Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the height of an equilateral triangle having side 4 cm?
उत्तर
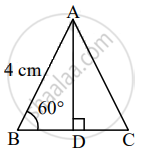
Let ∆ABC be the given equilateral triangle.
∴ ∠B = 60° ......[Angle of an equilateral triangle]
Let AD ⊥ BC, B – D – C.
In ∆ABD, ∠B = 60°, ∠ADB = 90°
∴ ∠BAD = 30° ......[Remaining angle of a triangle]
∴ ∆ABD is a 30° – 60° – 90° triangle.
∴ AD = `sqrt(3)/2` AB ......[Side opposite to 60°]
= `sqrt(3)/2 xx 4`
= `2sqrt(3)` units
∴ The height of the equilateral triangle is `2sqrt(3)` units.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The sides of triangle is given below. Determine it is right triangle or not.
a = 1.6 cm, b = 3.8 cm and c = 4 cm
A man goes 15 metres due west and then 8 metres due north. How far is he from the starting point?
In an isosceles triangle ABC, AB = AC = 25 cm, BC = 14 cm. Calculate the altitude from A on BC.
The foot of a ladder is 6 m away from a wall and its top reaches a window 8 m above the ground. If the ladder is shifted in such a way that its foot is 8 m away from the wall, to what height does its tip reach?
Two poles of height 9 m and 14 m stand on a plane ground. If the distance between their feet is 12 m, find the distance between their tops.
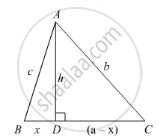
Using Pythagoras theorem determine the length of AD in terms of b and c shown in Figure.
In an isosceles triangle ABC, if AB = AC = 13 cm and the altitude from A on BC is 5 cm, find BC.
In an acute-angled triangle, express a median in terms of its sides.
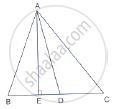
In Figure, D is the mid-point of side BC and AE ⊥ BC. If BC = a, AC = b, AB = c, ED
= x, AD = p and AE = h, prove that:
(i) `b^2 = p^2 + ax + a^2/4`
(ii) `c^2 = p^2 - ax + a^2/4`
(iii) `b^2 + c^2 = 2p^2 + a^2/2`
In the given figure, ∠B < 90° and segment AD ⊥ BC, show that
(i) b2 = h2 + a2 + x2 - 2ax
(ii) b2 = a2 + c2 - 2ax
∆ABD is a right triangle right-angled at A and AC ⊥ BD. Show that
(i) AB2 = BC x BD
(ii) AC2 = BC x DC
(iii) AD2 = BD x CD
(iv) `"AB"^2/"AC"^2="BD"/"DC"`
Determine whether the triangle having sides (a − 1) cm, 2`sqrta` cm and (a + 1) cm is a right-angled
triangle.
State the converse of Pythagoras theorem.
If D, E, F are the respectively the midpoints of sides BC, CA and AB of ΔABC. Find the ratio of the areas of ΔDEF and ΔABC.
Find the length of each side of a rhombus are 40 cm and 42 cm. find the length of each side of the rhombus.
From given figure, In ∆ABC, AB ⊥ BC, AB = BC then m∠A = ?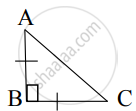
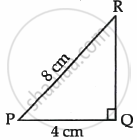
In the given figure, ΔPQR is a right triangle right angled at Q. If PQ = 4 cm and PR = 8 cm, then P is ______.