Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the particular solution of the differential equation `(x - y) dy/dx = (x + 2y)` given that y = 0 when x = 1.
उत्तर १
`dy/dx = (x + 2y)/(x - y)`
Putting y = Vx


उत्तर २
The given differential equation is
`(x - y) dy/dx = x + 2y`
`=> dy/dx = (x + 2y)/(x - y)`
This is a homogeneous differential equation.
Putting y=vx and `dy/dx = v + x dy/dx`, we get
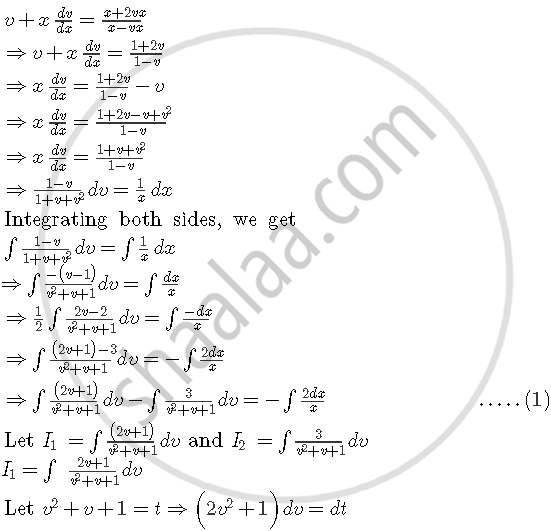
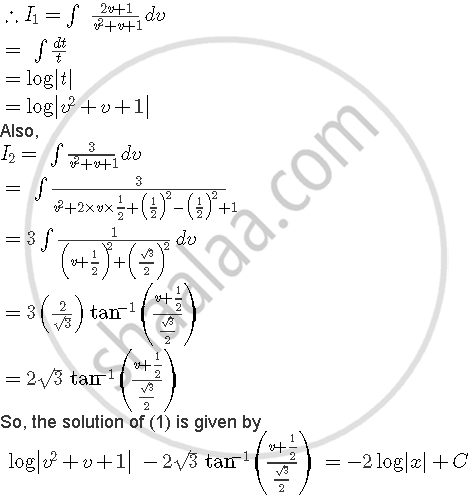

संबंधित प्रश्न
Solve the differential equation :
`y+x dy/dx=x−y dy/dx`
Show that the differential equation `2xydy/dx=x^2+3y^2` is homogeneous and solve it.
Show that the given differential equation is homogeneous and solve them.
`y' = (x + y)/x`
Show that the given differential equation is homogeneous and solve them.
`y dx + x log(y/x)dy - 2x dy = 0`
For the differential equation find a particular solution satisfying the given condition:
`[xsin^2(y/x - y)] dx + x dy = 0; y = pi/4 "when" x = 1`
Which of the following is a homogeneous differential equation?
Prove that x2 – y2 = c (x2 + y2)2 is the general solution of differential equation (x3 – 3x y2) dx = (y3 – 3x2y) dy, where c is a parameter.
(2x2 y + y3) dx + (xy2 − 3x3) dy = 0
Solve the following initial value problem:
(xy − y2) dx − x2 dy = 0, y(1) = 1
Solve the following initial value problem:
(y4 − 2x3 y) dx + (x4 − 2xy3) dy = 0, y (1) = 1
Solve the following initial value problem:
x (x2 + 3y2) dx + y (y2 + 3x2) dy = 0, y (1) = 1
Solve the following initial value problem:
\[\left\{ x \sin^2 \left( \frac{y}{x} \right) - y \right\}dx + x dy = 0, y\left( 1 \right) = \frac{\pi}{4}\]
Solve the following initial value problem:
\[x\frac{dy}{dx} - y + x \sin\left( \frac{y}{x} \right) = 0, y\left( 2 \right) = x\]
Find the particular solution of the differential equation x cos\[\left( \frac{y}{x} \right)\frac{dy}{dx} = y \cos\left( \frac{y}{x} \right) + x\], given that when x = 1, \[y = \frac{\pi}{4}\]
Which of the following is a homogeneous differential equation?
Solve the differential equation: ` (dy)/(dx) = (x + y )/ (x - y )`
Solve the following differential equation:
`"x" sin ("y"/"x") "dy" = ["y" sin ("y"/"x") - "x"] "dx"`
Solve the following differential equation:
(x2 + 3xy + y2)dx - x2 dy = 0
Solve the following differential equation:
(x2 – y2)dx + 2xy dy = 0
F(x, y) = `(sqrt(x^2 + y^2) + y)/x` is a homogeneous function of degree ______.
A homogeneous differential equation of the `(dx)/(dy) = h(x/y)` can be solved by making the substitution.
Find the general solution of the differential equation:
(xy – x2) dy = y2 dx
Read the following passage:
|
An equation involving derivatives of the dependent variable with respect to the independent variables is called a differential equation. A differential equation of the form `dy/dx` = F(x, y) is said to be homogeneous if F(x, y) is a homogeneous function of degree zero, whereas a function F(x, y) is a homogeneous function of degree n if F(λx, λy) = λn F(x, y). To solve a homogeneous differential equation of the type `dy/dx` = F(x, y) = `g(y/x)`, we make the substitution y = vx and then separate the variables. |
Based on the above, answer the following questions:
- Show that (x2 – y2) dx + 2xy dy = 0 is a differential equation of the type `dy/dx = g(y/x)`. (2)
- Solve the above equation to find its general solution. (2)
