to ______.
If a drop of liquid breaks into smaller droplets, it results in lowering of temperature of the droplets. Let a drop of radius R, break into N small droplets each of radius r. Estimate the drop in temperature.
The sufrace tension and vapour pressure of water at 20°C is 7.28 × 10–2 Nm–1 and 2.33 × 103 Pa, respectively. What is the radius of the smallest spherical water droplet which can form without evaporating at 20°C?
Two narrow bores of diameter 5.0 mm and 8.0 mm are joined together to form a U-shaped tube open at both ends. If this U-tube contains water, what is the difference in the level of the two limbs, of the tube?
[Take surface tension of water T = 7.3 × 10-2 Nm-1, angle of contact = 0, g = 10 ms-2 and density of water = 1.0 × 103 kgm-3]
A soap bubble of radius 3 cm is formed inside another soap bubble of radius 6 cm. The radius of an equivalent soap bubble which has the same excess pressure as inside the smaller bubble with respect to the atmospheric pressure is ______ cm.
When one end of the capillary is dipped in water, the height of water column is 'h'. The upward force of 105 dyne due to surface tension is balanced by the force due to the weight of water column. The inner circumference of capillary is ______.
(Surface tension of water = 7 × 10-2 N/m)
The surface tension of a soap solution is T. The work done in blowing a soap bubble of diameter d to that of a diameter 2d is ______.
Work done to blow a bubble of volume V is W. The work done in blowing a bubble of volume 2V will be ______.
